Database Configuration Files
In database management system, configuration files play a crucial role. This allows administrators to customize and optimize database settings to match specific requirements and workloads. This guide provides a detailed overview of the primary configuration files found in the AccuWeb.Cloud platform to manage database servers and organized by directory and database type.
Whether you’re working with PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB, Percona, or any other supported database and this guide will help you understand where and how to manage these critical files.
| Folder | Path | Database Types |
| conf | /var/lib/pgsql/data | PostgreSQL |
| etc | /etc | all |
| cron | /var/spool/cron | all |
| scripts | /var/lib/jelastic/bin | all |
| backup | /var/lib/jelastic/backup | all |
| keys | /var/lib/jelastic/keys | all |
| conf.d | /etc/httpd/conf.d | MySQL, MariaDB, Percona, PostgreSQL |
Main Configuration Directories and Files
Here, we’ll explore the various directories and key configuration files they contain, detailing their purpose and how they can be managed.
CONF Directory
Path: /var/lib/pgsql/data
Database Type: PostgreSQL
The `conf` directory is where the main configuration files for PostgreSQL are stored. Key files include:
postgresql.conf: Main configuration file for PostgreSQL settings.
pg_hba.conf: Client authentication configuration file.
PostgreSQL Configuration Management
AccuWeb.Cloud automatically manages two crucial parameters in the `postgresql.conf` file:
- shared_buffers: Allocated as a part of total RAM—quarter if a container has eight or more cloudlets and seventh otherwise (minimum 128 KB).
- max_stack_depth: Set to 1024 less than the maximum stack size (response of the `ulimit -s` command), converted to MB.
To manually adjust these settings, remove the `#Jelastic autoconfiguration mark.` line at the beginning of the file to prevent your changes from being overwritten.
ETC Directory
Path: /etc
Database Type: All
The `etc` directory contains configuration files applicable to all database types and including:
`php.ini`: Configuration file for PHP settings.
MySQL, MariaDB, and Percona Configuration
The `my.cnf` file in this directory includes critical settings for database management:
- key_buffer_size
- table_open_cache
- myisam_sort_buffer_size
- Innodb_buffer_pool_size
To manually change any of these settings and remove the `#Jelastic autoconfiguration mark.` line at the start of the file. Alternatively and you can override settings in the `/etc/my.cnf` file by specifying them in the `/etc/mysql/conf.d/custom.cnf` file.
CRON Directory
Path: /var/spool/cron
Database Type: All
The `cron` directory houses configuration files for cron jobs, which can be used for scheduled tasks like automated database backups. A default cron expression is included in the configuration file, which you can uncomment and adjust as needed.
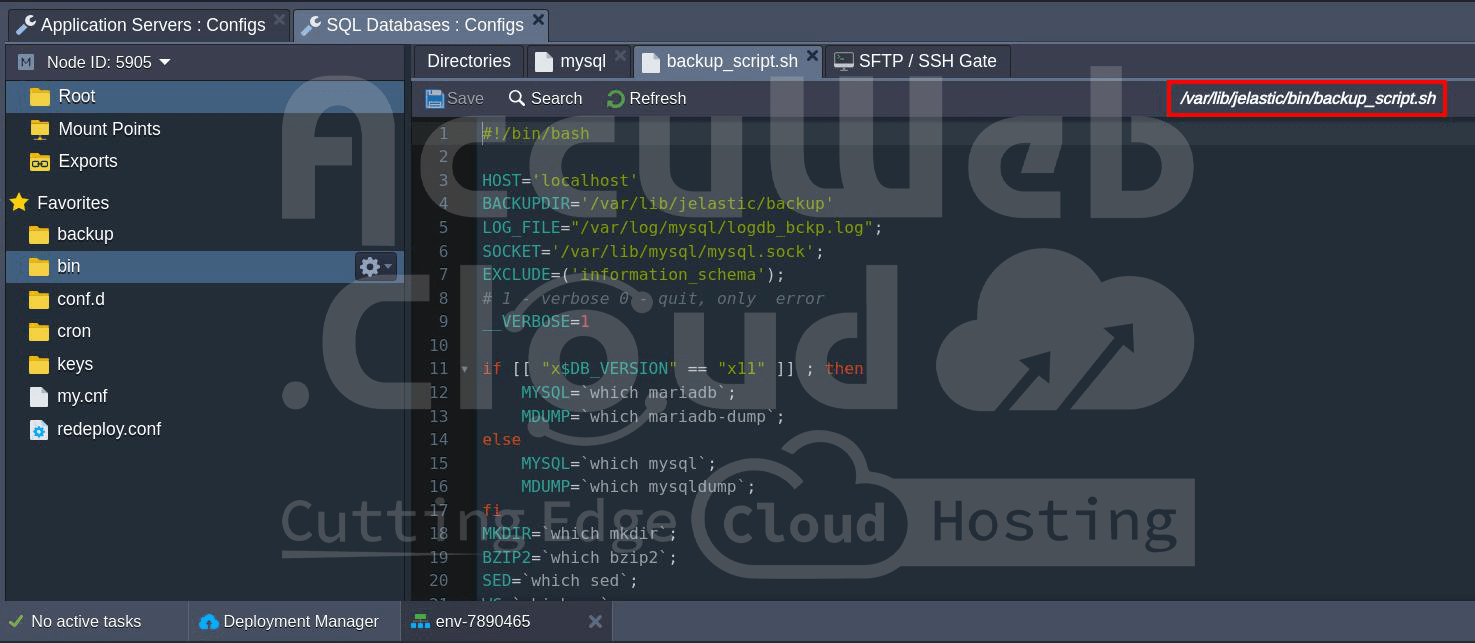
Scripts Directory
Path: /var/lib/jelastic/bin
Database Type: All
The `scripts` directory contains the `backup_script.sh` script for default backup procedures. You can also upload and manage your custom scripts in this directory.
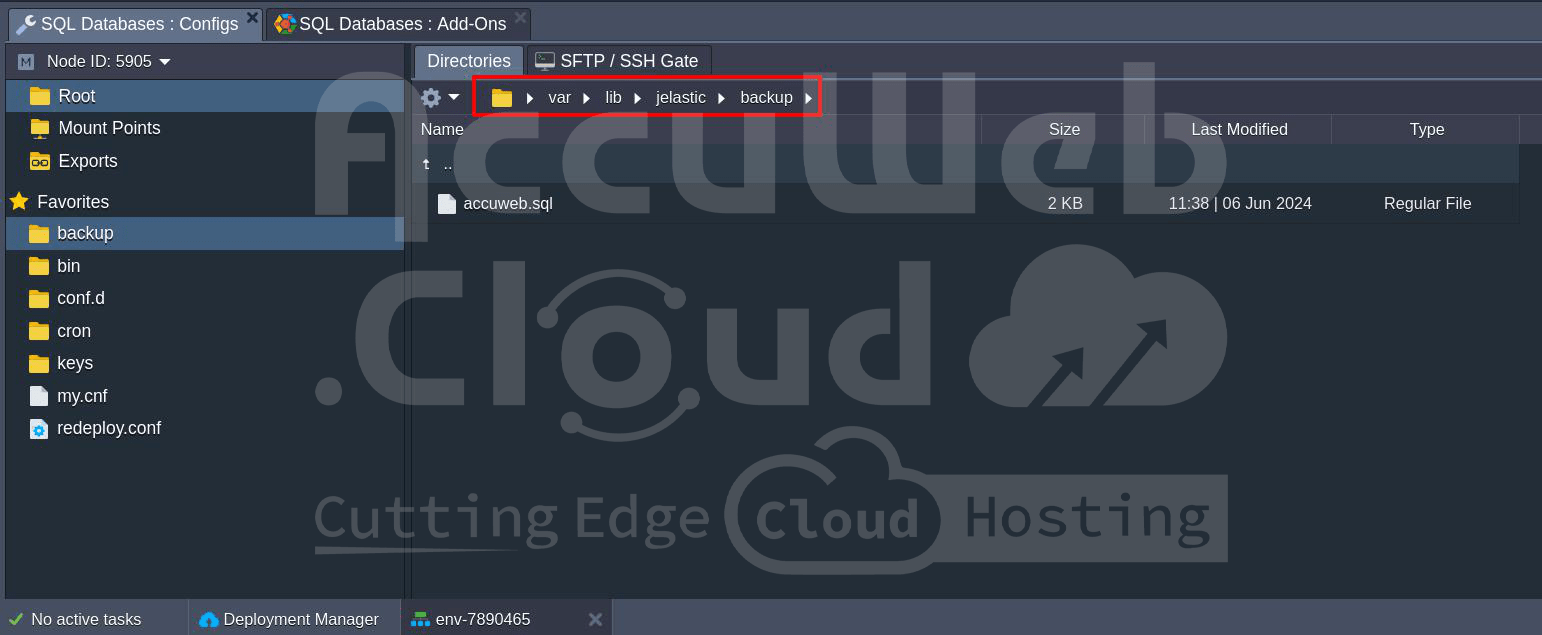
Backup Directory
Path: /var/lib/jelastic/backup
Database Type: All
The `backup` directory is used to store database backup files. These files can be crucial for restoring database data in case of failure or data loss.
Keys Directory
Path: /var/lib/jelastic/keys
Database Type: All
The `keys` directory is where private keys needed for application security are stored. Generate the key, save it as a simple file, and upload it to this directory. Use the path `/var/lib/jelastic/keys/{keyName}` to reference your key in applications.
Conf.d Directory
Path: `/etc/httpd/conf.d`
Database Type: MySQL, MariaDB, Percona, PostgreSQL
The `conf.d` directory is used to store and manage sub configurations for various services. For instance, the `phpMyAdmin jel.conf` file for MySQL can be found here, allowing administrators to set access criteria based on IP address or domain.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing the configuration files of your database is crucial for optimizing performance, ensuring security and automating tasks.
This guide has provided an overview of the main directories and configuration files used in platform managed database servers, covering multiple database types including PostgreSQL, MySQL, MariaDB and Percona.
By familiarizing yourself with these files and directories, you can take full control of your database environment and customize settings to fit your needs and ensure smooth and efficient database operations.
Whether you’re adjusting memory allocation in `my.cnf`, scheduling automated backups through cron jobs, or managing private keys for secure access, this guide serves as a comprehensive reference for effective database management.