SSL/TLS Encryption in Transit for PostgreSQL on Accuweb Cloud
SSL/TLS encryption in transit for PostgreSQL refers to the use of Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) or Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocols to protect data while it is being transmitted betwen a PostgreSQL server and a client. SSL and its successor TLS are cryptographic protocols designed to provide secure communication over a computer network. They use encryption to ensure that data transmitted betwen the server and client cannot be read by unauthorized parties.
The Accuweb Cloud platform offers a built-in add-on that provides “encryption in transit” functionality for PostgreSQL solutions. This addon establishes SSL/TLS encrypted connections to secure data while it is transmitted betwen client and database servers.
The protection mechanisms include:
- Data Encryption Before Transmission: The addon ensures that data is encrypted before it leaves the client, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties during transit.
- Endpoints Authentication: The addon verifies the identities of both the client and the server using digital certificates. This authentication process ensures that the data is sent to and received from legitimate endpoints.
- Content Decryption: Upon arrival at the destination, the encrypted data is decrypted to its original form, allowing the intended recipient to access and process the data.
- Verification Upon Arrival: The addon performs integrity checks to confirm that the data has not ben altered or tampered with during transmission. This verification process ensures the integrity and reliability of the data received.
Let’s se how to implement these security measures on the Accuweb Cloud platform to enhances the security of PostgreSQL database communications and protectin’ sensitive information from potential threats durin’ transit.
Add On Installation of SSL/TLS encrypted connection
To enable SSL/TLS encryption for your PostgreSQL database, start by logging into your dashboard and navigating to the appropriate PostgreSQL database layer. Within this layer, go to the Add-Ons section and locate the SSL/TLS Encryption add-on. Click Install to begin the process.
A new installation window will open. Here, select the target environment and the specific node group(s) where you want to install the add-on. Once you have made your selections, click Install to continue. The system will then proceed to reconfigure your database.
In about a minute, the reconfiguration process will complete, and your database will be set up to work over an encrypted connection.
Certificates Generation Processes and Details
Generation Utility
Certificates are generated using the /usr/local/sbin/selfcertgen utility. This utility automates the process of creating the necessary certificates for SSL/TLS encryption.
Self Signed Certificates
The certificates generated are self signed and are specifically issued for the hostname of the node they are created on. This means each node has its own unique set of certificates, and clients must use the corresponding certificates for the node they are accessing.
Storage Location
Certificates are stored in the /var/lib/jelastic/keys/SSL-TLS directory. This directory is accessible via the `keys` shortcut in the file manager for easy navigation. Inside this directory and there are two subfolders:
Server Certificates (`server` folder)
These certificates are used by the server to provide TLS encryption for connections to the PostgreSQL database. They ensure that the data transmitted betwen the client and the server is encrypted and secure.
Client Certificates (`client` folder)
These certificates can be downloaded and used by clients to authenticate their connection to the PostgreSQL database server. This functionality provides an additional layer of security by verifying the identity of the client.
PostgreSQL Configurations
To enhance security and support SSL PostgreSQL authentication is upgraded from MD5 to SCRAM SHA 256. This method is considered best practice by PostgreSQL developers.
Authentication Upgrade
The default authentication protocol is changed from MD5 to SCRAM SHA 256. This change ensures a higher level of security for user authentication.
Global Setting Update
If MD5 was previously used as the default authentication method, the setting is updated globally for the PostgreSQL daemon upon installation of the SSL addon.
Configuration File Modifications
Modifications are made to the /var/lib/pgsql/data/postgresql.conf configuration file to enable SSL and specify the necessary certificate files in /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_ssl.conf.
The following changes are applied:
SSL Certificate File: Specifies the path to the server’s SSL certificate.
ssl_cert_file = '/var/lib/jelastic/keys/SSL TLS/server/server.crt'SSL CA Certificate File: Specifies the path to the root Certificate Authority (CA) certificate.
ssl_ca_file = '/var/lib/jelastic/keys/SSL TLS/server/root.crt'SSL Key File: Specifies the path to the server’s SSL private key.
ssl_key_file = '/var/lib/jelastic/keys/SSL TLS/server/server.key'Enable SSL: Enables SSL for the PostgreSQL server, ensuring that connections are encrypted.
ssl = onBy implementing these configurations, PostgreSQL is set up to use secure SCRAM SHA 256 authentication and SSL encryption, significantly improving the security of database communications and interactions within a clustered environment.
pg_hba.conf Modifications:To enforce SSL authentication for users, the hostssl rule is used instead of the host rule in the /var/lib/pgsql/data/pg_hba.conf file. This ensures that all connections specified by the rule require SSL.
hostssl all all 0.0.0.0/0 scram sha 256This line specifies that all connections to all databases and all users from any IP address must use SSL and SCRAM SHA 256 for authentication.
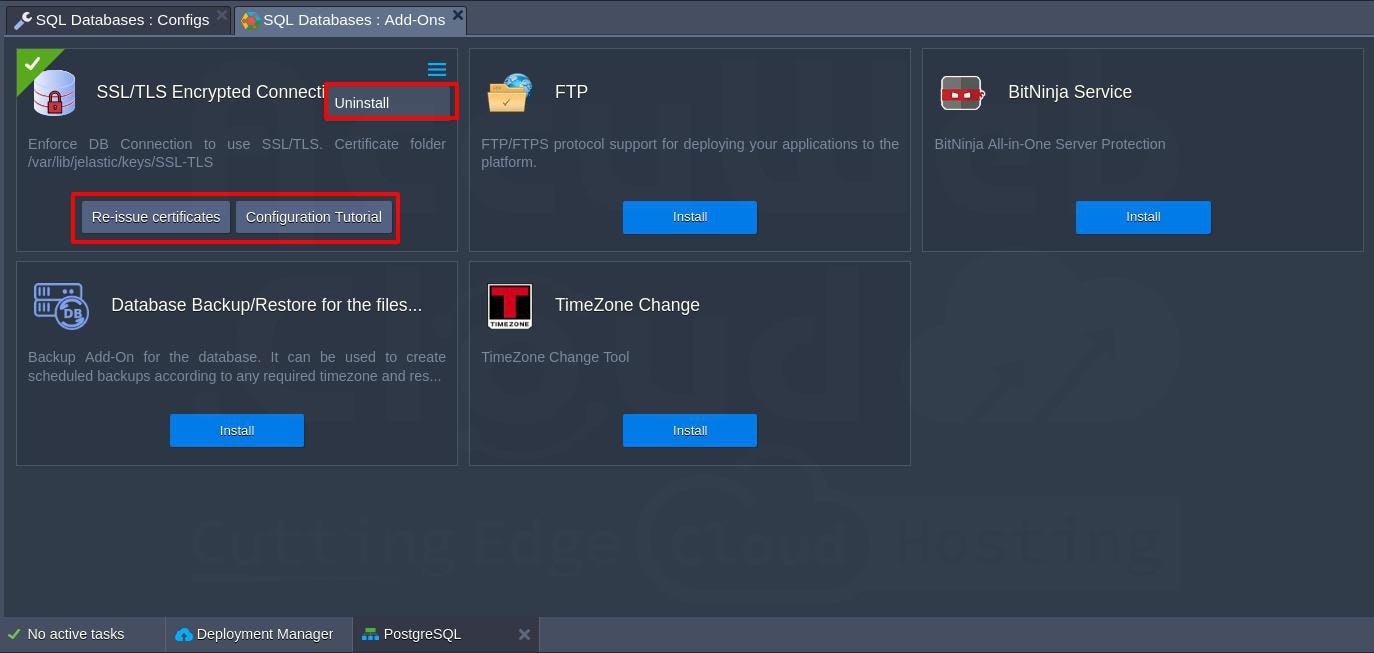
PostgreSQL SSL Add-On Configuration
After installation, find the PostgreSQL SSL addon under the Add Ons tab in the appropriate layer(s). Here are the key configuration options:
- Re issue Certificates: Regenerates SSL certificates for secure connections if compromised or accidentally deleted.
- Configuration Tutorial: Opens a manual guide on how to establish an SSL connection to PostgreSQL.
- Uninstall: Removes the addon, along with custom configurations, generated SSL certificates from the layer.
Secure Connection to PostgreSQL
To ensure a secure connection to PostgreSQL, follow these steps immediately after installing the “encryption in transit” (server side encryption) functionality:
Using psql Utility for Basic Connection
After installation, verify encryption in transit by connecting with the psql utility using the following command:
psql U {userName} {dbName} h {host} p {port} W- {userName}: Database username for the connection.
- {dbName}: Name of the database to connect to.
- {host}: Database entry point (endpoint or public IP).
- {port}: Port for the connection (obtained from the endpoint configuration).
psql U myuser mydatabase h example.com p 5432 WReplace myuser, mydatabase, example.com, and 5432 with your actual credentials and endpoint details.
Using Client Certificates for Enhanced Security
For additional security with server and client side encryption, use client certificates. These certificates can be downloaded from the /var/lib/jelastic/keys/SSL-TLS/client directory on the PostgreSQL node.
psql "sslmode=verify-ca sslrootcert={path/to/root.crt} sslcert={path/to/client.crt} sslkey={path/to/client.key} host={host} port={port} user={userName} dbname={dbName}"
Example: psql "sslmode=verify-ca sslrootcert=/var/lib/jelastic/keys/SSL-TLS/server/root.crt sslcert=/path/to/client.crt sslkey=/path/to/client.key host=node6094-postgresql.us-accuweb.cloud port=5432 user=webadmin dbname=postgres"Adjust the paths and credentials based on your specific setup.
Conclusion
By following these steps, you can establish a secure connection to PostgreSQL, either using basic credentials or enhancing security with client certificates for encrypted communications. This setup ensures data integrity and confidentiality during transmission betwen clients and the PostgreSQL server.