HTTP Headers
HTTP headers are important in HTTP requests and responses that provide more information, including such requested pages, clients’ browsers, etc.
Here are the main headers that are frequently used while deploying apps in environments:
| Header | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| host | Provides the host and port number of the resource (server) being requested. | {envName}.{platformDomain} |
| x-forwarded-proto | Identifies the protocol (HTTP or HTTPS) used to connect to your proxy or load balancer. | http/https |
| x-forwarded-for | Identifies the originating IP addresses of a client connecting to a web server using an HTTP proxy or load balancer. |
xx.xx.xx.xx, xx.xx.xx.xx IP or IPs chain (if a request goes through multiple proxies) |
| x-real-IP | The final IP address in the x-forwarded-for chain, or the client’s most recent proxy when connecting to a web server | xx.xx.xx.xx the right-most IP address in x-forwarded-for |
| x-host | The server’s originating domain name (for virtual hosting) and, if applicable, the TCP port number. | {envName}.{platformDomain} |
| x-uri | Identifies a certain name or web resource. | / |
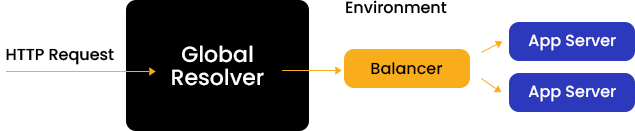
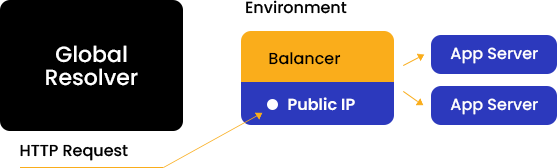
The list of supported HTTP headers may differ depending on the topology of the connected environment. There are four potential scenarios when working with the platform, influenced by external access methods (such as resolver/SLB or public IP).
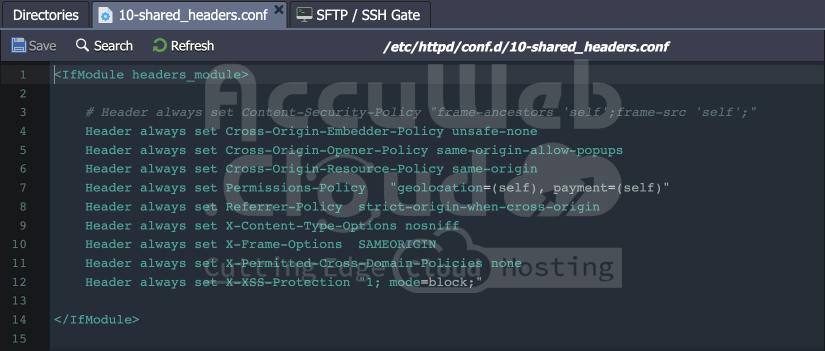
To Configure Security Headers, You Can Edit The Appropriate Configuration File Based On The Server You Are Using:
- For Apache (with PHP, Ruby, Python), MySQL, and MariaDB:
- Path: /etc/httpd/conf.d/10-shared_headers.conf
- For NGINX (with PHP, Ruby) and LEMP:
- Path: /etc/nginx/conf.d/headers/10-shared_headers.conf
- For LiteSpeed and LLSMP:
- Path: /var/www/conf/vhconf.xml (adjustments via the admin panel only)
- For Tomcat and TomEE:
- Path: /opt/tomcat/conf/web.xml
Remember to restart your server after making changes to the configuration file to ensure that the modifications take effect.
The Following Additional HTTP headers Are Utilized By Default On The Stacks Listed Above:
| Header | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Cross-Origin-Embedder-Policy | Allows the server to declare an embedded policy for the specified document. | unsafe-none; |
| Cross-Origin-Opener-Policy | Prevents other domains from opening or controlling a window. | same-origin-allow-popups |
| Cross-Origin-Resource-Policy | This header prevents other domains from viewing the response of the resources to which it is applied. | same-origin |
| Content-Security-Policy | Controls what resources the user agent can load on a given page. Disabled by default. | frame-ancestors ‘self’;frame-src ‘self’; |
| Expect-CT (only with SSL enabled) | Allows sites to enforce Certificate Transparency rules, preventing the usage of incorrectly issued certificates for the site (i.e., any certificate for that site must appear in public CT logs). | max-age=3600, enforce |
| Permissions-Policy | Provides a means for allowing and disallowing browser functionality in its frames and embedded iframes. | payment=(self) geolocation=(self) |
| Strict-Transport-Security (only with SSL enabled) | Forces HTTPS communication instead of HTTP. | max-age=5; includeSubDomains |
| X-Content-Type-Options | Disables MIME sniffing and compels the browser to use the type specified in Content-Type. | nosniff |
| X-Frame-Options | Allows browsers to render pages as <frame>, <iframe>, <embed>, or <object>. | SAMEORIGIN |
| X-Permitted-Cross-Domain-Policies | Specifies whether a cross-domain policy file (crossdomain.xml) is permitted. The file may establish a policy that allows clients to handle data across domains that would otherwise be restricted by the Same-Origin Policy. | none |
| Referrer-Policy | Determines how much referrer information (provided via the Referer header) should be included in requests. | strict-origin-when-cross-origin (default) |
|
X-XSS-Protection |
Allows cross-site scripting screening. | 1; mode=block |