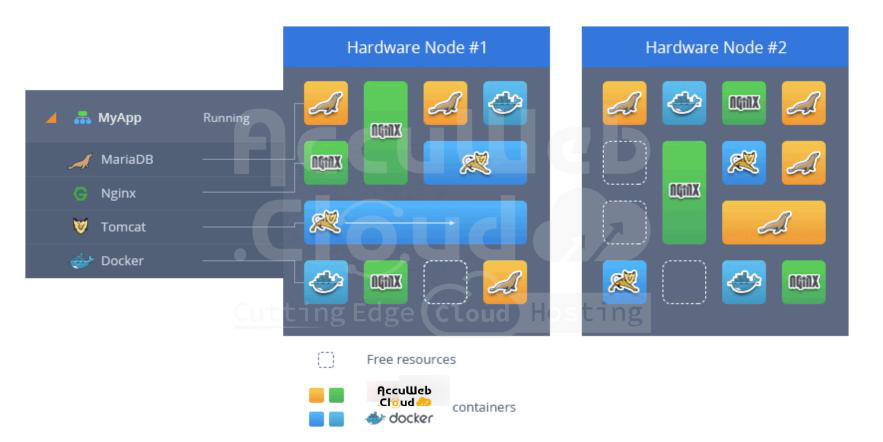
Isolated Containers
All the components in the environment, such as databases and application servers, are housed in isolated containers spread across various hosts.
The platform offers individual role-based servers for three key reasons:
Isolated Containers Live Migration
Sometimes, as your application demands grow, the physical server hosting your node might struggle to meet those demands. In such situations, the platform can swiftly move your node to another host within just 30 seconds through a process called live migration. This ensures that your application continues to receive the resources it needs without any interruptions.
During the migration, your application won’t miss a beat, it’ll keep running and even scale vertically within its server as needed. To make room for this growth, we can shuffle around other applications to different servers. With our live migration feature, we can ensure that your applications always have the resources they need without any hiccups or downtime. Plus, it’s a lifesaver during planned maintenance, automatically moving containers from one server to another without skipping a beat.
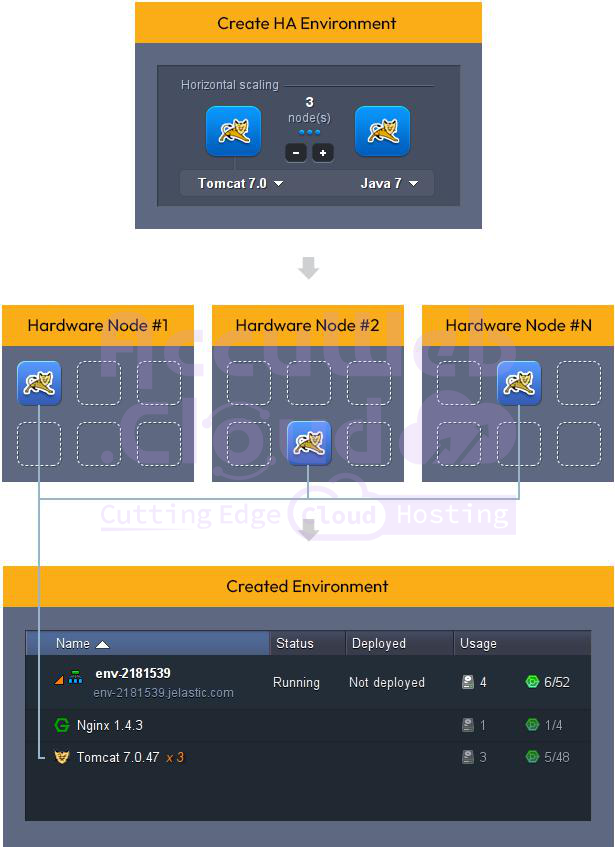
You can easily add more instances to your environment through horizontal scaling, without needing to concern yourself with available space on the host. Our platform automatically selects a host with sufficient free space and relocates your server to ensure optimal performance for each node.
High Availability for Applications
To ensure top-notch availability, the platform evenly spreads containers across various physical servers (hardware nodes). This is made possible through anti-affinity groups, which are set up to prevent specific containers from running on the same physical server.
As a result, the platform eradicates any potential for application downtime in the event of performance issues with one of the physical servers.
Security of Isolated Containers
The platform employs virtualization to run multiple containers concurrently on a single host. These containers are completely isolated, ensuring that they cannot interfere with one another. In the event that the security of one container on the hardware node is compromised, the remaining containers remain unaffected.