Websockets Support for Apache & NGINX
WebSocket technology is a widely used method for instant messaging between a client and server within an application. It establishes a continuous, two-way communication link over TCP, resulting in minimal latency and rapid interaction. This technology can also traverse proxies and firewalls efficiently.
Our platform offers robust WebSocket support by integrating it with the Shared Load Balancer and NGINX balancer node. This allows you to use WebSocket features even without an external IP address, by consolidating various WebSocket app ports into a single port (80 for HTTP and 443 for HTTPS).
The simplest way to set up WebSocket support for your application is by using an NGINX balancer (see detailed instructions in our documentation).
However, if this approach doesn’t meet your needs, the platform fully supports WebSockets on available application servers like Apache (for PHP, Ruby, and Python apps) and NGINX (for PHP and Ruby apps).
The process of integrating WebSockets can vary depending on your application. We provide configuration samples for each of these server nodes, making it easy to enable WebSocket support by uncommenting and adjusting a few settings, such as the listener port number, to fit your app’s requirements.
In the step-by-step tutorial below, we’ll demonstrate an example of configuring WebSockets for a simple PHP chat project deployed without a balancer server, utilizing WebSocket technology. Let’s begin from the start.
Create an Environment and Deploy the Application
Using the platform, you can easily create the environment you need in just a few clicks. Simply log into your PaaS account and follow these steps:
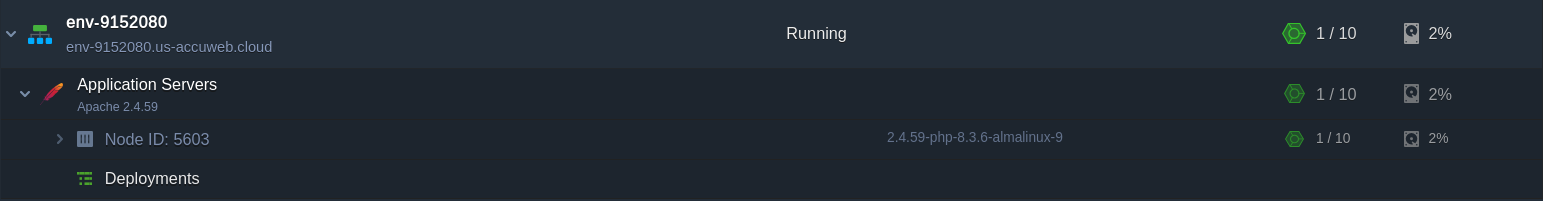
Step 1. Click the “New Environment” button located in the top left corner of the dashboard.
Step 2. In the Environment Wizard window that appears, navigate to the tab for your chosen programming language. Select the desired application server (for our example, we’ll use Apache to serve our PHP application). Use the cloudlet sliders to allocate the necessary resources. Enter a name for your environment (e.g., apache-WebSockets) and then click “Create.”
Step 3. Your new environment will appear on the dashboard in a few minutes.
Step 4. Upload and deploy your application using the platform’s Deployment Manager or through a remote GIT/SVN repository. Detailed instructions for deploying based on your chosen engine can be found in our Deployment Guide.
As a result, your deployed project will appear in the corresponding section within the environment’s panel.
Server and Application Configurations
WebSocket support in the Apache server is enabled through the proxy_wstunnel_module module, which is included in the default server build. NGINX, on the other hand, can proxy WebSocket connections directly within the application server, similar to how NGINX-balancer operates.
Now, let’s configure your application server.
Step 1. Click the “Config” button next to your application server node.
Step 2. In the Configuration Manager tab that opens, follow the steps in one of the instruction sections based on your chosen server:
For Apache application server
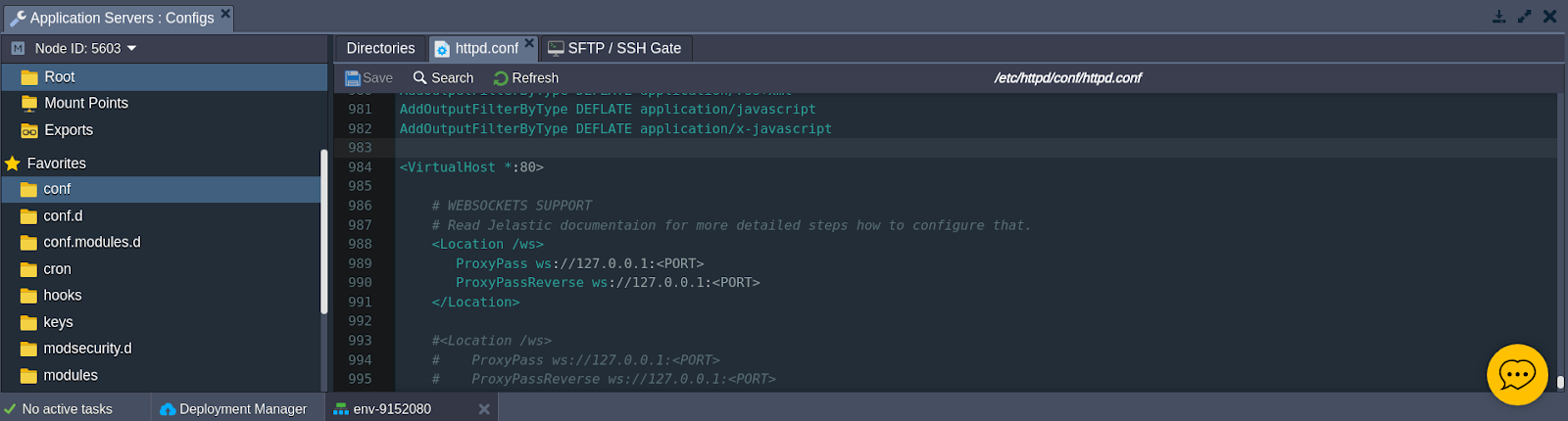
Locate the `httpd.conf` file in the `conf` directory and uncomment the specific lines at the end of the file (around line 962).
<Location /ws>
ProxyPass ws://127.0.0.1:<PORT>
ProxyPassReverse ws://127.0.0.1:<PORT>
</Location>Now, update both parameters to match the port number used by your WebSocket application (for example, ours uses port 9000).
Ensure that it matches the configuration shown in the image below.
Save the changes by clicking the button labeled with the same name above the editor.
For NGINX application server
Locate the `nginx.conf` file in the `conf` directory and uncomment the specific lines in the “#Websocket support” section.
upstream websocket {
server 127.0.0.1:<PORT>;
}
…
location /ws {
proxy_pass http://websocket;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "Upgrade";
}Next, replace the `<PORT>` placeholder with the actual port number used by your WebSocket application, and then save the changes you made.
Step 3. That’s all the server configurations you need to complete. Now, configure your deployed application by accessing its configuration file responsible for WebSocket settings. Adjust the `ws` path within the file to follow this format:
```
ws://{env_domain}{path_to_ws_file}
```Here’s what each part should be replaced with:
- `{env_domain}`: Substitute this with your environment domain (found under the environment name on the dashboard, such as `apache-websockets.jelastic.com` in our case).
- `{path_to_ws_file}`: Modify this to reflect the path to the file that should be accessed when establishing the WebSocket connection.
Ensure it resembles the example shown in the image below:
Step 4. Save the changes and then restart your application server using the appropriate button.
Step 5. Excellent, now it’s finished! Click on “Open in Browser” to launch your application in a new browser tab.
Step 6. As you can see, our example chat application is working perfectly.
Even when running a simple chat application like this, you’ll experience the benefits of fast message transfer thanks to using the WebSocket protocol. Enjoy!