How to Connect Java with MariaDB/MySQL/Percona?
MariaDB, MySQL, and Percona are very popular databases used by developers all around the world. In this guide, we’ll show you how to connect your Java application to these databases, whether it’s a single server or a clustered setup.
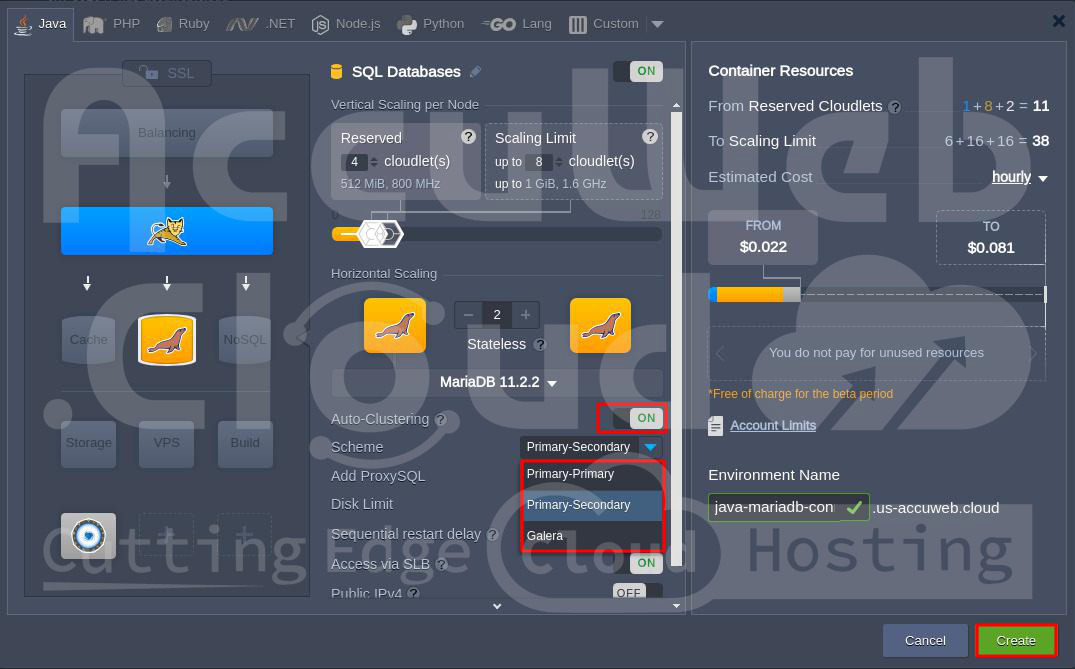
Step 1. Log in to your Accuweb.cloud dashboard and create an environment with either MariaDB or MySQL.
You can choose between setting up a standalone database server
or an Auto-Clustering solution.
We’ve also included a Tomcat node to demonstrate how to connect your application server to the database.
Step 2. Check your email inbox for the administration details of the MariaDB or MySQL server you created. If you’re using a clustered solution, you’ll connect to a ProxySQL load balancer.
Step 3. Go back to the dashboard and click “Open in Browser” for your MariaDB or MySQL node. If you’re using a clustered solution, click on “Open in Browser” next to the master database node (marked as M). Log in using the credentials provided in the email.
Step 4. Choose an existing database (test) or create a new one.
Step 5. Create a file with the name mydb.cfg and paste the following php code.
- Host: jdbc:mysql://{host}/{db_name}
- Username: {user}
- Password: {password}
- Driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
You can find all this info in the email you got from MariaDB or MySQL:
- {host}: The link to your database without the http part
- {db_name}: The name of your database (we used “test” in our example)
- {user} and {password}: Your admin login details (for security, it’s best to use a special account with the right permissions)
If you’re connecting to a cluster, you’ll use ProxySQL as the entry point, and each database type has its own connector. Put this info in the mydb.cfg file:
For MariaDB
- Host: jdbc:mariadb://{hostname}/{db_name}?usePipelineAuth=false
- Username: {user}
- Password: {password}
- Driver: org.mariadb.jdbc.Driver
You’ll find this info in your email:
- {hostname}: The link to your database cluster’s load balancer (ProxySQL)
- {db_name}: The name of your database (we used “test” earlier)
- usePipelineAuth: This should be set to false for ProxySQL to work properly.
For MySQL
- Host: jdbc:mysql://{host}/{db_name}
- Username: {user}
- Password: {password}
- Driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
You’ll find this info in your email too:
- {host}: The link to your database cluster’s load balancer (ProxySQL)
- {db_name}: The name of your database (we used “test” earlier)
- {user} and {password}: Your admin login details (again, it’s best to use a special account)
This way, all the connection settings are in one file, and your application can read them easily.
Step 6. Go to the Accuweb.cloud
dashboard and choose the environment where you want to check the database connection.
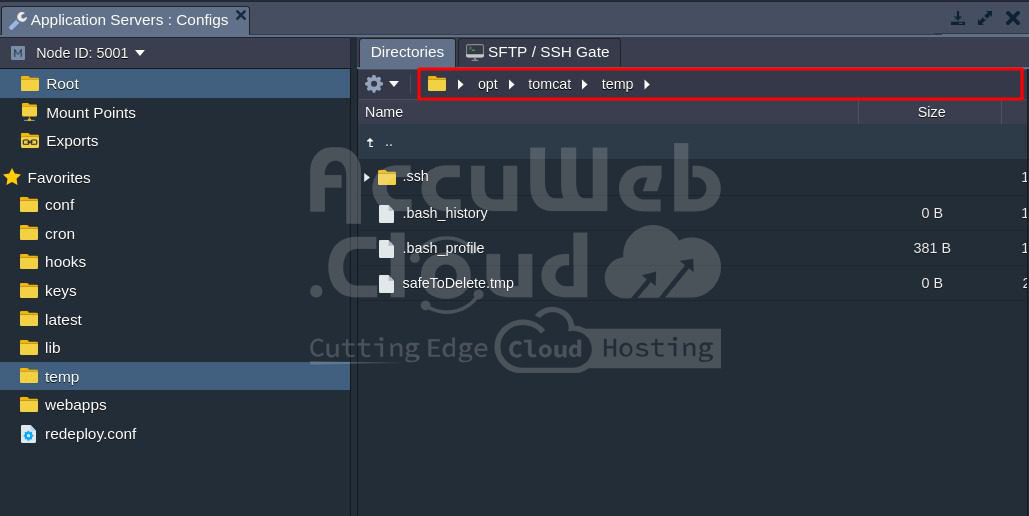
Step 7. Select the Application Server and the Node server. Then click on Config next to the Node server.
Step 8. Navigate to the temp path (/var/www/webroot/ROOT).
Then click on the Settings icon and choose Upload.
Step 9. In the Upload Files window, go to Local Files and select the file from your computer. Click Upload to add the file to the Accuweb.cloud environment.
Step 10. Once the file is successfully uploaded, you will get the file in the temp path.
Step 11. We’ll use a sample application to deploy and connect. This application helps us connect to databases. It sets up a table with a unique name based on the current date and time.
package connection;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
public class DbManager {
public String date = new SimpleDateFormat("dd-MM-yyyy-HH-mm").format(new Date());
private final String createTable = "CREATE TABLE `" + date + "` (id INT, data VARCHAR(100));";
private static final int LoginTimeout = 10;
public DbManager() {}
public Connection createConnection() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, SQLException {
Properties prop = new Properties();
System.out.println("\n\n=======================\nJDBC Connector Test " + date);
System.out.println("User home directory: " + System.getProperty("user.home"));
String host;
String username;
String password;
String driver;
try {
prop.load(new java.io.FileInputStream(System.getProperty("user.home") + "/mydb.cfg"));
host = prop.getProperty("host").toString();
username = prop.getProperty("username").toString();
password = prop.getProperty("password").toString();
driver = prop.getProperty("driver").toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Unable to find mydb.cfg in " + System.getProperty("user.home") + "\n Please make sure that configuration file created in this folder.")
host = "Unknown HOST";
username = "Unknown USER";
password = "Unknown PASSWORD";
driver = "Unknown DRIVER";
}
System.out.println("host: " + host + "\nusername: " + username + "\npassword: " + password + "\ndriver: " + driver);
Class.forName(driver);
System.out.println("--------------------------");
System.out.println("DRIVER: " + driver);
System.out.println("Set Login Timeout: " + LoginTimeout);
DriverManager.setLoginTimeout(LoginTimeout);
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(host, username, password);
System.out.println("CONNECTION: " + connection);
return connection;
}
public String runSqlStatement() {
String result = "";
try {
Statement statement = createConnection().createStatement();
System.out.println("SQL query: " + createTable);
statement.execute(createTable);
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException ex) {
Logger.getLogger(DbManager.class.getName()).log(Level.SEVERE, null, ex);
System.out.println("Exception occurred: " + ex);
result = ex.getMessage();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
result = ex.getMessage();
}
return result;
}
}</Step 12. Deploy our sample application to your Tomcat server using this link:
Notes:– The sample app already has the necessary connectors for MariaDB/MySQL.
– For your own project, you’ll need to upload these connectors to the webapps/{app_context}/WEB-INF/lib folder on your server.
Remember to restart your server after making changes to mydb.cfg by pressing the Restart Node button.
Step 13. After deployment, click “Open in Browser” next to your application server.
Step 14. In the browser tab that opens, click “Create test table in your database.”
Step 15. To make sure everything’s working, go back to the phpMyAdmin panel and find the test database. You’ll see a new table with a name based on the creation date and time. This means the Java app successfully accessed and modified the database. It’s that simple!
Conclusion
In summary, connecting a Java app to MySQL/MariaDB/Percona is crucial for working with databases. By setting up JDBC drivers and connection details, you enable smooth communication between your Java app and the database.
Make sure to handle errors and use secure authentication for a successful connection. Once connected, your Java app can perform different database tasks, helping you retrieve, edit, and organize data effectively.