Auto-Clustering of Instances
The AccuWeb.Cloud platform offers an on-demand automated clusterization for a number of the managed templates. Such automation drastically simplifies and quickens the introduction of a dependable manufacturing-ready cluster for your project.
Below, we’ll explore the following aspects:
- Supported stacks, along with details on clusterization specifics.
- Management of auto-clustering.
- Utilization of cloud scripting.
Templates with Supported Auto-Clustering
At present, the clustering feature is supported by the following templates, with plans to incorporate additional stacks in the future:
- Application servers: Tomcat/TomEE, GlassFish, Payara, Jenkins, WildFly
- SQL databases: MySQL, MariaDB, Percona, PostgreSQL
- NoSQL databases: Couchbase, MongoDB, Redis, OpenSearch
- Storage server: Shared Storage Container
Tomcat/TomEE
A highly available Tomcat/TomEE cluster is configured to distribute the workload across compute nodes, boosting performance and resilience. This setup includes session replication, context attribute replication, and cluster-wide deployment of WAR files.
Note: The Auto-Clustering feature for Tomcat and TomEE is accessible from the following stack versions:
Tomcat – 10.0.5; 9.0.45; 8.5.64; 7.0.108
TomEE – 9.0.0-M3; 8.0.5
GlassFish
The GlassFish servers are set up to work together seamlessly, with session replication and load balancing already configured to optimize performance and reliability.
Payara
The Payara servers are connected, with session replication and load balancing already configured to ensure smooth operation and optimize performance.

Jenkins
Within Jenkins, there’s a master node operating in master-slave mode. It’s equipped with auto-scalable Java Engine workers and comes with pre-installed plugins. These plugins support automation for building and deploying, enabling the organization of continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) pipelines.
WildFly
The WildFly nodes operate in Domain Mode with clustering enabled, ensuring high availability and continuous performance for deployed Java EE applications.
MySQL
Auto-Clustering is available for MySQL versions 5.7.x and 8.x exclusively.
The automatic clusterization of databases includes pre-configured replication and auto-discovery of nodes.
You have the option to choose from the following schemes based on your requirements:
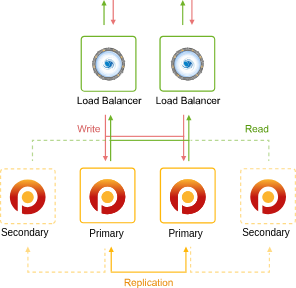
1. Primary-Primary with Extra Secondaries: This scheme features pre-configured replication with two interconnected primary databases. As the cluster scales horizontally, additional secondary nodes are seamlessly integrated.
2. Primary-Secondary with Extra Secondaries scheme entails pre-configured replication with one primary and one secondary database. As the cluster scales horizontally, additional secondary nodes are seamlessly integrated.
Learn more: https://github.com/jelastic-jps/mysql-cluster
MariaDB
Auto-Clustering is exclusively available for MariaDB versions 10.x.
The automatic clusterization of databases includes pre-configured replication and auto-discovery of nodes.
You can choose from the following Scheme types based on your requirements:
1. Primary-Primary with Extra Secondaries: This scheme features pre-configured replication with two interconnected primary databases. As the cluster scales horizontally, additional secondary nodes are seamlessly integrated.
2. Primary-Secondary with Extra Secondaries: This scheme involves pre-configured replication with one primary and one secondary database. During horizontal scaling, the cluster expands with additional secondary nodes.
3. Galera Cluster: In this setup, all servers can accept updates concurrently, even if issued simultaneously.
Percona
The automatic clusterization of databases includes pre-configured replication and auto-discovery of nodes.
Based on your requirements, you have the option to select from the following scheme types:
1. Primary-Primary with Extra Secondaries: This scheme entails pre-configured replication with two interconnected primary databases. As the cluster scales horizontally, additional secondary nodes are seamlessly integrated.
2. Primary-Secondary with Additional Secondaries: This configuration involves pre-configured replication with one primary and one secondary database. As the cluster expands horizontally, additional secondary nodes are seamlessly incorporated.
Moreover, you have the option to utilize the XtraDB Cluster, a robust database clustering solution designed to ensure high availability, mitigate risks of downtime and data loss, and provide linear scalability to support a growing environment.
PostgreSQL
A pre-configured PostgreSQL database cluster is established with asynchronous primary-secondary replication, allowing for the automatic addition of new nodes into the cluster as secondaries.
Couchbase
The Couchbase servers are automatically interconnected with pre-configured auto-scaling and rebalancing, ensuring a unified, highly available data storage system.
Learn more: https://github.com/jelastic-jps/couchbase
MongoDB
Automatically configure a highly-available and reliable MongoDB replica set, complete with auto-discovery of new nodes for seamless integration.
Redis
Automatization is provided for the distributed implementation of a Redis Cluster, an open-source, in-memory data structure store. Typically used for caching, data storage, acting as a message broker, and various other tasks. The topology includes a minimum of three Primary servers, each accompanied by a Secondary node to facilitate read load distribution and auto-recovery in case of Primary server failure.
OpenSearch
Automatic clustering of a community-driven, open-source search engine that offers distributed, multitenant full-text search. The solution has built-in options for integrating OpenSearch Dashboards for data visualization and Logstash for log processing.
Shared Storage Container
The AccuWeb.Cloud platform automatically configures a dependable storage cluster using the Gluster solution, guaranteeing data safety. In the event of node failure, the AutoFS client seamlessly switches to operational instances, ensuring high availability of storage resources.
Auto-Clustering Management
1. The Auto-Clustering feature can be activated for the node group using the corresponding switcher located in the central part of the topology wizard, provided it is available for the selected stack.
I. It could be mandatory, requiring automatic activation (e.g., for the Couchbase database).
II. It may be mandatory with additional settings available (e.g., cluster scheme and ProxySQL load balancer for the MySQL database).
III. It might come with restrictions, such as minimum/maximum node counts or scaling modes (e.g., for the MariaDB Galera type).
2. Additionally, to obtain further details about the cluster being created, hover over the question mark icon adjacent to the switcher. In the resulting pop-up frame, you’ll find a brief description, often accompanied by a topology scheme and a link to a more comprehensive overview.
3. Other settings can be configured similarly to any regular environment.
Note: Once configured, auto-clustering cannot be disabled from the topology wizard.
4. If necessary, you can monitor the cluster configuration logs through the platform console at:
https://app.{platformDomain}/console
For example, this information can be used for debugging purposes when developing packaged solutions with Cloud Scripting, which make use of the auto-clustering feature.
Setting Up Auto-Clusterization with Cloud Scripting
To define auto-clustering settings in your JPS solutions, you can use a new cluster property. Here’s how you can do it:
1. Use the relevant cluster property to enable or disable auto-clustering for the specific layer.
"nodeGroup": "couchbase",
"cluster": true | false2. Provide additional parameters for auto-clustering, such as selecting a database cluster scheme, by specifying them in the cluster property.
"nodeGroup": "mysql",
"cluster": {
"scheme": "master"
}3. If necessary, substitute the default JPS manifest with a custom one that includes the desired clusterization steps.
"nodeGroup": "mysql",
"cluster": {
"jps": "http://.../custom-manifest.jps",
"settings": {
"scheme": "master"
}
}4. Depending on the specific cluster requirements, you may need to impose certain topology restrictions, such as defining the minimum/maximum number of nodes or the scaling mode. This can be implemented through the validation property.
You can specify these parameters for any JPS package. Here’s an example in YAML format:
type: install
name: Validation
nodes:
image: alpine
nodeGroup: cp
count: 2
validation:
minCount: 2
maxCount: 3
scalingMode: statefulWith these steps, you can easily leverage the auto-clustering solutions supported by the AccuWeb.Cloud platform and benefit from their implementation specifics.