How To Perform Connection Pooling In JDBC With Payara Application Server?
Java application servers like GlassFish and Payara use JDBC connection pooling to speed up and improve database access. This means they reuse database connections from a pool instead of creating new ones each time.
Setting up a JDBC connection pool on your server can reduce delays and use fewer resources, which improves database performance, especially for dynamic applications.
Here are simple steps to set up JDBC for Payara with AccuWeb.Cloud.
Create Environment
Step 1. Log into your AccuWeb.Cloud dashboard and click the “New environment” button.
Step 2. In the topology wizard, go to the Java tab, select Payara as your application server, and add the required database (e.g., MySQL). Set the resource limits for your containers and choose an environment name.
Step 3. Click “Create,” wait a few minutes for your new environment to be ready, and then proceed to create the JDBC connection pool.
Setting Up Database
Step 1. Open your MySQL node in the browser by clicking the “Open in browser” button. Then, use the email you received with database credentials to log into the phpMyAdmin panel.
Step 2. Once logged in, go to the User Accounts tab and click “Add user account”. Fill in all the necessary information in the form, and make sure to check the box that says “Create a database with the same name and grant all privileges”.
Finally, click “Go” at the bottom of the page to add the database and user for connection pooling.
Setting Up Java Application Server
Step 1. The JDBC MySQL connector is already included in the stack by default, so there’s no need to manually upload it. You can find it in the path /opt/payara/glassfish/domains/domain1/lib.
Step 2. Log in to the Payara Admin panel using the credentials provided in the email.
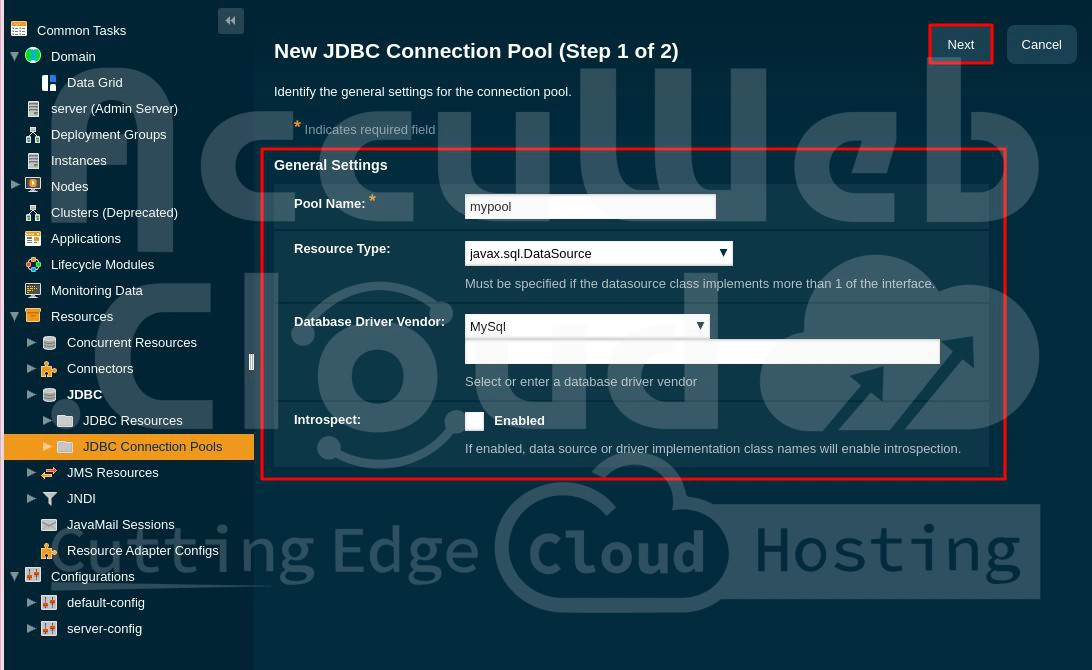
Step 3. Navigate to Resources > JDBC > JDBC Connection Pools and click the New button.
In The Form That Appears, Fill In The Following Fields
- Pool Name: Choose any name you prefer.
- Resource Type: Select javax.sql.DataSource.
- Database Driver Vendor: Choose MySQL from the options.
Click Next to continue.
Step 4. Modify the following Additional Properties:
- User: Enter your database login (for pooling).
- ServerName: Specify your database host without the protocol (e.g., node5211-connection-pooling.us-accuweb.cloud).
- Port: Set the port number to 3306.
- DatabaseName: Enter your database name (for pooling).
- Password: Provide a password for the specified user.
- URL or Url: Set the JDBC connection string in the jdbc:mysql://{db_host}:3306/ format. Replace {db_host} with either the node hostname (node5211-connection-pooling.us-accuweb.cloud) or IP address (192.168.2.155).
Once these properties are specified, click Finish.
Once you click on the finish button, the new pool will be added and shown in the Pools section.
Step 5. To verify accessibility, select the newly created connection pool and click the Ping button. You should see a “Ping Succeeded” message if everything is working correctly.
Step 6. Navigate to Resources > JDBC > JDBC Resources and click the New button to create JDBC resources for pooling.
Step 7. In the window that appears, provide a desired JNDI Name and choose your Pool Name from the drop-down list. Confirm the creation of resources by clicking OK at the top.
Step 8. Once you click on the OK button, the new resource will be added and displayed in the Resources section.
Connecting from Java Code
Insert the following lines into your application’s Java class:
- InitialContext ctx = new InitialContext();
- DataSource ds = (DataSource)ctx.lookup(“{resources}”);
- Connection conn = ds.getConnection();
Replace the {resources} placeholder with your JNDI name from the previous section (e.g., jdbc/mypool in our case).
Now, you can deploy your Java application to the AccuWeb.Cloud environment you created and take advantage of Payara connection pooling!
Conclusion
In conclusion, connecting a Payara app to MySQL is essential for database operations. Configuring JDBC drivers and connection details establishes smooth communication between your Payara app and the database.
Setting up a JDBC connection pool on your server can reduce delays and save resources, which improves database performance, especially for dynamic applications.