What is The Difference Between Virtualization and Containerization?
Virtualization & Containerization are advanced technologies that enable the execution of multiple applications or workloads on a single physical machine or host.
Virtual machines & Containers are the two most preferred methods for establishing a software infrastructure for your organization.
Containers have established themselves as a significant component in cloud-native development. Whether used individually or integrated with virtual machines (VMs), they offer countless advantages for your IT system.
Even though they have different capabilities, they share similarities in certain aspects. Both technologies enhance efficiency, provide scalability, introduce flexibility, assist DevOps, & optimize the software development lifecycle.
To boost the efficiency of your IT team and fulfill business needs, you can use containerization and virtualization together.
Difference between Virtualization and Containerization
| Aspect | Virtualization | Containerization |
|---|---|---|
| Isolation | It provides complete isolation from the host operating system and the other VMs | It generally offers lightweight isolation from the host and other containers but doesn’t provide as robust a security boundary as a VM |
| Operating System | Runs a complete operating system, including the kernel, as a consequence, requires more system resources like CPU, memory, and storage | Operates the user-mode portion of an operating system and can be customized to accommodate the needed services for your app using scarce system resources |
| Deployment | Deploy VMs using Hypervisor technology | Deploy containers using Docker or use an orchestrator such as Kubernetes to deploy multiple containers |
| Persistent storage | Uses a Virtual Hard Disk (VHD) for local storage of a single VM & storage shared by multiple servers Use a Server Message Block (SMB) for file sharing. | Uses local disks for local storage of a single node & for storage shared by multiple nodes or servers SMB is used |
| Load balancing | In case of a failover cluster virtual machine load balancing is done by running VMs in other servers. | To manage changes in load and availability, an orchestrator automatically starts or stops containers on cluster nodes. |
| Networking | It uses virtual network adapters | Uses an isolated perspective of a virtual network adapter. Thus, it provides less virtualization. |
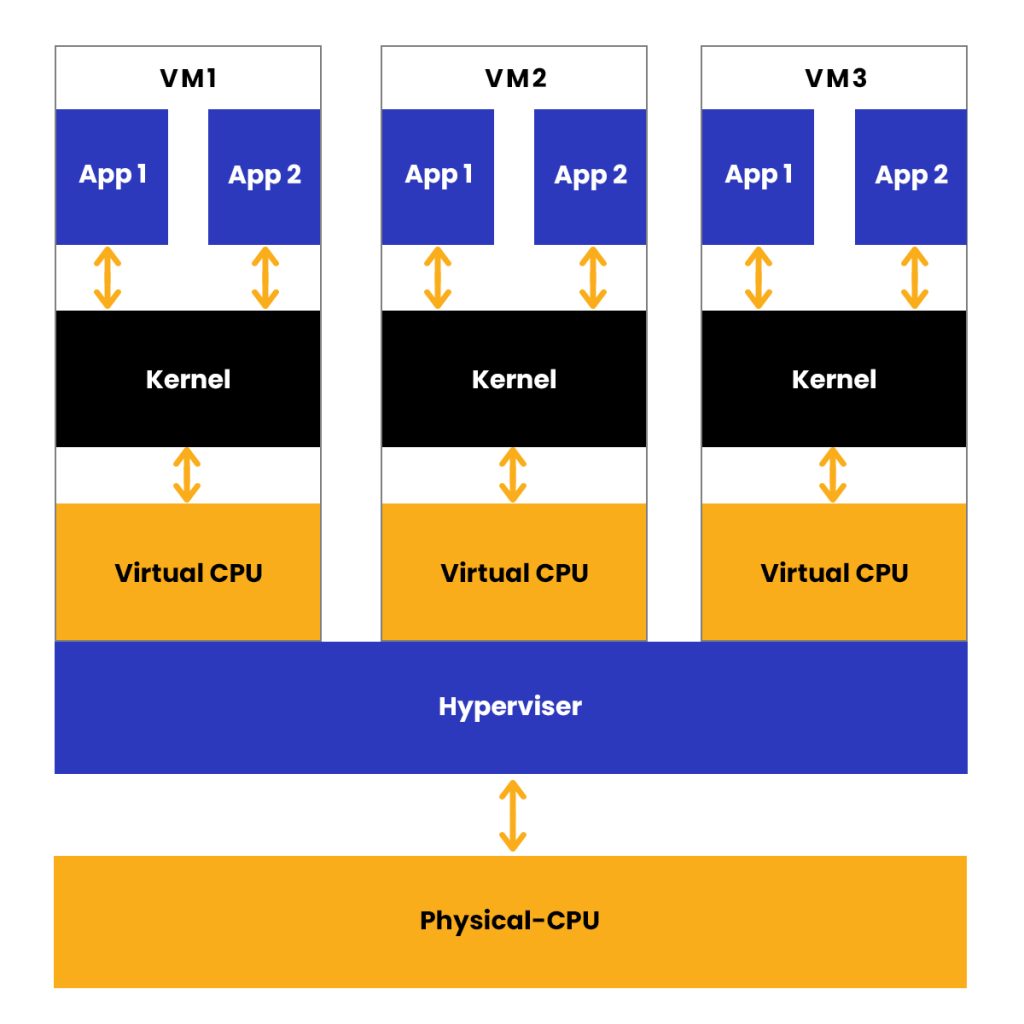
What are virtual machines and virtualization?
Before the emergence of the containers, the “virtual machine” was the preferred choice for optimizing server capacity. Programmed to emulate the hardware and complete operating system of a physical computer, Virtual machines (VMs) and hypervisors enable multiple computers, each with different operating systems on a single physical server’s hardware.
What is a Hypervisor?
The hypervisor, also referred to as the virtual machine monitor, is a prerequisite for virtualization. The software or firmware layer allows multiple operating systems to run simultaneously, granting them access to the same physical server resources. The hypervisor effectively partitions and allocates the available computing power, memory, storage, and other resources to each virtual machine as per its requirements.
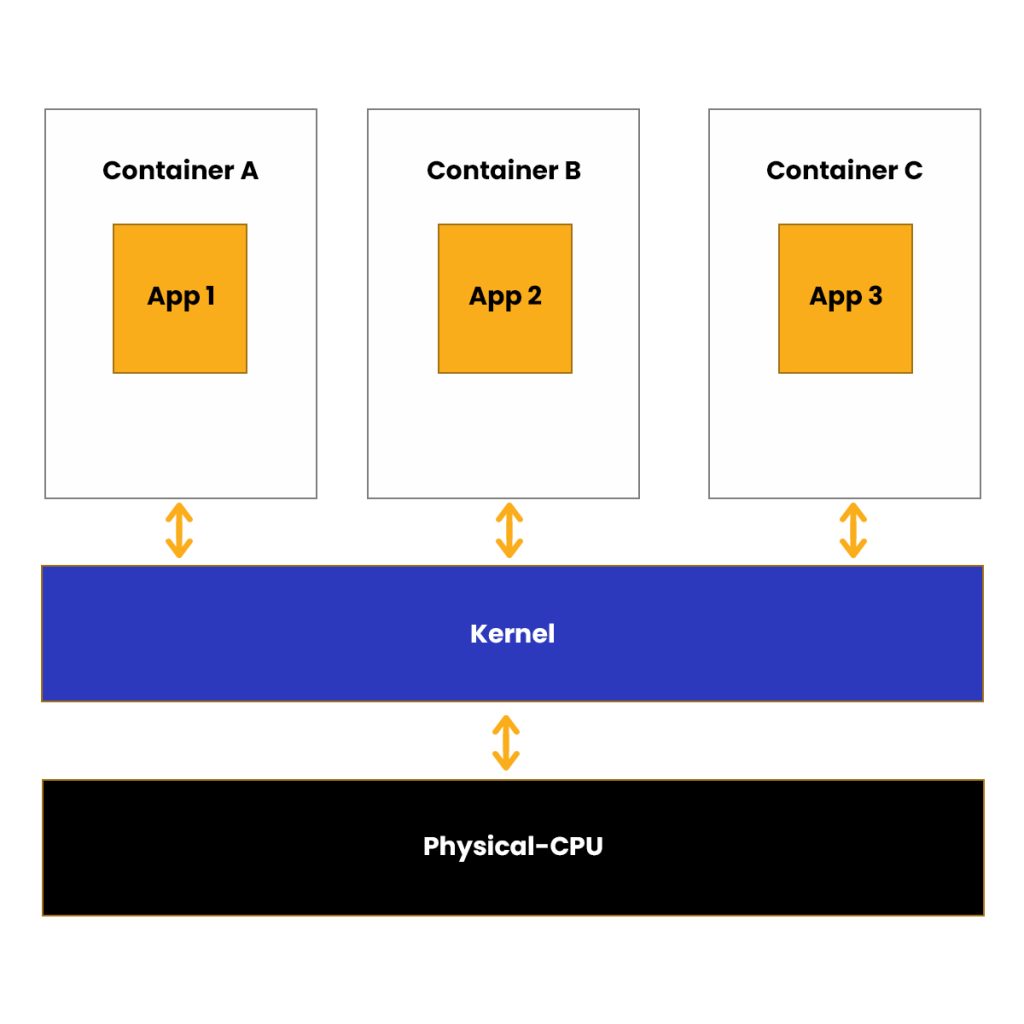
What are Containers?
The container uses the host operating system’s kernel, sharing it with other containers, while the shared part of the OS remains read-only. Consequently, the containers are lightweight, enabling the deployment of multiple containers on a single server or a VM.
It quashes the need for dedicating an entire server to a single application, and you only need to manage a single operating system. Scaling up becomes rapid and swift without the need for additional server space.
The container isolates an application from its surroundings by encapsulating its dependencies and configurations within a single unit. After that, the containerized unit can be seamlessly exported to other environments, including private clouds, public clouds, and data centers.
What is Containerization?
Containerization is a type of virtualization that imitates your machine’s operating system. Containers carry out functions akin to virtual machines but do not encompass hardware virtualization.
Docker is the most extensively used container technology, which uses a public repository. Dependencies like system libraries, external third-party code packages, and other operating system-level programs can be included within a container.
Additionally, an application container allows you to package all the required applications within a portable environment. You can also run multiple containers simultaneously.
Complete Guide on Multi-Primary Replication in MySQL
With this platform, you can effortlessly establish two kinds of replication in MySQL – primary-secondary and primary-primary. It will help address various issues concerning performance, database backups, system failures, etc.
You can find instructions on configuring master-slave replication for your MySQL database here.
This tutorial will guide you through the configuration of MySQL’s master-master (multi-master) replication, focusing on its application in various environments. Although the process is relatively straightforward, paying close attention to some crucial details is essential.
So let’s get started!
Create Environments
You must have two or more database servers to set up replication. We will create two environments with MySQL instances for this purpose.
Steps 1. To get started, log in to the platform. Once on your dashboard, navigate to the top panel and click “Create Environment.”
Steps 2. Please utilize the topology wizard to create the following environments:
The First Master DB environment
Please add the Apache application server, PHP support, and MySQL database. Remember to set the Cloudlet limits for each container. Once you’re done, give your environment a name (e.g., mysql-master-1) and click the Create button to proceed.
The Second Master DB environment
To set up a second master DB environment (master-MySQL-2), you can either follow the same steps as creating the first environment or simply clone the first environment and provide the appropriate name in the designated section.
Please note that the versions and configurations of environments may differ based on your requirements. That is also possible if you prefer a Java or Ruby application instead of PHP. However, please remember that the instructions in the article are specifically for replicating MySQL servers on this platform.
Configure the First Master DB
After installing and activating MySQL servers, it is necessary to configure them for replication.
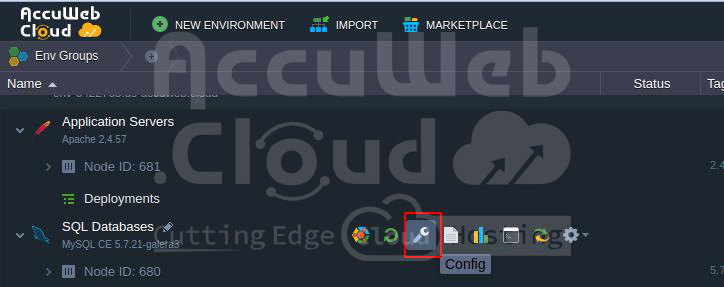
Steps 1. To begin, navigate to mysql-master-1 and select the MySQL Config icon for your environment.
To access the Configuration Manager, follow these steps:
- Open the Configuration Manager.
- Navigate to the /etc/my.cnf file.
- Locate the #skip-networking string.
- Insert the parameters as shown below.
server-id = 1
binlog-do-db = example
binlog-do-db = teste
log-bin = /var/log/mysql/mysql-bin.log
auto_increment_increment= 1
auto_increment_offset = 1Let’s look at what we are configuring with these options.
- The server-id is a standard option used by replication servers to identify themselves. It should be unique for each server.
- The server is instructed to limit binary logging to updates for the specified databases using “bin-log-do-db = example” and “bin-log-do-db = teste.”
Please note that these databases should still need to be created. You can add your databases once you feel confident with the Multi-Master Replication.
- MySQL’s “log-bin” setting determines whether the binary log is enabled. If an option value is provided, it serves as the base name for the log sequence.
- The setting ‘auto_increment_increment’ regulates the gap between each consecutive value in a column.
Setting the auto_increment_offset to 1 when using multi-master replication can help prevent replication conflicts. Specifically, for the master-mysql-1 server, we recommend using a value of 1, while for the master-mysql-2, we recommend using a value of 2.
When using master-to-master replication, setting both the auto_increment_increment and auto_increment_offset options is essential according to your application’s needs. We recommend setting the auto_increment_offset option to prevent replication conflicts to match the server-id parameter’s value.
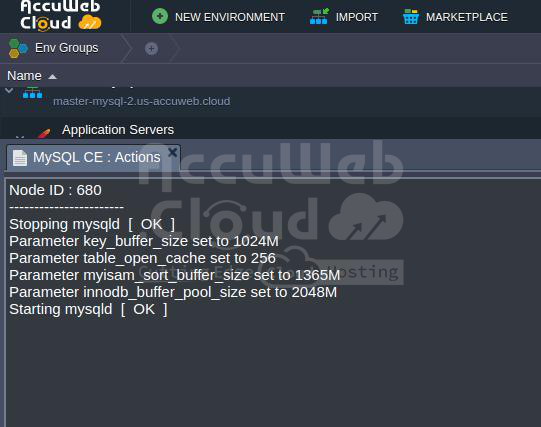
Steps 2. After making modifications to the /etc/my.cnf file, click Save and restart the MySQL node in the master-mysql-1 environment, following the below steps.
Steps 3. To confirm that MySQL has been restarted successfully, go to the actions tab that opens automatically.
If an error occurs during this stage, need to repeat the procedure. If the issue persists, please contact your technical support for further assistance.
Configure the Second Master DB
Steps 1. It’s time to begin setting up the second DB server. Follow the same procedure as we did for the First Master DB.
Steps 2. After creating the second master database., please navigate to the my.cnf file again and locate the #skip-networking parameter. After that, kindly paste the following lines.
server-id = 2
binlog-do-db = example
binlog-do-db = teste
log-bin = /var/log/mysql/mysql-bin.log
auto_increment_increment= 1
auto_increment_offset = 2
Steps 3. After making changes to the /etc/my.cnf file, save the modifications and restart the MySQL node in the master-mysql-1 environment. To confirm that the restart was successful, simply go to the actions tab that automatically opens up.
Enabling Master-Master Replication
To modify the replication, you must execute specific commands using the phpMyAdmin panel.
Steps 1. To access the MySQL server in the first environment (master-mysql-1), please click “Open in Browser.”
Steps 2. You will be redirected to the admin panel.
Steps 3. Please log in using the root user credentials.
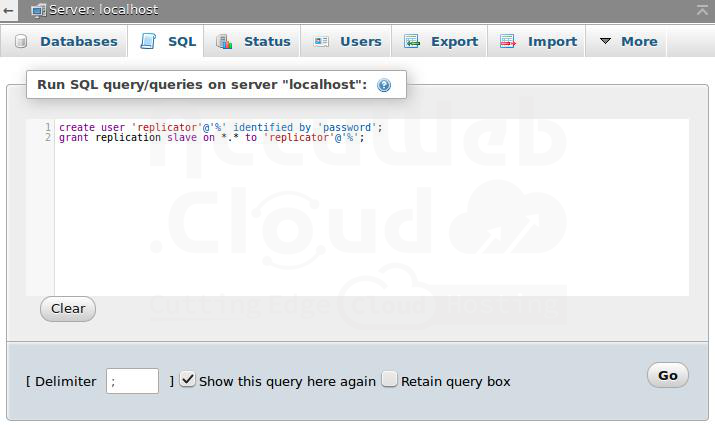
Steps 4. Once logged in, navigate to the SQL tab and execute the commands provided in the open window.
Steps 5. We have created a new user for replication and given them global permissions to perform replication operations.
Steps 6. Please remember the login details you provided and click the Go button below.
Steps 3. To ensure that the configuration is correct, run the following command:
Please remember the name of the binlog file and its position, as we will need this information for future configurations.
Steps 4. To set up the second MySQL server, replicate steps 1-3, which include creating a user with the same name and noting the log file settings.
Steps 5. It is now time to activate replication.
To do this, open the SQL tab located in the phpMyAdmin panel of the second MySQL server (which is included in the master-mysql-2 environment) and execute the following command:
STOP SLAVE
CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST = 'first_server_IP', MASTER_USER = 'replicator', MASTER_PASSWORD = 'password', MASTER_LOG_FILE = 'binlog_file_name', MASTER_LOG_POS = binlog_file_position;
START SLAVE;Where
Steps 1. first_server_IP – To set up replication between servers hosted by different providers, you’ll need to link external IP addresses to both DB nodes and specify the internal IP address of the MySQL server in the first environment as a parameter.
Steps 2. Password – The username you specified when creating the database user for the initial MySQL server.
Steps 3. binlog_file_name – Please provide the value listed under the “File” column in the status table of the initial server.
Steps 4. binlog_file_position – position of the binlog file from the same table
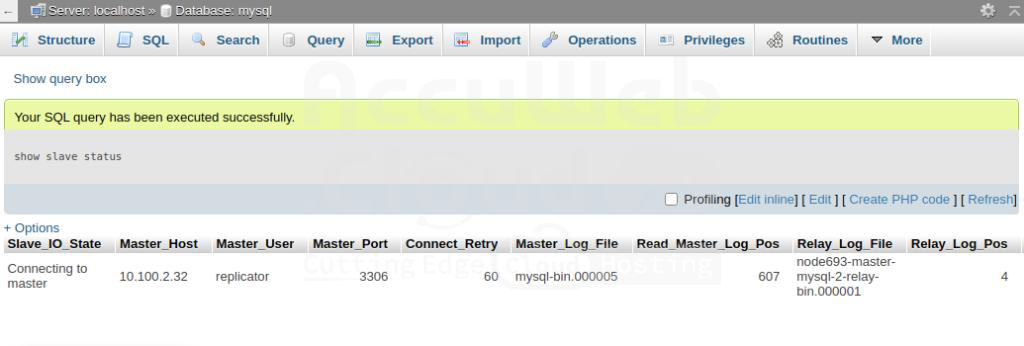
Step 5. To verify if the commands run successfully or not, run the following\
show slave status;
Step 6. To access the administrator panel for the MySQL node of the master-MySQL-1 environment, run the same lines but replace the parameter values with the information of the second DB server.
STOP SLAVE;
CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST = 'second_server_IP', MASTER_USER = 'replicator', MASTER_PASSWORD = 'password', MASTER_LOG_FILE = 'binlog_file_name', MASTER_LOG_POS = binlog_file_position;START SLAVE;
Step 8. Please verify if everything was configured correctly in the same manner.
show slave status;
Congratulations! The replication feature is successfully enabled on both servers.
Testing the Replication
Lastly, let’s make sure everything is functioning perfectly.
Steps 1. Log onto the first DB server & create a new example database:
As you can see, it is already marked as a replicated within the Master replication column.
Steps 2. Access the second server in your MySQL cluster and verify if the new database was added or not.
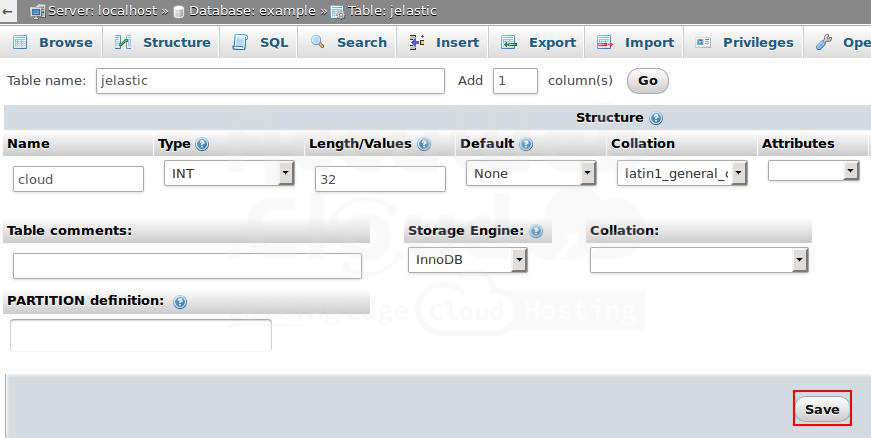
Once confirmed, select the database and create a new table with at least one column.
Steps 3. Please input your desired values and click on the Save button.
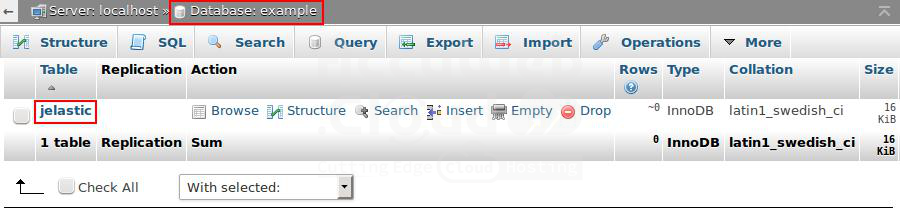
Steps 4. Please switch back to the admin panel of the first MySQL server and verify that the replicated example database now includes the “Jelastic” table.