How to Configure Node Resources in an Environment?
Node resources refer to the essential components (CPU, memory, storage, and networking capabilities) available on a computer or server within a network or system.
These resources determine the capacity and performance of each computer or server in handling tasks and running software applications. Managing node resources involves ensuring that these components are effectively utilized to support the smooth operation of programs and services running on the network.
Let’s see how to configure Node Resources in an AccuWeb.Cloud environment.
Step 1: Sign in to your AccuWeb.Cloud account.
Step 2: Choose the environment where you want to set up Node resources. For example, we’ll use nicktest.us-accuweb.cloud.
Step 3: Find the section for your chosen environment and click “Change Environment Topology” to view its setup.
Step 4: In the Topology window, you can adjust various settings like cloudlet allocation for different components: Load balancer, Application server, Cache server, SQL server, and NoSQL server.
You can also view cloudlet settings for Storage cluster and VPS.
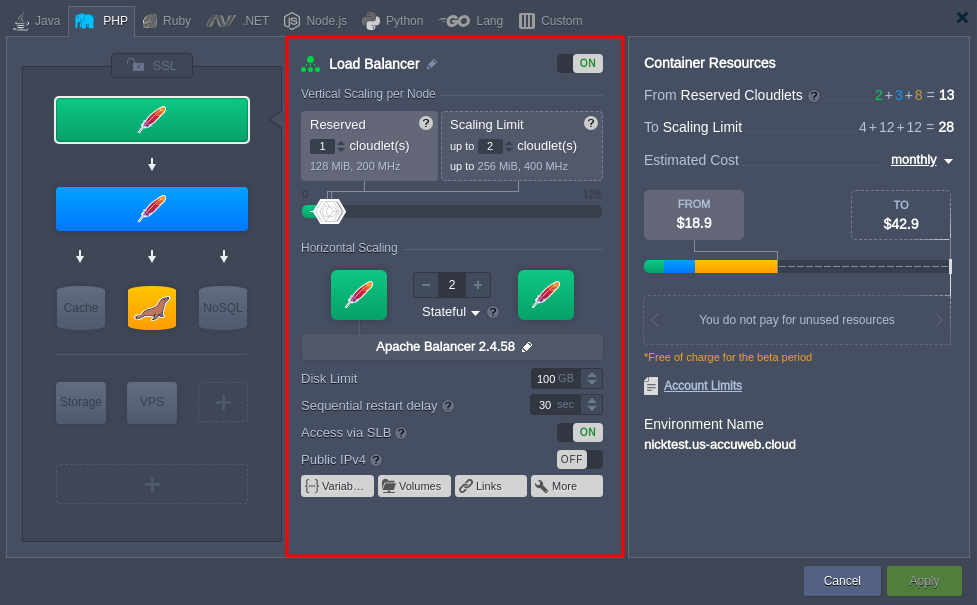
Configure the Node resources of the Load Balancer
Step 5: To change the Load Balancer’s resources, choose the Load Balancer option in the SSL section.
This will display Load Balancer settings alongside SSL settings.
Step 6: In the Vertical Scaling per Node section, adjust the cloudlet settings for Reserved and Scaling limits based on your needs.
- Reserved cloudlets are fixed resources you pay for regardless of usage.
- Dynamic cloudlets adjust based on usage and are charged only when used.
You can use the slider to make adjustments.
Learn more about allocation strategy for Reserved and Dynamic Cloudlets resources.
For example,
if you set 1 cloudlet as Reserved and 2 cloudlets as Scaling and want to change it to 2 cloudlets Reserved and 4 cloudlets Scaling, adjust these settings in the Vertical Scaling per Node section.
Note: Changes made here apply to all nodes in the Load Balancer; you can’t adjust cloudlets for individual nodes.
Learn more about how automatic & Vertical scaling works in AccuWeb.Cloud.
For instance, if you have 2 nodes in the Load Balancer, the Reserved cloudlets total 4 (2 + 2), and the Scaling Limit totals 8 (4 + 4).
Step 7: In the Horizontal Scaling section, you can add nodes as needed. Use the “+” and “-” buttons or type the desired number in the central panel. You can also use a slider for adjustments.
Learn more about how to upgrade resources in AccuWeb.Cloud.
When adding nodes, choose between two options:
- Stateless: Creates all new nodes simultaneously from a base image template.
- Stateful: Sequentially copies the file system of the master container into new nodes.
For example,
If you have 2 nodes in the load balancer and want to add one more manually, click the “+” button to add a node to the application server. This increases Horizontal Scaling to 3 nodes.
Adding a node will increase the Reserved and Scaling cloudlet limits, resulting in higher environment costs.
Step 9: In the Disk Limit section, set the disk space limit for each node/server. The maximum disk space per server is 200GB.
For instance, if you set 200GB disk space per node and have 3 nodes, the total allocated disk space for the Load Balancer will be 600GB (200GB per node x 3 nodes).
Step 10: Specify the sequential restart delay time (in seconds) for container restarts.
Step 11: Enable or disable access via the Shared Load Balancer (SLB) by toggling the “Off” button. The SLB processes all incoming requests to the environment domain name through open ports. By default, this feature is enabled.
Step 12: To assign a public IPv4 address to a node, toggle the “Off” button. Each node will receive a separate IP address. For example, if you have 3 nodes, each node will be allocated its IP address.
Configure the Node resources of the Application Server
Step 13: Choose the application server from the SSL section.
Learn more about how to launch the new application on the new server.
Step 14: After selecting the application server, its settings will appear alongside the SSL section.
Step 15: Navigate to the Vertical Scaling per Node section to adjust the cloudlet settings for Reserved and Scaling limits according to your needs.
For example:
If you initially set 1 cloudlet as Reserved and 4 cloudlets as Scaling and want to change it to 2 cloudlets Reserved and 8 cloudlets Scaling, make these adjustments in the Vertical Scaling per Node section.
Note: With 3 nodes in the Application Server, the Reserved cloudlets total 6 (2 + 2 + 2), and the Scaling Limit totals 24 (8 + 8 + 8).
Step 16: In the Horizontal Scaling section, add nodes as needed. Use the “+” and “-” buttons or type the desired number in the central panel. You can also adjust using a slider that appears automatically.
For example:
If you have 3 nodes in the Application server and want to add one more manually, click the “+” button to add a node. This increases the number of nodes to 4 in the Horizontal Scaling.
Adding nodes will increase the Reserved and Scaling cloudlet limits, resulting in higher environmental costs.
Step 17: Set the disk space limit for the node/server in the Disk Limit section. The maximum disk space available for each server is 200GB.
For instance, if you allocate 200GB of disk space per node and have 3 nodes, the total disk space allocated to the Load Balancer will be 600GB (200GB for each of the 3 nodes).
Step 18: Specify the sequential restart delay time (in seconds). This determines how long to wait before restarting containers in the layer.
Step 19: Toggle the Access via the Shared Load Balancer (SLB) setting. Click the “Off” button if you want to access the environment through the shared load balancer. By default, this feature is enabled.
Step 20: Enable public IPv4 addresses for nodes by clicking the “Off” button. Each node will receive its separate IP address. For example, if you have 3 nodes, each node will have its unique IP address assigned.
Configure the Node resources of the database server
Step 21: Choose the database server from the SSL section.
Step 22: After selecting the database server, its settings will appear alongside the SSL section.
Learn more about how to install and enable the Database backup/restore add-on.
Step 23: Navigate to the Vertical Scaling per Node section to adjust the cloudlet settings for Reserved and Scaling limits based on your needs.
For example:
If you initially set 4 cloudlets as Reserved and 6 cloudlets as Scaling, and you want to change it to 6 cloudlets Reserved and 12 cloudlets Scaling, make these adjustments in the Vertical Scaling per Node section.
Note: With 2 nodes in the database Server, the Reserved cloudlets total 12 (6 + 6), and the Scaling Limit totals 24 (12 + 12).
Step 24: In the Horizontal Scaling section, add nodes as needed. Use the “+” and “-” buttons or type the desired number in the central panel. You can also adjust using a slider that appears automatically.
For example:
If you have 2 nodes in the database server and want to add one more manually, click the “+” button to add a node. This increases the number of nodes to 3 in the Horizontal Scaling.
Adding nodes will increase the Reserved and Scaling cloudlet limits, resulting in higher environmental costs.
Step 25: In the Disk Limit section, set the disk space limit for the node/server. The maximum disk space available for each server is 200GB.
For example, if you allocate 200GB of disk space per node and have 3 nodes, the total disk space allocated to the Load Balancer will be 600GB (200GB for each of the 3 nodes).
Step 26: In the sequential restart delay setting, specify the time delay (in seconds) for container restarts.
Learn more about how to install and use database corruption diagnostic add-on.
Step 27: Toggle the Access via the Shared Load Balancer (SLB) setting. Click the “Off” button if you want to access the environment through the shared load balancer. This feature is enabled by default.
Step 28: Enable public IPv4 addresses for nodes by clicking the “Off” button. Each node will receive its separate IP address. For example, if you have 3 nodes, each node will have its unique IP address assigned.
Step 29: Once you make the changes in the environment, click on the Apply button to update the settings.
Step 30: The update process may take a few minutes to complete. Once completed, the settings will be applied, and the update will be listed in the environment.
Conclusion
Configuring Node Resources in an environment involves several steps to optimize resource allocation and scalability. By following these steps, you can effectively manage cloudlet settings, horizontal and vertical scaling, disk space limits, and access settings like SLB and public IPv4 allocation.
These configurations ensure efficient resource utilization, scalability, and accessibility for your application or server environment. Adjusting these settings based on your specific requirements helps to optimize performance and manage costs effectively.