OpenSearch Cluster
Open-source ideas and community collaboration underlie the OpenSearch Cluster search engine. It makes it simple for users to search, aggregate, examine, and analyze their data, making it perfect for application searches or log analytics. A safe, excellent search and analytics package that can be expanded with new capabilities is provided by OpenSearch.
Note: OpenSearch is based on Elasticsearch 7.10.2, licensed under Apache 2.0, which means it can be used, modified, extended, monetized, and resold freely.
This guide covers:
- OpenSearch Cluster Components Overview
- OpenSearch Cluster Installation
- OpenSearch vs Elasticsearch Performance
OpenSearch Cluster Components Overview
The platform provides an OpenSearch Cluster using three certified stacks integrated into a unified auto-clustering solution:
- OpenSearch: A community-driven, open-source search engine with distributed, multitenant full-text search capabilities.
- OpenSearch Dashboards (optional): A visualization tool for data stored in OpenSearch nodes, derived from Kibana 7.10.2.
- Logstash (optional): Data processing tool.
In this setup, Beats Data Shippers collect data on client nodes, send it to Logstash for processing, and store it in OpenSearch. OpenSearch Dashboards serves as the visualization tool.
OpenSearch
The OpenSearch stack is the core and mandatory component of the cluster. It operates in cluster mode even with a single node, facilitating easier, faster, and safer horizontal scaling.
Once created, the OpenSearch node communicates internally on port 9200 and externally on port 4848 through a shared load balancer, using HTTP basic authentication (password can be reset via the Reset Password button).
The OpenSearch stack includes functionality found in other certified templates, such as the dashboard file manager, Web SSH, and dashboard log viewer.
The platform’s redeploy functionality simplifies updates, allowing redeployment only to the same or newer versions, as downgrades are not permitted.
OpenSearch Dashboards
The OpenSearch node is accessible via a browser, displaying only JSON API responses necessary for API interactions.
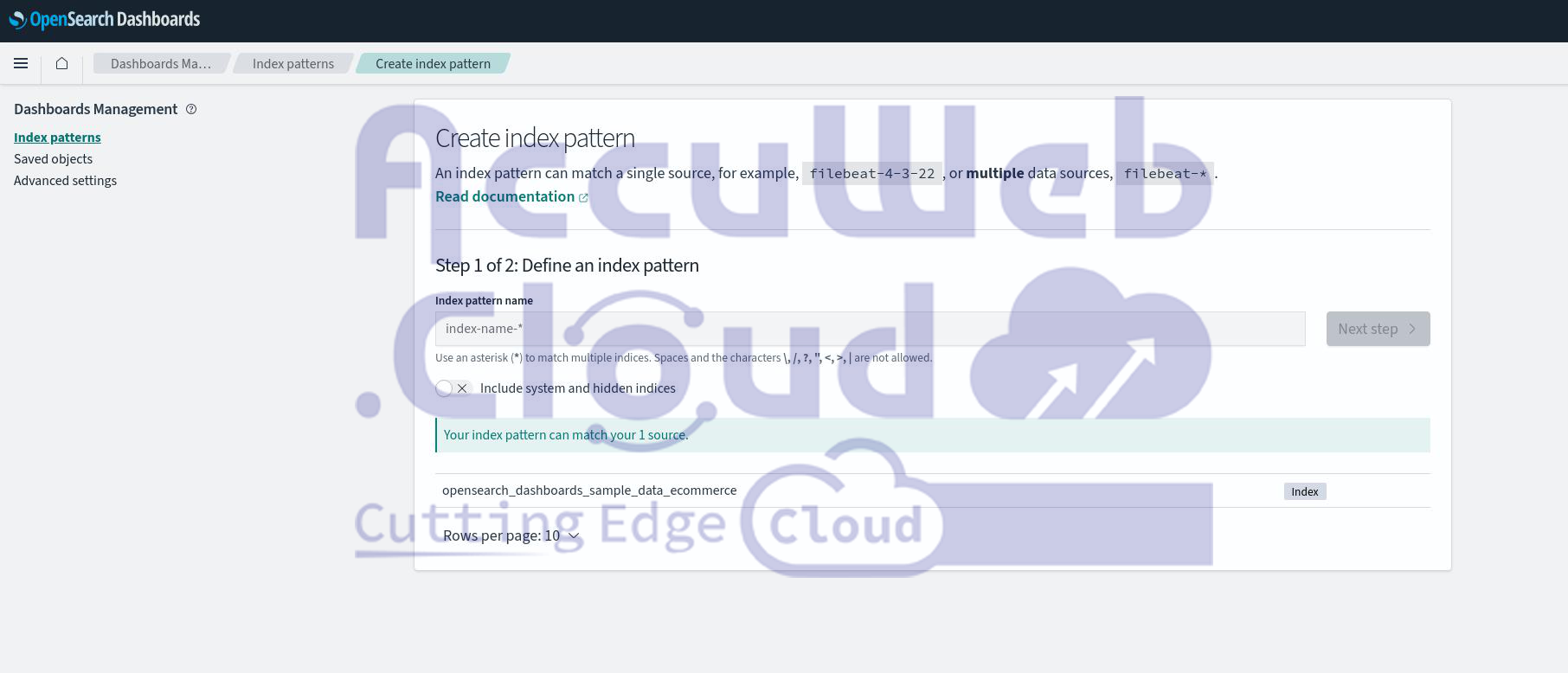
The primary tool for visualizing data is OpenSearch Dashboards, which replaces Kibana. All interconnection configurations are handled automatically, making the solution ready to use immediately without any manual setup. You can access it with the same credentials as the OpenSearch node.
Once logged in, the OpenSearch Dashboards interface appears. This dashboard provides a user-friendly interface for interacting with the OpenSearch API and editing your data after creating the index pattern.
All standard features of certified templates, such as the dashboard file manager, Web SSH, firewall, and logs, are available for this node.
Logstash
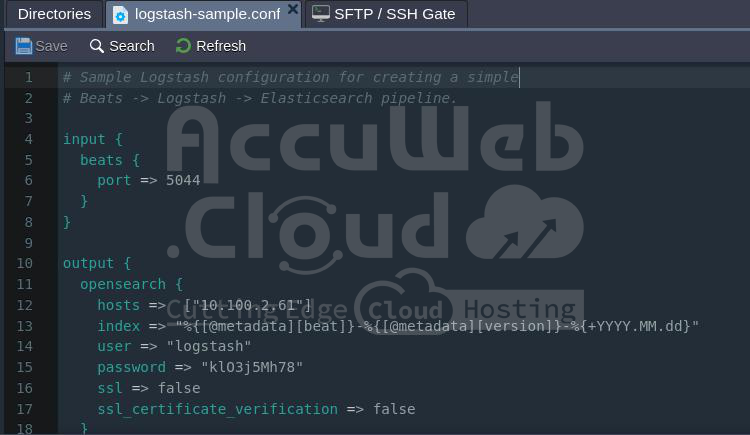
Logstash is a data processor component within the OpenSearch cluster that the platform configures automatically. Below is an example of the default auto-configuration found in /etc/logstash/conf.d/logstash-sample.conf:
The input for Beats is set on port 5044. The OpenSearch output is configured by specifying the hosts, username, and password for interconnection.
Additional input plugins can be installed using the logstash-plugin tool, and configurations can be added to the same file with a different port.
Beats Add-On
Beats is an open platform for single-purpose data shippers that send data from client nodes to Logstash or OpenSearch.
You can install the Beats add-on on any node (except alpine-based ones) created within the platform and specify credentials to connect to the OpenSearch cluster or a custom Docker with an Elasticsearch instance. Two versions of the add-on are available:
- 7.12.1: Ships data directly to OpenSearch (see compatibility charts).
compatibility.override_main_response_version: true- Latest: Ships data to OpenSearch through Logstash
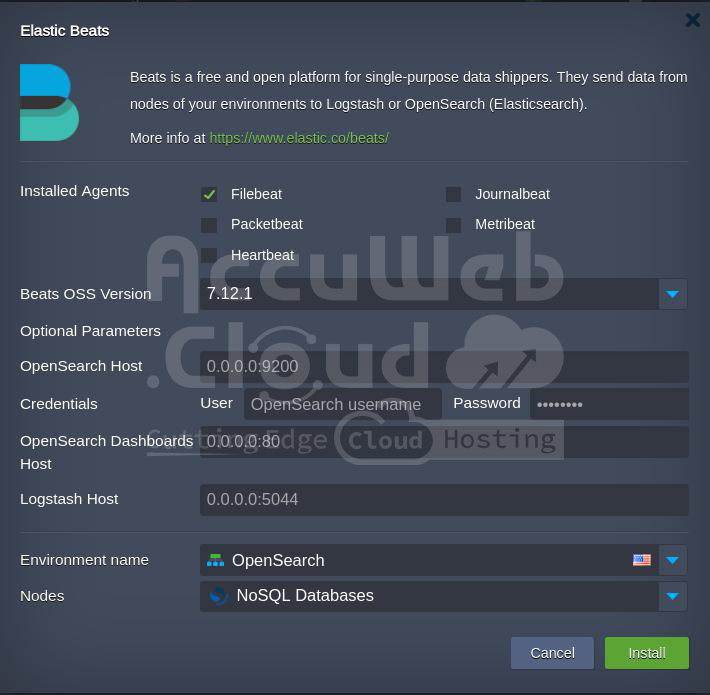
During installation, provide the following information:
- Installed Agents: Select the required Beats types:
- Filebeat: Centralizes logs and files with presets available for many certified nodes: Apache, NGINX, HAProxy, Redis, Postgres, MySQL, MariaDB, Percona, MongoDB, and Tomcat/TomEE (requires special configurations).
- Metricbeat: Collects metrics from systems and services.
- Journalbeat: Forwards log data from systemd journals to OpenSearch or Logstash.
- Packetbeat: Monitors network traffic for performance and security, acting as a lightweight network packet analyzer.
- Heartbeat: Monitors service availability with active probing and ships the data for further analysis.
- Beats OSS Version: Select the desired version of the agent.
- OpenSearch Host: Enter the OpenSearch (or Elasticsearch) host.
- Credentials: Provide user and password information for the specified OpenSearch host.
- OpenSearch Dashboards Host: Enter the OpenSearch Dashboards host, if needed for visualization.
- Logstash Host: Enter the Logstash host if data interconnection is through Logstash.
- Environment Name: Choose the target environment.
- Nodes: Select the target layer.
These settings can be edited for an already installed add-on using the Configure button.
Installing an OpenSearch Cluster
Creating an OpenSearch Cluster on the platform is a simple, automated process that you can perform using the topology wizard.
Go to the NoSQL database section and select the OpenSearch stack.
The auto-clustering feature ensures the stack is configured as a cluster automatically. You also have the option to add OpenSearch Dashboards and Logstash components.
OpenSearch vs. Elasticsarch Performance
The OpenSearch project, which was forked from the final Elasticsearch release under the Apache 2.0 license, offers nearly identical functionality. The APIs are completely compatible.
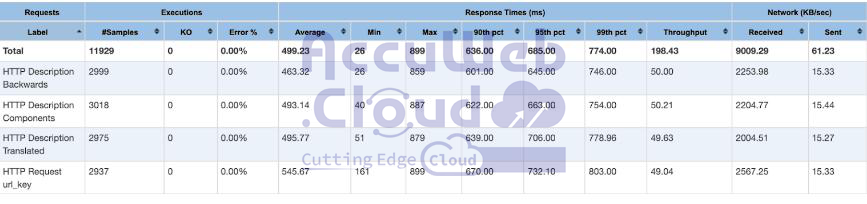
Here, we present performance test results from two Magento environments with identical topologies:
- Magento with Elasticsearch
- Magento with OpenSearch