GlassFish Clustering in the Cloud
GlassFish is a robust and reliable open-source application server designed for enterprise-level Java EE projects. It offers extensive functionality and high performance, including full clustering capabilities.
With GlassFish, you can not only host your Java applications on a standalone server but also create highly available clustered instances with full replication. Let’s explore two straightforward methods to set up a GlassFish cluster on the platform:
GlassFish Cluster Automatic Deployment via JPS Package
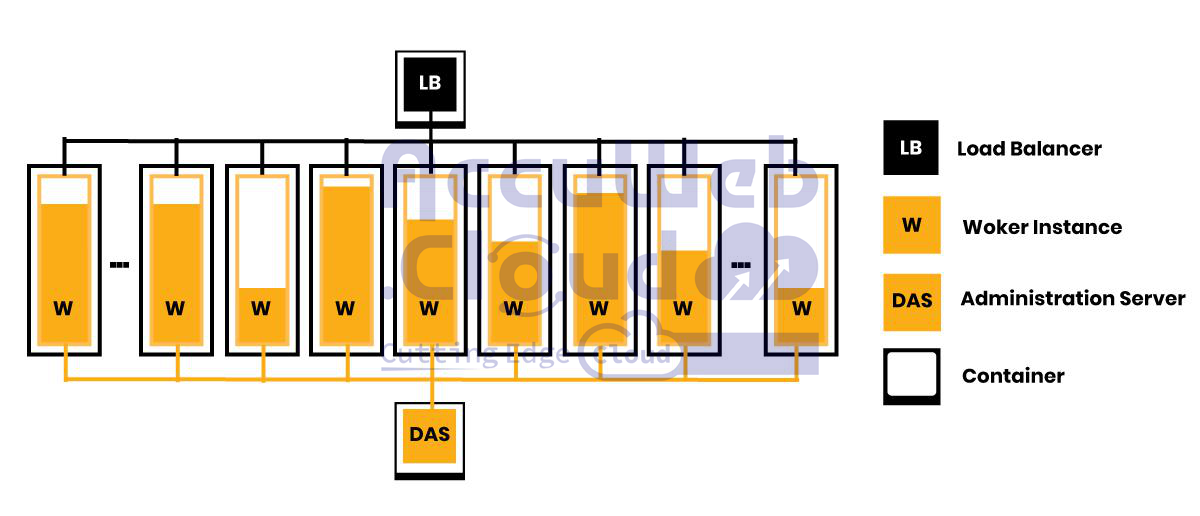
The GlassFish clustered solution, when set up with this option, utilizes Docker containers as its foundation. This approach enhances reliability by running each component—such as the Load Balancer, Worker Nodes, and Domain Administration Server—as a separate, isolated instance. In this configuration, a HAProxy Docker image functions as the Load Balancer, while GlassFish templates are used to create the Worker Nodes and the Domain Administration Server.
Tip:
GlassFish Cluster Manual Deployment
If you’re looking to fully manage your GlassFish cluster’s configuration and deployment, the following instructions will be helpful. They detail the key aspects of GF cluster configuration and how to implement them on the platform.
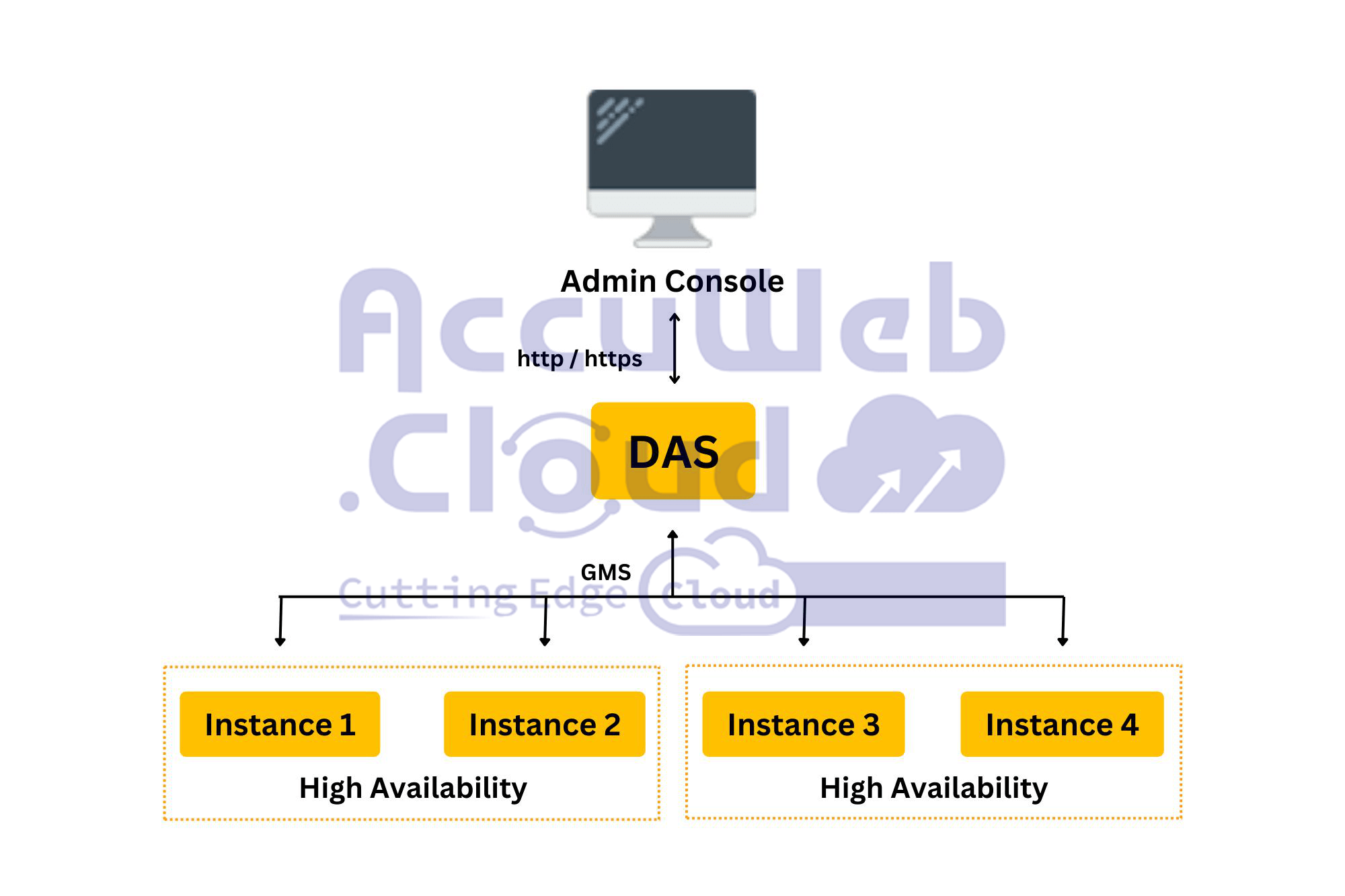
GlassFish clustering architecture relies on the concept of an administrative domain. These domains include clusters and instances that are overseen by the Domain Administration Server (DAS).
To manage a central repository, you can utilize the Admin Console, an interactive graphical user interface that supports all the features available in GlassFish. The Group Management Service (GMS) offers details about clusters, while the Domain Administration Server (DAS), as previously noted, oversees the management of Java instances within the administrative domain.
Sessions Replication in GlassFish: How Does It Work?
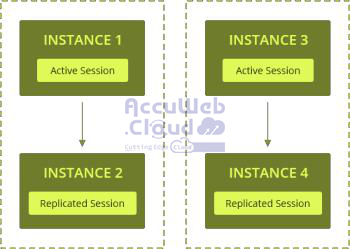
In each cluster, instances are paired. If the primary instance in a cluster fails, all users on that instance are automatically redirected to the backup instance. Users won’t notice any changes because the backup instance has all the sessions from the failed one. If both instances in a cluster fail, users are redirected to another cluster. This redirection is managed by an NGINX load balancer, which distributes requests among clusters and instances based on load and availability.
Additionally, the platform offers a comprehensive scaling system. You can easily adjust the size and number of clusters either manually or automatically in response to changing loads, supporting both horizontal and vertical scaling.
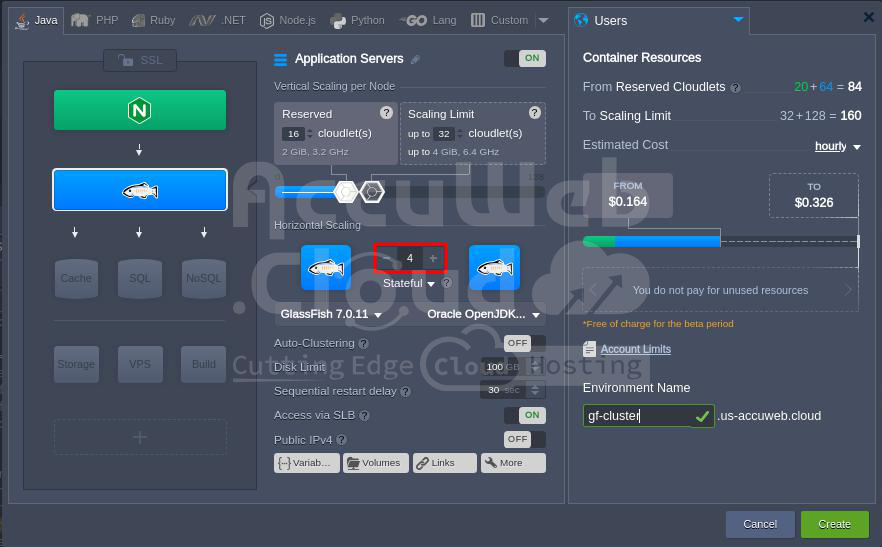
To set up a highly available GlassFish clustered environment on the platform, simply select GlassFish as your application server and increase the number of nodes as shown in the below image.
You have everything set up just right! Simply press the “Create” button, and in no time, you’ll have a dependable environment. Each group of servers will be duplicated, and the whole environment will be backed up to make sure it stays reliable.