How to integrate .Net Core with MSSQL Server in Linux System?
Setting up .NET Core with SQL Server on Linux helps developers build apps that work across different platforms with a strong database. This setup includes installing SQL Server, setting up .NET Core dependencies, and configuring the database connection using Entity Framework Core or ADO.NET.
With the right setup, your .NET Core app can easily connect to SQL Server while taking advantage of Linux’s speed and flexibility.
Requirements Before Installation
– .NET Core SDK and SQL Server must be installed on Linux.
– Root access to the Linux system is required.
Here, we will create an MVC Employee Management System and integrate it with the MSSQL Server.
Step 1: Create an MVC Project
Open your terminal and run this command to create a new MVC project named EmployeeManagement:
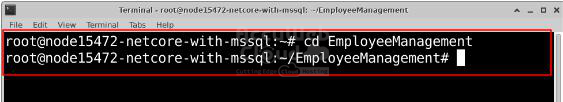
dotnet new mvc -o EmployeeManagementGo to the newly created project folder:
cd EmployeeManagementStep 2: Install Required Entity Framework Core Packages
Entity Framework Core lets your .NET app interact easily with the MSSQL Server. Run these commands to install the needed packages:
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCoredotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServerdotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Designdotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.ToolsStep 3: Create a Database
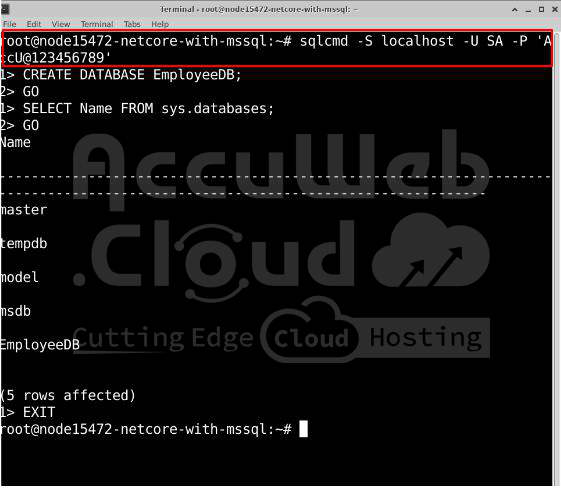
Log into your SQL Server using this command (replace ‘YourPassword’ with your actual password):
sqlcmd -S localhost -U SA -P 'YourPassword'Create a new database named EmployeeDB:
CREATE DATABASE EmployeeDB;
GOCheck if the database is created:
SELECT Name FROM sys.databases;
GOExit SQLCMD:
EXITStep 4: Install EF Core Tool Globally
The EF Core Tool helps manage database migrations, create models, and update database schemas. Installing it globally means you can use EF commands in any .NET Core project without reinstalling them each time.
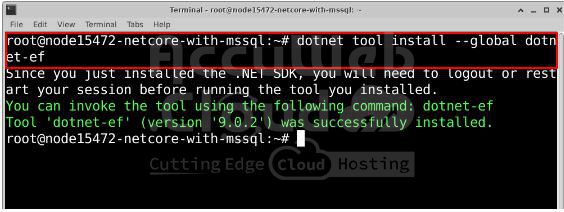
Install the EF Core Tool
Run this command in the terminal:
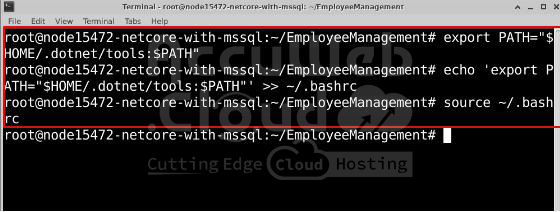
Update the System Path
Run these commands to make sure the tool works everywhere:
export PATH="$HOME/.dotnet/tools:$PATH"
echo 'export PATH="$HOME/.dotnet/tools:$PATH"' >> ~/.bashrc
source ~/.bashrcCheck the Installation
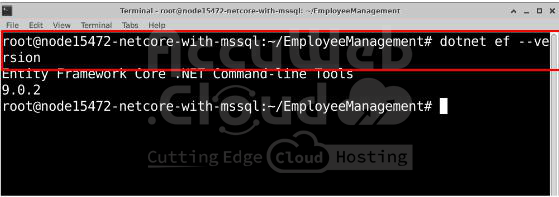
Verify that EF Core is installed by checking its version:
dotnet ef --versionIf installed correctly, it will show the EF Core version.
Step 5: Add the Database Connection in appsettings.json
The connection string in appsettings.json helps .NET Core connect to the SQL Server database. Storing it here makes it easy to change settings without modifying the code. It also supports different environments like development and production.
Add the Connection String
Open the appsettings.json file using this command:
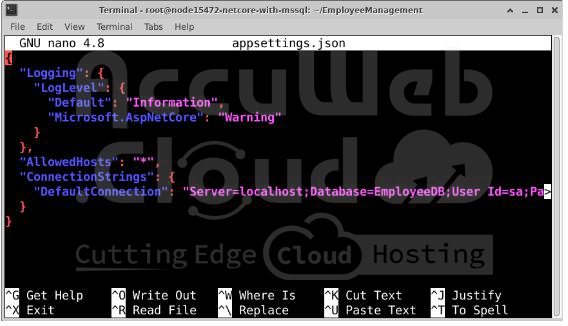
nano appsettings.jsonThen, add the following code:
{
"Logging": {
"LogLevel": {
"Default": "Information",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore": "Warning"
}
},
"AllowedHosts": "*",
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=localhost;Database=EmployeeDB;User Id=sa;Password=YourPassword;TrustServerCertificate=True"
}
}-> Replace YourPassword with your actual SQL Server SA password.
-> If SQL Server is on another server, replace localhost with the server’s IP address.
Step 6: Create Database Context
The DbContext in Entity Framework Core (EF Core) is like a bridge between your .NET Core application and the SQL database. It helps manage database connections, transactions, and queries using LINQ (instead of writing SQL manually).
It also:
Tracks changes in data
Supports migrations (database updates)
Helps with Create, Read, Update, Delete (CRUD) operations
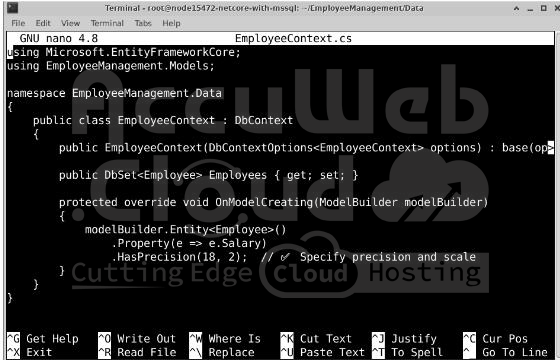
Create the EmployeeContext.cs File
Make sure the file EmployeeContext.cs is inside:
EmployeeManagement/Data/
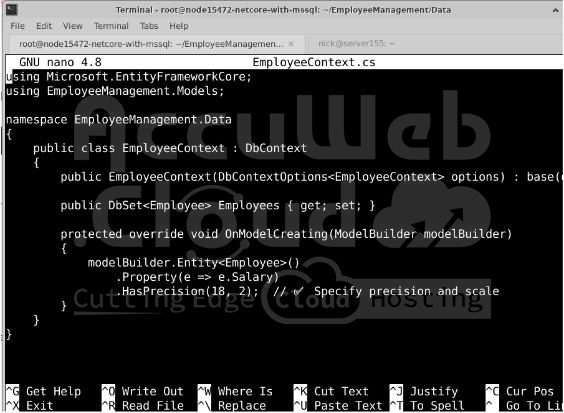
If the file does not exist, create it and add the following code:
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using EmployeeManagement.Models;
namespace EmployeeManagement.Data
{
public class EmployeeContext : DbContext
{
public EmployeeContext(DbContextOptions<EmployeeContext> options) : base(options) { }
public DbSet<Employee> Employees { get; set; }
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder modelBuilder)
{
modelBuilder.Entity<Employee>()
.Property(e => e.Salary)
.HasPrecision(18, 2); // ✅ Sets precision and scale for Salary
}
}
}What does this do?
- Defines a DbSet<Employee>, which represents the Employees table in the database.
- Ensures the Salary field has a decimal precision of 18,2 (18 digits, 2 decimal places).
If EmployeeContext.cs is missing, create it inside EmployeeManagement/Data/.
If the file is missing, create it inside EmployeeManagement/Data/.
Step 7: Add Database Context in Program.cs
To use Entity Framework Core (EF Core) in your .NET Core application, you need to register the database context in Program.cs. This allows your application to connect to the SQL Server database and manage data efficiently.
Why is this important?
Enables database access for controllers and services
Manages database connections automatically
Supports scalability by controlling how database connections are handled
How to Add DbContext in Program.cs?
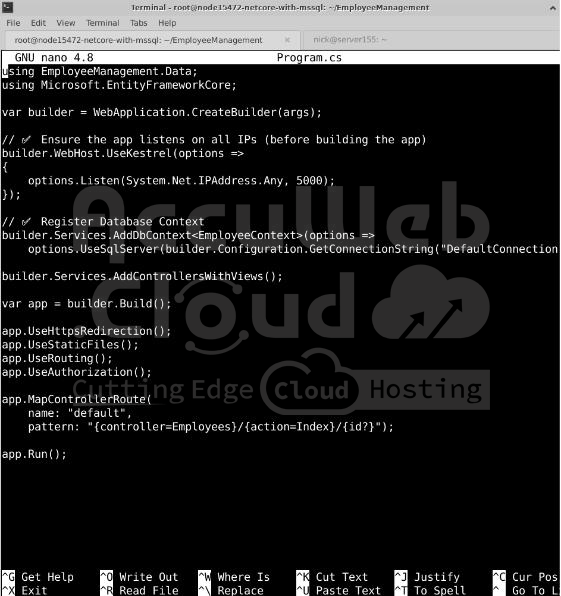
Open Program.cs and add the following code:
builder.Services.AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(options =>
options.UseSqlServer(connectionString));This step is necessary for EF Core to work with your database. Without it, your application cannot interact with the SQL Server database.
Step 8: Create the Employee Model
In .NET Core, a model is a C# class that represents a database table. It allows you to easily add, update, delete, and retrieve data using Entity Framework Core (EF Core). Instead of writing complex SQL queries, you can use LINQ to interact with the database.
Why is this important?
- Maps data between the application and database
- Ensures data validation and integrity
- Supports migrations and database relationships
How to Create the Employee Model?
Inside the Models/ folder, create or update the Employee.cs file with the following code:
namespace EmployeeManagement.Models
{
public class Employee
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public string Position { get; set; } = string.Empty;
public decimal Salary { get; set; }
}
}Step 9: Apply Migrations and Update the Database
Migrations help keep the database structure in sync with your application’s data model. Instead of writing SQL scripts manually, Entity Framework Core (EF Core) tracks changes and applies them automatically.
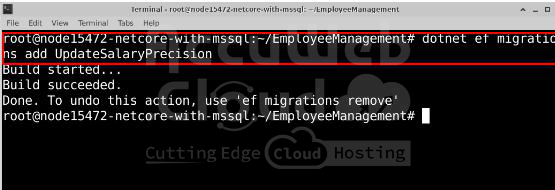
Run the following commands to update the database:
dotnet ef migrations add UpdateSalaryPrecisiondotnet ef database updateIf the commands run successfully, the Employees table will be created inside EmployeeDB.
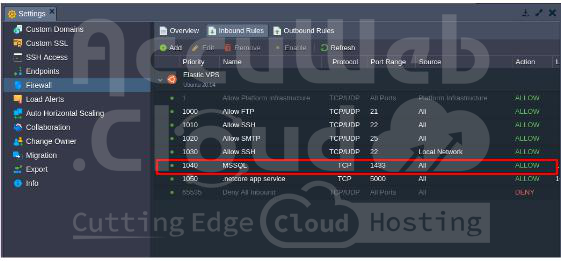
Step 10: Allow the Application Port number in AccuWeb.Cloud web base Firewall
By default, the .Net core application port is not enabled in the AccuWeb.Cloud firewall. To allow it, follow these steps:
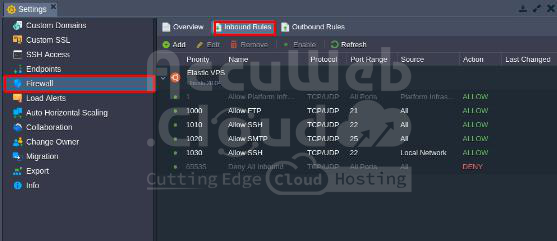
Step 1: Log into AccuWeb.Cloud dashboard.
Step 2: Select the environment where .NET Core and MSSQL Server are installed. Here, we use netcore-with-mssql as an example. Then, click the Settings icon.
Step 3: In the Settings window, go to Firewall -> Inbound Rules.
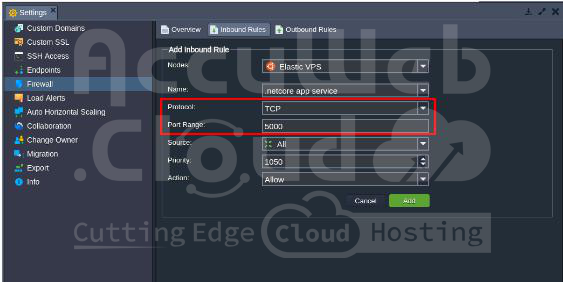
Step 4: Click Add to create a new rule and enter the following details:
Name: Enter a descriptive name for the rule.
Protocol: Choose TCP, UDP, or Both.
Port Range: Enter 5000 for .Net Core app service. Leave blank to apply to all ports.
Source: Define the source (specific IP addresses or network interface).
Priority: Set the order in which the rule should be applied.
Action: Select Allow to enable the MSSQL port in AccuWeb.Cloud.
Step 5: Click Add to apply the rule.
Step 6: Verify the changes in the Inbound Rules panel to confirm the port is open.
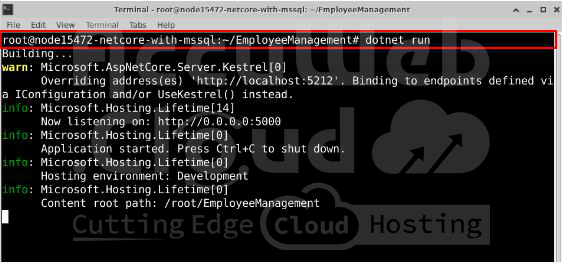
Step 11: Test the Application
Before deploying, it’s important to test the application to make sure everything is working.
1. Start the application by running:
dotnet run2. If there are no errors, your application will run successfully.
3. Open a web browser (Chrome, Firefox, etc.) and go to:
http://your-server-ipaddress:5000
Replace your-server-ipaddress with your actual server IP address.
You should see the Employee Management System running if everything is set up correctly!
Conclusion:
Connecting .NET Core with MSSQL Server on Linux helps build applications that work on different platforms. By installing .NET Core, setting up MSSQL Server, and configuring Entity Framework Core with DbContext, you can easily manage and interact with the database.
This setup makes data handling efficient, scalable, and high-performing, which is great for modern web applications.