Stateless vs. Stateful Scaling on AccuWeb.Cloud
In AccuWeb.Cloud, scaling solutions are designed to handle varying application needs. There are two primary approaches: stateless scaling and stateful scaling, each suited to different types of applications.
Stateless Scaling
In AccuWeb.Cloud, stateless scaling creates additional nodes using the same basic image, making it ideal for applications like web servers that don’t need to store data. This approach ensures high scalability and easy management.
When traffic increases, new nodes are quickly and independently created from a standard base image, allowing them to handle requests without relying on shared data. This makes stateless scaling perfect for web servers, load balancers, and similar applications.
Benefits
- Fast and easy to manage: Adding nodes is quick and hassle-free.
- Highly scalable: Need more capacity? Just add more nodes!
Ideal for
- Web servers
- Load balancers
- Applications that don’t require storing data on the server
Stateful Scaling
Conversely, stateful scaling is used for applications like databases that need to maintain consistent data across instances. It involves copying a master node to new nodes, ensuring data integrity and consistency. This approach guarantees that all nodes have the same information, making it essential for databases and applications that require reliable and synchronized data.
Benefits
- Data integrity: All nodes have the same information, ensuring accuracy.
Ideal for
- Databases
- Applications that need consistent data across servers
Understanding Stateless Scaling with an Example
Let’s explore how stateless scaling works with a MariaDB and Apache environment as an example.
Here are two images showing the Apache server before adding stateless nodes, along with the index file content and its output.
To see how stateless scaling operates, click on the “Change Environment Topology” icon from your environment, as shown in the image. This action allows you to add more nodes to your setup.
Under the horizontal scaling section, click the “+” sign to add more nodes and select “Stateless” from the list and click Apply.
Once the new node is added, your environment will look like this, with the new node integrated into the application servers.
Now, click on the “Open in Browser” icon for the newly added node.
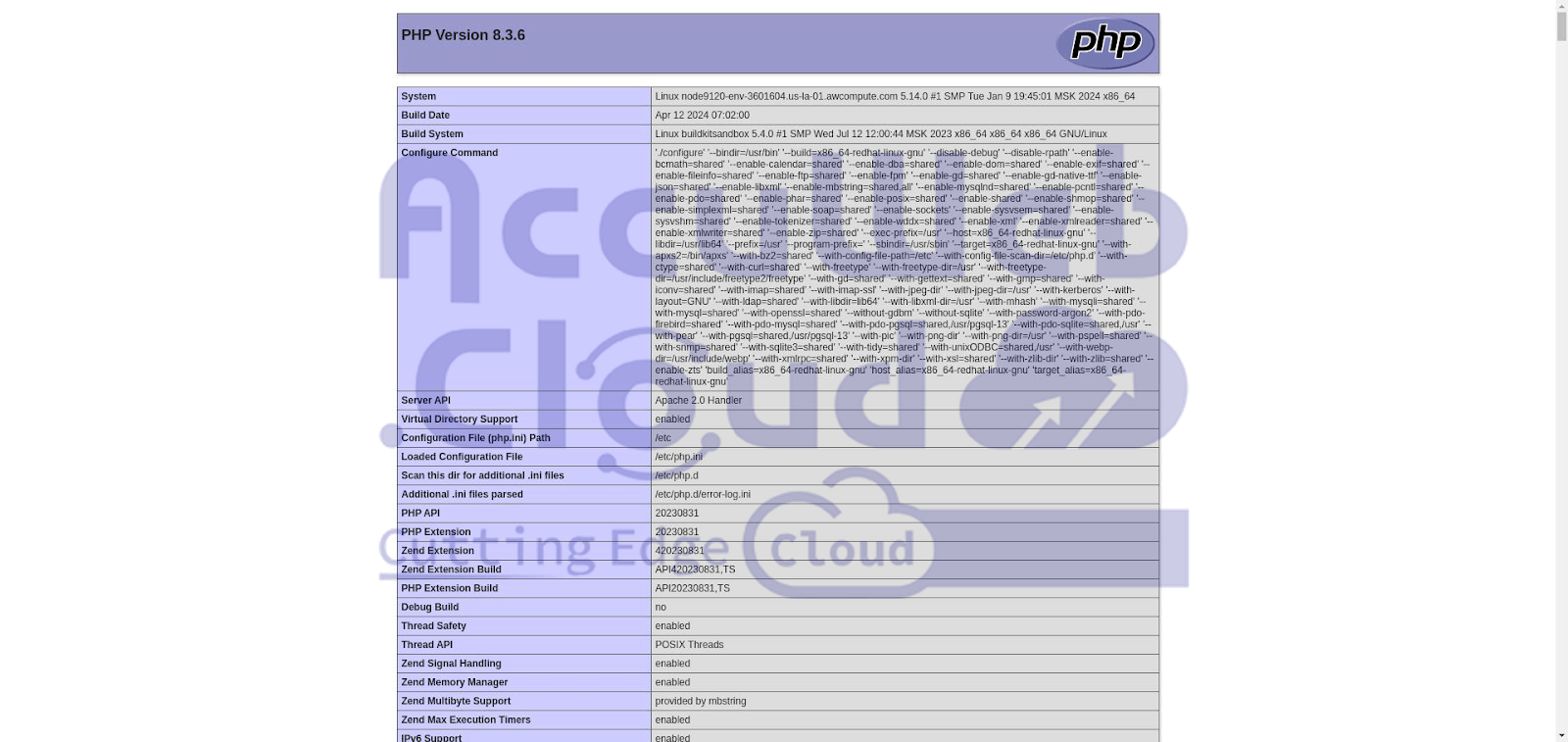
It will display the default index file content, which is phpinfo, as shown in the images below.
Stateless scaling replicates nodes from a base image without copying or modifying content from the main node, ensuring uniformity across all nodes.
Next, we will show how stateful scaling works.
Understanding Stateful Scaling with an Example
Step 1. Click on the “Open in Browser” icon from the MariaDB node to open phpMyAdmin.
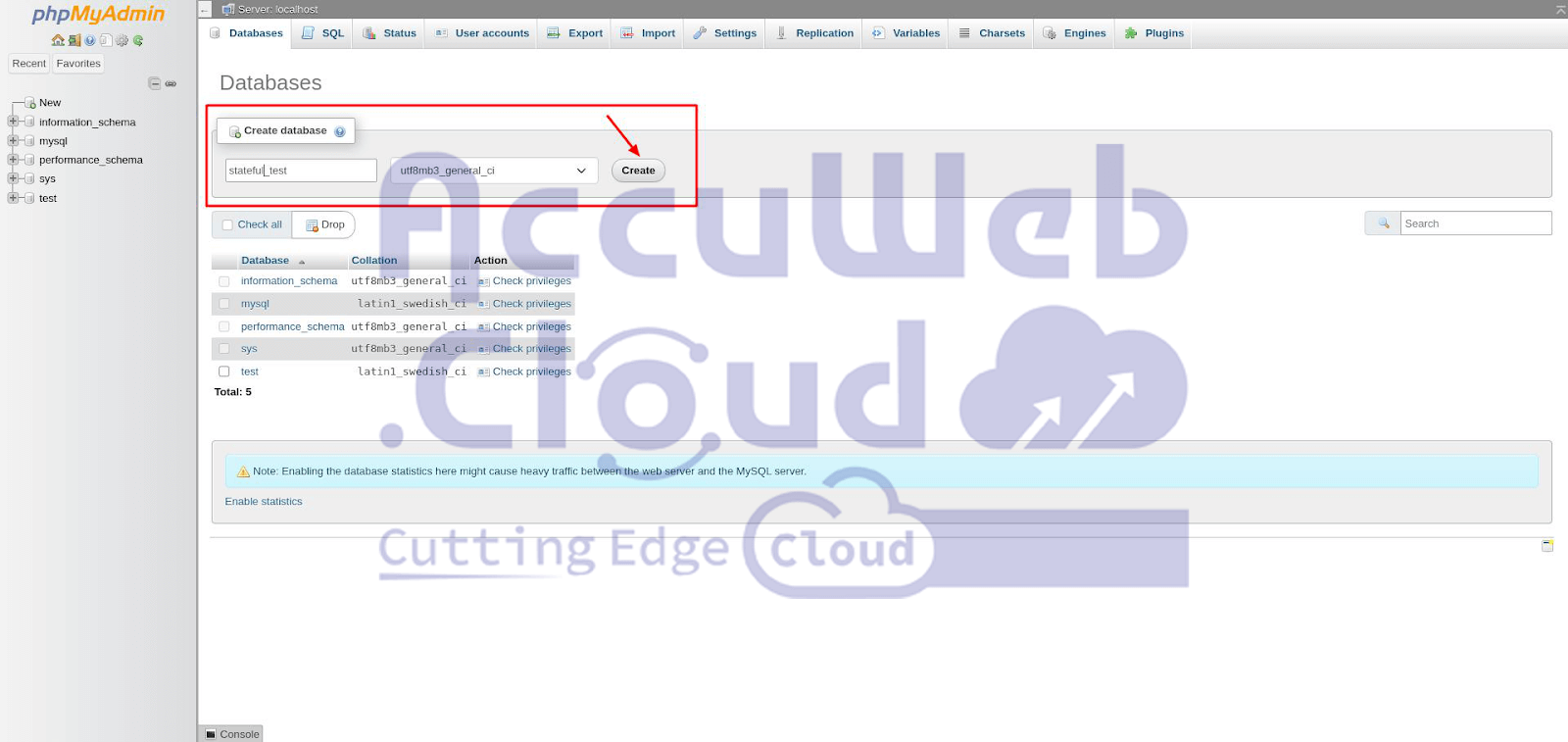
Step 2. Log in with the root credentials and create a test database.
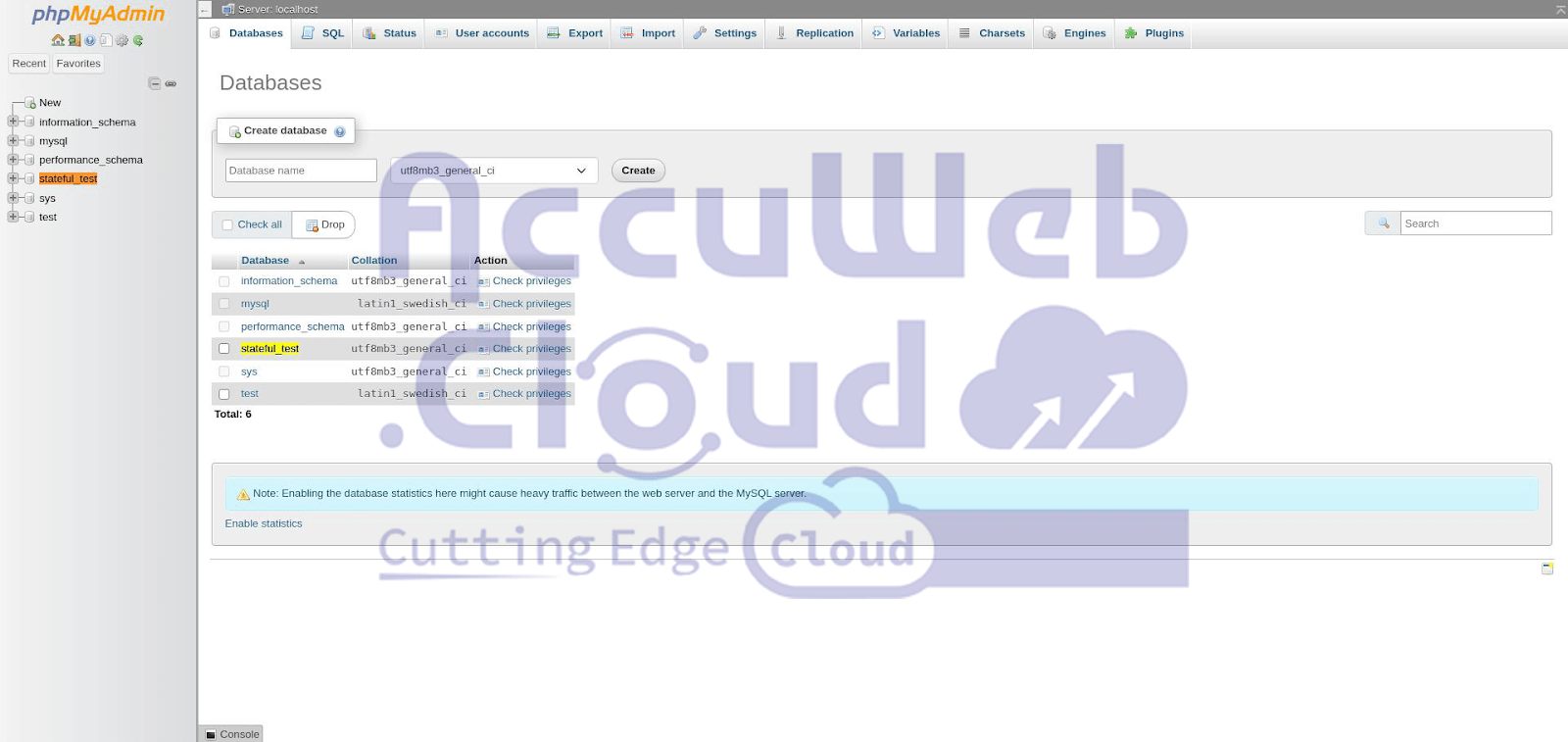
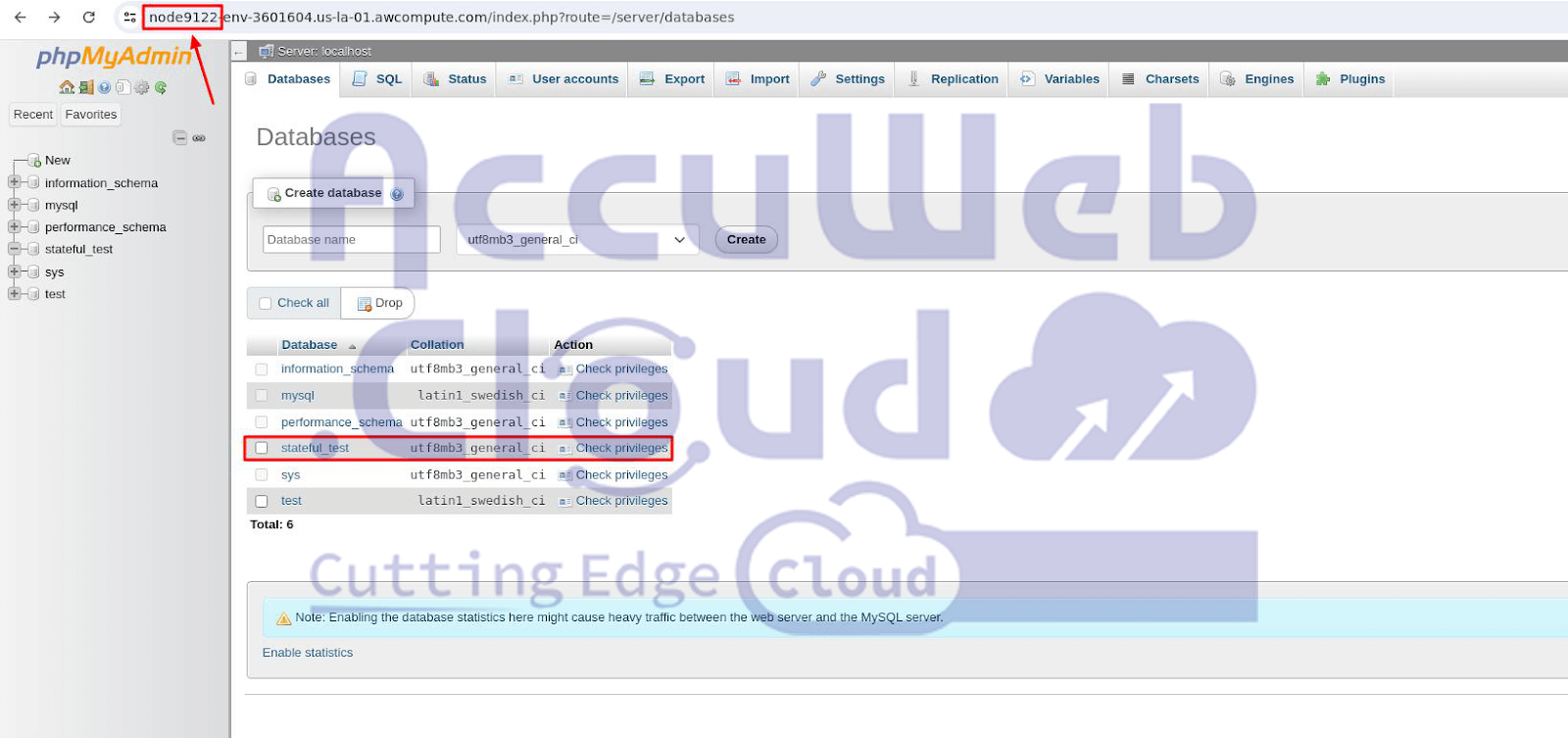
Step 3. Check and confirm that the newly created database appears in the databases list.
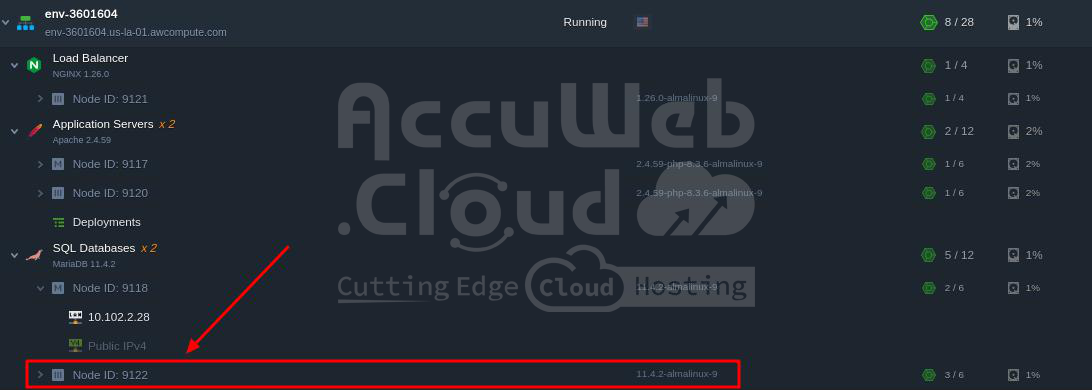
Step 4. Now, go to “Change Environment Topology,” select the MariaDB layer, increase the number of nodes by clicking the “+” sign, choose the “Stateful” option from the list under horizontal scaling, and click Apply.
The system will start applying the changes to the environment, which may take a few moments. Afterward, the new MariaDB node will appear.
Access the new node’s phpMyAdmin in your browser and log in with the same credentials. You will see that the same database exists, demonstrating how stateful scaling works.
Choosing the right approach depends on your application’s needs. Stateless scaling is perfect for applications without data storage requirements, while stateful scaling is essential for those that rely on consistent data.
Let AccuWeb.Cloud handles the scaling complexity – you focus on serving your customers!