How to Access Your Kubernetes Cluster Remotely?
After the successful installation of a cluster, there are multiple ways to access it to start management:
Using Kubernetes Dashboard
Step 1: After installation, you’ll receive important connection details like a link and access token.
Copy the Access Token provided and keep it safe on your local system.
This token is needed to log in to the Kubernetes dashboard.
The same information will also be sent to you via email.
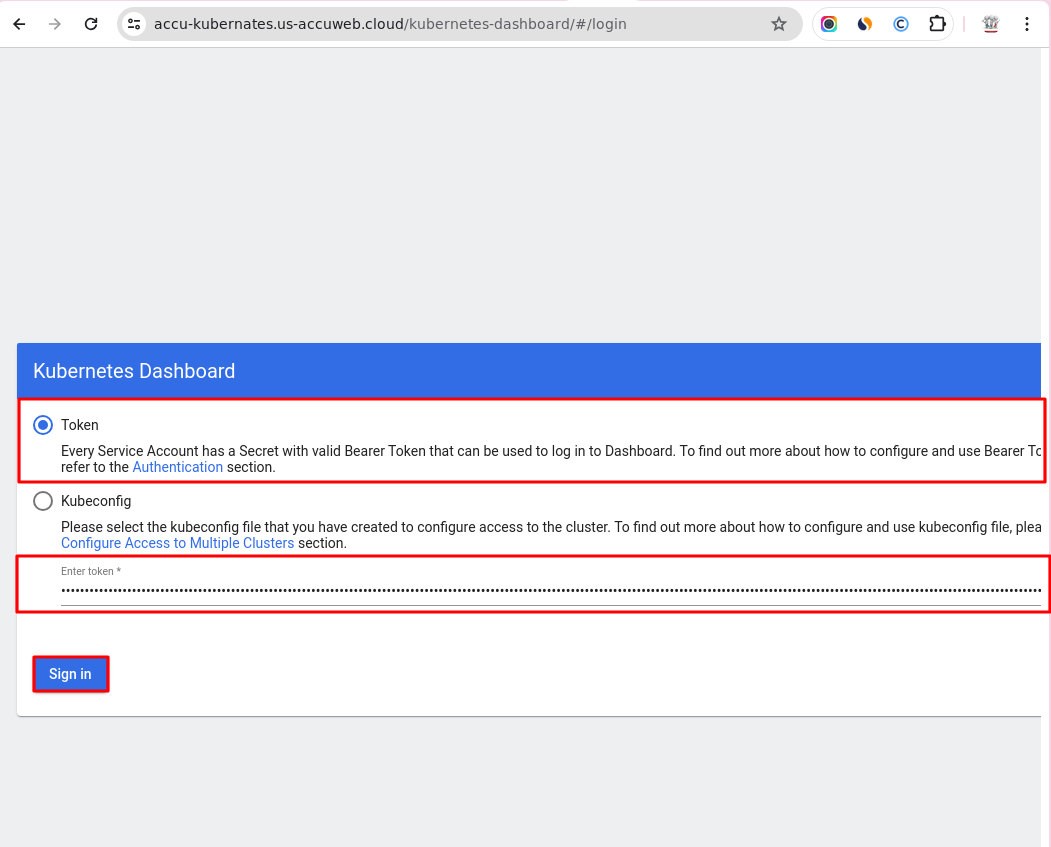
Step 2: Click on the Kubernetes dashboard link to open the dashboard.
Step 3: Select the Token option in the dashboard and paste the copied token from Step 1.
Step 4: After clicking “Sign in” , you’ll access the Kubernetes Cluster dashboard.
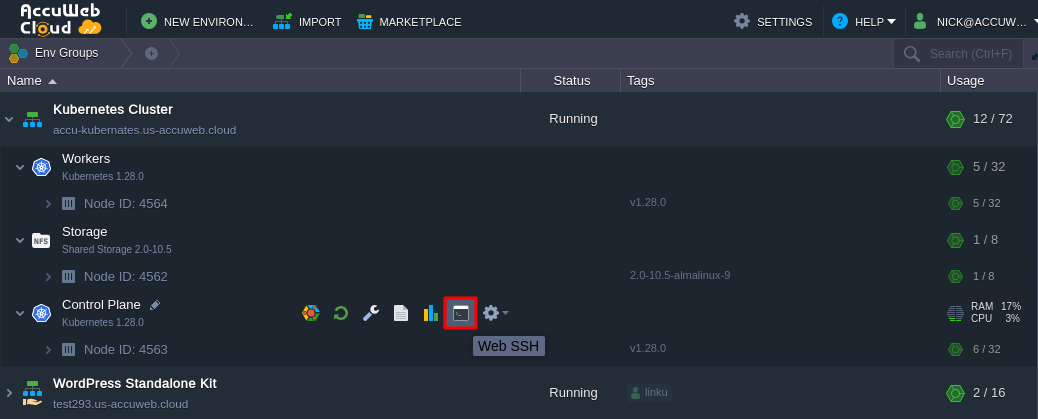
Step 5: If you’ve lost the email with the access token, you can retrieve it by running a specific command on the master node via Web SSH:
Navigate to the Kubernetes Cluster environment and open it. Then, access the Control Plane and choose the Web SSH option.
Enter the following command in the Web SSH window to get the access token.
Now, you can reaccess the Kubernetes Dashboard.
Using Kubectl Client
Kubectl is a tool you can use from the command line to control a Kubernetes cluster. It’s automatically installed on all master nodes when setting up the environment.
Step 1: Follow these installation steps to use kubectl locally. Then, run a command to set up a remote connection:
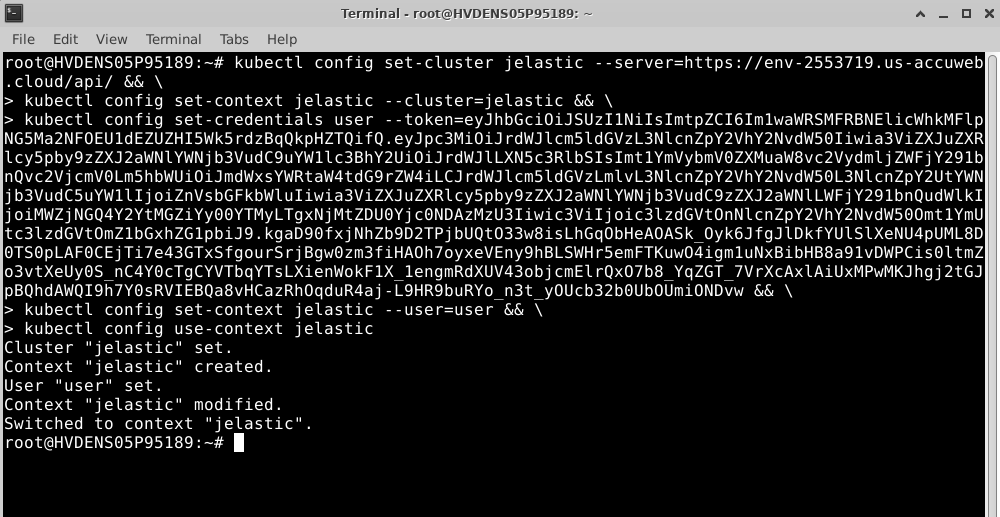
kubectl config set-context jelastic –cluster=jelastic && \
kubectl config set-credentials user –token={token} && \
kubectl config set-context jelastic –user=user && \
kubectl config use-context jelastic
Here, we have installed the kubectl on Ubuntu 20.04 and executed the command mentioned above.
The API endpoint and token details will be in the email you received when you set up Kubernetes in the environment.
Go to the email and right-click on the link Remote API Endpoint and select the Copy link address option.
Once you click on it, the address will be copied and you need to replace it with the {api-endpoint} in the command in Step 1.
Again, go to the Email and copy the token. You need to replace it with the {token} in the command in.
Tip: If Remote API wasn’t enabled during installation, you can do it using the built-in add-on for master nodes in the platform dashboard.
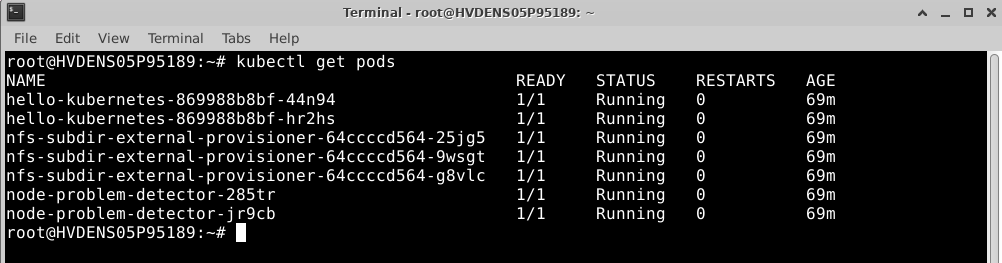
Step 2: Check if kubectl has access to the cluster with this command:
You should see information about pods in the default namespace.