How To Connect A PHP Application With Mysql/MariaDB/Percona for PHP?
MySQL, MariaDB, and Percona are very famous databases that anyone can use for free. Developers worldwide like to use them. Read the steps below to find out how to link your PHP program, which is on the same platform, to one of these database servers (MySQL, MariaDB, and Percona).
Environment Creation
Step 1. Sign in to your AccuWeb.cloud account and make a setup with either MySQL or MariaDB database server (both are options in the SQL wizard).
We’ve included an Apache PHP Application Server to show how to connect.
Step 2. Once your setup is done, you’ll receive an email containing details for administering and connecting to MySQL (or MariaDB).
Step 3. Return to your account dashboard and click the “Open in Browser” button for the right database node (MySQL or MariaDB). Log in to the admin panel using the login details sent to you in the email.
Step 4. Navigate to the “Databases” section and create a new database (like “accutest_db“).
Step 5 . Now, you’re set to deploy your application (either from an archive or a GIT/SVN repository) to the setup you’ve created.
Connecting to the Database
Once your project is set up, you’ll need to connect it to your database. You can do this by configuring your application properly, like using the built-in MySQLi extension.
Check the official documentation page for all available functions. Here, we’ll cover the basics:
1. To Connect To Your Mysql/MariaDB Node, Use This Function
- mysqli_connect(‘{host}’, ‘{user}’, ‘{password}’, ‘{db_name}’);Replace the placeholders with your actual connection data:
- {host}: the link to your DB node without the protocol part
- {user} and {password}: your database admin credentials (for safety, it’s best to make a dedicated account with the right permissions)
- {db_name}: the name of the database you want to use (like the one you created before)
2. If You Need To Switch To A Different Database On The Same Server, Use This Function
mysql_select_db('{connect}','{db_name}');Replace {connect} with the connection string you got from the mysqli_connect function.
3. To Close The Connection To Your Database, Use This Function
mysqli_close();
Remember, you need to include these functions in every *.php page that needs to connect to the database.
Checking Connection
Step 1. Create a file with the name mysql-connection.php in your local system and paste the following PHP code.
<?php
$link = mysqli_connect('{host}', '{user}', '{password}', '{db_name}');
// If connection fails, you'll see an error message
if (!$link) {
die('Could not connect: ' . mysql_error());
}
// If connection is successful, you'll see this message
echo 'Connected successfully';
mysqli_close($link);
?>Remember to replace {host}, {user}, {password}, and {db_name} with the actual values you got from the Connection to Database section.
Step 2. Go to the AccuWeb.Cloud dashboard and choose the environment where you want to check the database connection.
Step 3. Select the Application Server and the Node server. Then click on Config next to the Node server.
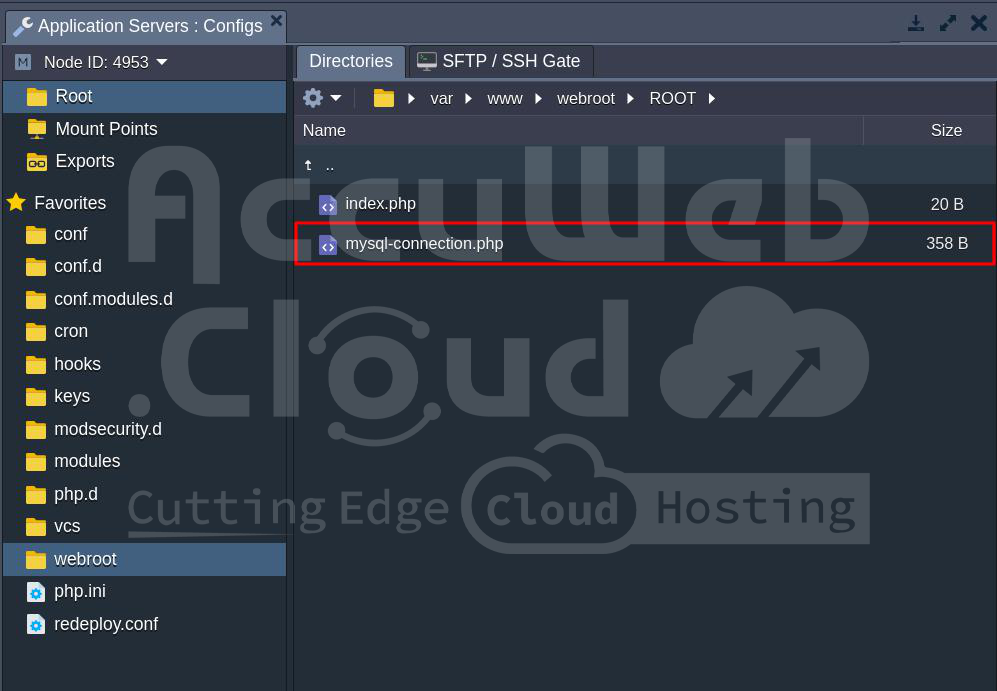
Step 4. Navigate to the Apache document path (/var/www/webroot/ROOT).
Step 5. Then click on the Settings icon and choose Upload.
Step 5. In the Upload Files window, go to Local Files and select the file from your computer. Click Upload to add the file to the AccuWeb.Cloud environment.
Step 6. Once the file is uploaded, you can see the file in the Apache document path.
Step 7. Click Open in Browser to load the Apache default page or PHP site. Then, add the file name at the end of the page.
If everything’s fine, you’ll see the “Connected successfully” message when you open this page in your browser.
Running a Simple Query
Here’s an example of how to run a basic query on your database and display the results in a table.
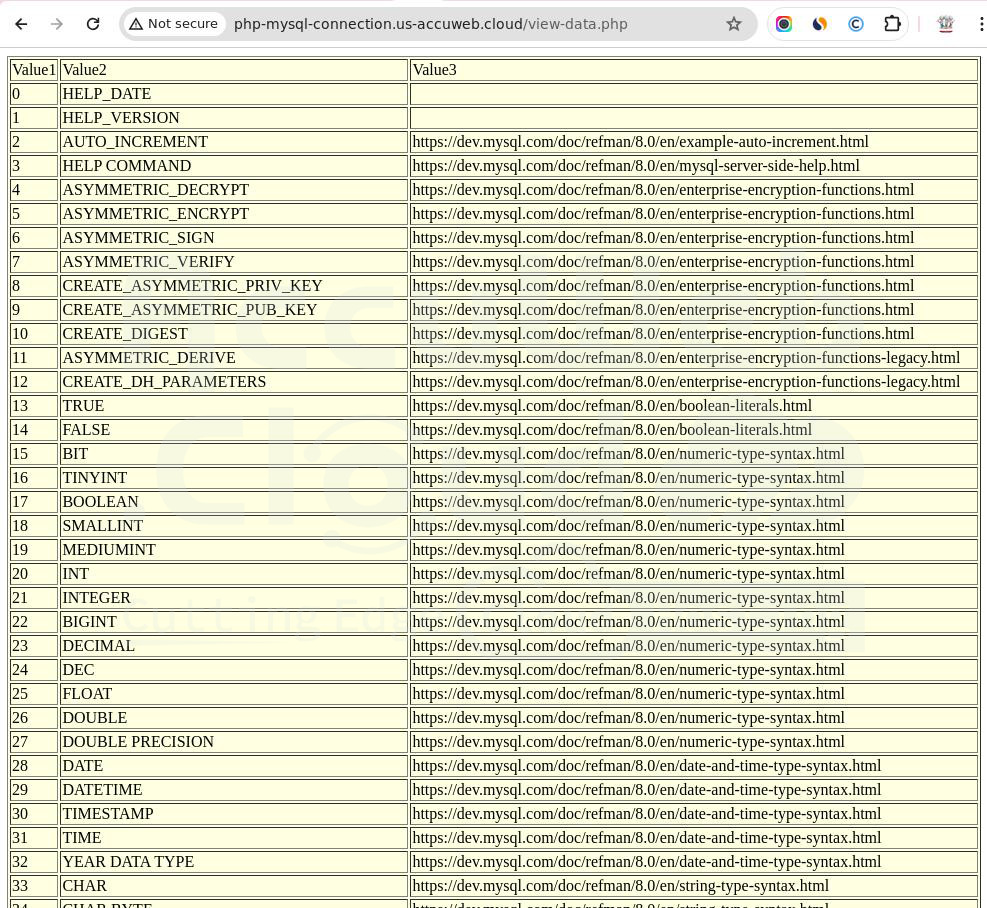
This PHP script will connect to your database server (make sure to use the correct hostname and credentials), switch to the default MySQL database, fetch values from the help_topic table, and show them in a table.
Step 1. Create a file with the name view-data.php in your local system and paste the following PHP code.
<?php
// Check connection:
$link = mysqli_connect('{host}', '{user}', '{password}', '{db_name}');
if (!$link)
{
echo "<h2>MySQL Error!</h2>";
exit;
}
// Switch to a different database:
$db="mysql";
mysqli_select_db($link, $db);
// Table header:
echo "<table border=\"1\" width=\"100%\" bgcolor=\"#FFFFE1\">";
echo "<tr><td>Value1</td><td>Value2</td><td>Value3</td>";
// SQL query:
$q = mysqli_query ($link, "SELECT * FROM help_topic;");
// Output the table result:
for ($c=0; $c<mysqli_num_rows($q); $c++)
{
echo "<tr>";
$f = mysqli_fetch_array($q);
echo "<td>$f[0]</td><td>$f[1]</td><td>$f[5]</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
echo "</table>";
?>Step 2. Go to the AccuWeb.Cloud dashboard and choose the environment where you want to check the database connection.
Step 3: Pick the Application Server, then select the Node server. Click on Config next to the Node server.
Step 4. Navigate to the Apache document path (/var/www/webroot/ROOT). Then click on the Settings icon and choose Upload.
Step 5. In the Upload Files Window, go to Local Files and select the file from your computer. Click Upload to add the file to the AccuWeb.Cloud environment.
Step 6. After you upload the file, you’ll be able to find it in the Apache document path.
Step 7. Click Open in Browser to load the Apache default page or PHP site. Then add the file name at the end of the page.
This will give you an index of all available MySQL functions with links to instructions on how to use them.
Now, you can easily connect your PHP application to a MySQL or MariaDB database.
Conclusion
In summary, connecting your PHP app to MySQL/MariaDB/Percona is crucial to working with databases in your web app. You can do this by creating a connection file with the right info and uploading it to your hosting.
Remember to replace placeholders with actual database details to ensure a successful connection. Once connected, you can easily manage data in your database, like retrieving, adding, updating, and deleting, to add dynamic features to your PHP app.