How to Create Multi-Region [Cross-Region] MongoDB Replication in AccuWeb.Cloud?
MongoDB has established itself as one of the most versatile and scalable NoSQL databases available today, empowering businesses to efficiently manage and distribute their data. As organizations grow globally, the need for faster data access, enhanced security, and uninterrupted availability becomes critical. Multi-region replication in MongoDB addresses these demands by allowing data to be distributed across geographically distinct locations.
With AccuWeb.Cloud, you can easily deploy infrastructure across multiple regions and set up MongoDB replication (Community or Enterprise edition) on top of it. Our platform provides the secure networking, performance, and intuitive dashboard to simplify provisioning the servers and connectivity, while you remain in full control of the MongoDB configuration.
This guide explains how to set up multi-region MongoDB replication hosting on AccuWeb.Cloud. Customers can deploy MongoDB (Community or BYOL Enterprise edition) on our platform and manually configure replication across regions to ensure their data is always available.
Table of Contents
- What is Multi-Region MongoDB Replication Hosting?
- Why Choose AccuWeb.Cloud for Multi-Region Replication?
- Steps to Set Up Multi-Region MongoDB Replication Hosting on AccuWeb.Cloud
- Benefits of Multi-Region MongoDB Replication on AccuWeb.Cloud
- Detailed Example of Setting Up a Replica Set
- Setting Up a Hidden Node in MongoDB Replica Set
- Monitoring Secondary Node Synchronization with rs.printSecondaryReplicationInfo()
- Important Considerations for MongoDB Replica Set Setup
- Conclusion
What is Multi-Region MongoDB Replication Hosting?
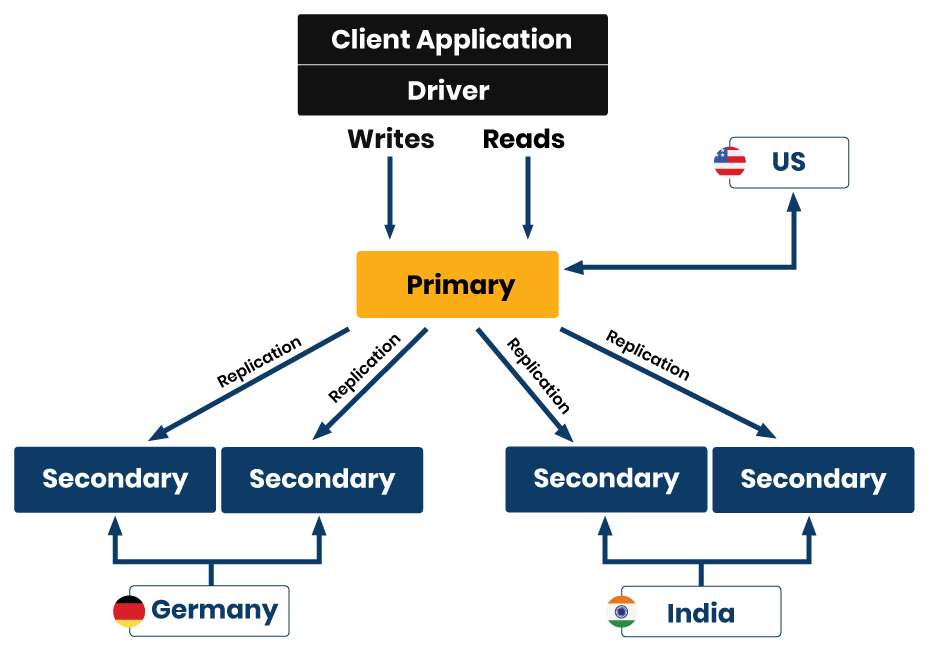
Multi-region MongoDB replication is an advanced configuration that distributes your database across multiple geographic locations. Unlike single-region replication, which limits redundancy and resilience to a specific area, multi-region setups allow you to achieve global scalability and availability.
Key components in multi-region replication include:
- Primary Node: Handles all write operations and maintains the oplog (operation log).
- Secondary Nodes: Replicate the oplog from the primary node to maintain data consistency. These nodes can be promoted to primary in case of failure.
- Arbiter Node (Optional): Participates in the election process but does not store data.
Multi-region replication enhances:
- Performance: By reducing latency for geographically dispersed users.
- Availability: Ensuring your application remains operational even during regional outages.
- Disaster Recovery: Providing an effective failover mechanism in case of catastrophic events.
Why Choose AccuWeb.Cloud for Multi-Region Replication?
AccuWeb.Cloud offers a unique set of features designed to make multi-region MongoDB replication both efficient and secure. Here are some key advantages:
1. Private IP Configuration
- AccuWeb.Cloud assigns private IPs to MongoDB nodes, ensuring secure communication between regions. Unlike public networks, private IPs significantly reduce the attack surface, safeguarding your data.
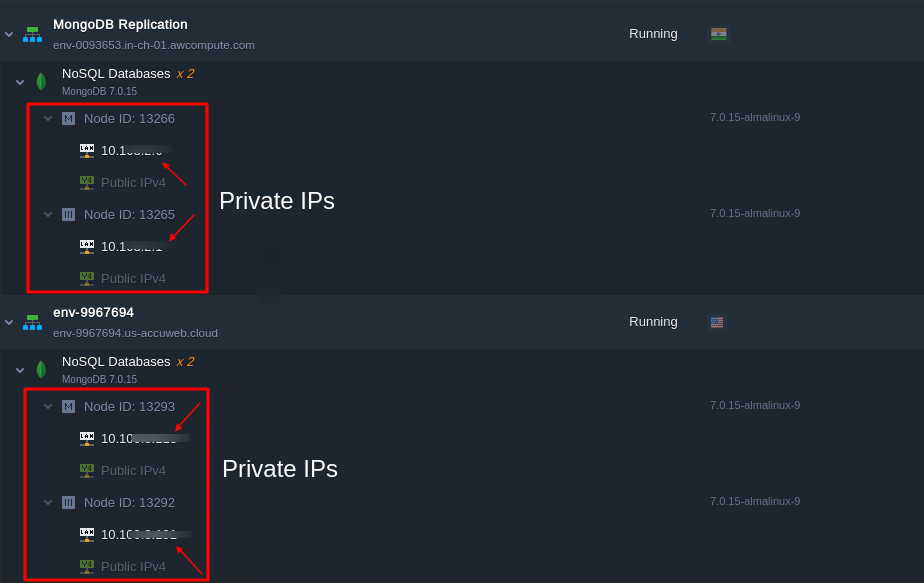
2. Enhancing Latency
- With optimized private network connections, AccuWeb.Cloud minimizes latency, enabling faster query responses and smoother application performance for users worldwide.
3. Ensuring High Availability
- Geographically distributed nodes ensure uptime even during regional outages. Automated failover mechanisms guarantee uninterrupted access.
4. Scalability
- Whether you need to add more nodes or expand to additional regions, AccuWeb.Cloud’s scalable infrastructure supports growing database needs effortlessly.
5. User-Friendly Dashboard
- The intuitive interface allows users to design, deploy, and manage their multi-region setups with ease, reducing administrative overhead and complexity.
6. Cost Efficiency
- By utilizing private IPs, you can lower network transfer costs while maintaining high-speed communication between nodes.
Steps to Set Up Multi-Region MongoDB Replication Hosting on AccuWeb.Cloud
Follow these step-by-step instructions to create a secure and efficient multi-region MongoDB replication setup in AccuWeb.Cloud:
Step 1: Log In to the AccuWeb.Cloud Dashboard
Access your AccuWeb.Cloud account and navigate to the Topology section. From here, you can create environments in multiple regions by deploying virtual machines (nodes) where MongoDB will run.
Customers may install MongoDB manually (Community Edition or BYOL Enterprise Edition) on these nodes, or run MongoDB as a custom Docker image, fully self-managed and outside the scope of licensing restrictions. Running your own MongoDB Docker image gives you full control over configuration and access to the latest versions.
Step 2: Configure MongoDB Nodes Across Regions
You can configure your MongoDB replica set based on your specific requirements, whether it’s across 2 regions, 3 regions, or more.
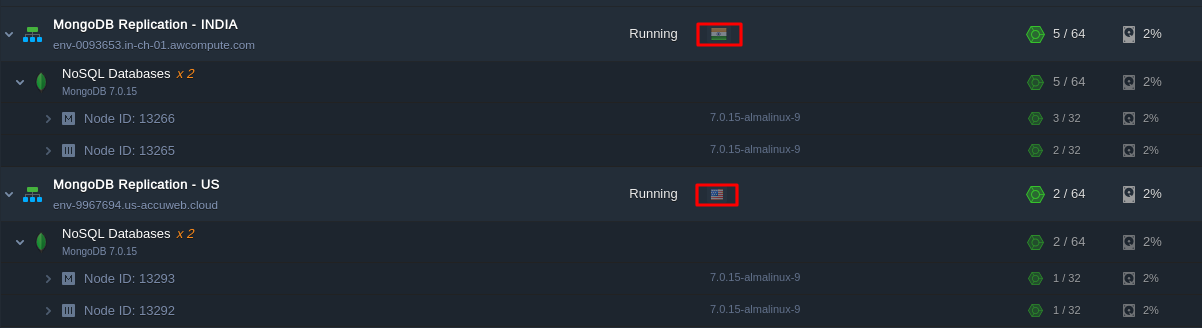
To begin, choose the regions where your MongoDB nodes will be located. For instance:
- Region 1: New York (USA) – 2 nodes
- Region 2: Chennai (India) – 2 nodes
This setup provides redundancy and high availability by distributing your database across different geographical locations. For enhanced resilience, ensure at least one secondary node is deployed per region.
To set up the replica set, mirror this configuration from the Topology section for each region, specifying the required number of nodes you want to include in the replication process.
Understanding MongoDB Replication Basics
MongoDB replication is fundamental to ensuring data availability, scalability, and resilience in a distributed database system. Below are the core components and benefits of replication:
Key Components of a Replica Set:
- Primary Node: Handles all write operations and maintains the oplog (operation log).
- Secondary Nodes: Synchronize data from the oplog of the primary node asynchronously and can be promoted to primary during failover.
- Arbiter Node (Optional): Participates in the election process to maintain quorum but does not store data.
Replication Workflow:
- Write Operations: Directed to the primary node.
- Oplog Replication: Secondary nodes copy and apply changes from the primary’s oplog to synchronize data.
- Automatic Failover: A new primary node is elected if the current primary becomes unavailable, ensuring continuous operations.
Benefits of Replication:
- Data Redundancy: Prevents data loss by maintaining multiple copies.
- High Availability: Applications remain operational even during node failures.
- Read Scalability: Secondary nodes can be used to handle read queries and distribute the load.
- Disaster Recovery: Enables data recovery in case of catastrophic events.
Benefits of Multi-Region MongoDB Replication on AccuWeb.Cloud
Optimized Performance:
Minimized latency for users across the globe through strategically distributed nodes, ensuring faster query responses and improved user experience.
Robust Security:
Private IP configurations limit exposure to external threats by enabling secure communication between replica set members.
Geographical Redundancy:
Distributing nodes across multiple regions enhances uptime and resilience, even in the event of regional failures or outages.
Cost Efficiency:
By utilizing private network communication, AccuWeb.Cloud reduces network transfer costs while maintaining high-speed data replication.
Simplified Management:
The user-friendly dashboard offers intuitive tools for designing, deploying, and monitoring your multi-region setups, reducing administrative complexity.
Detailed Example of Setting Up a Replica Set
1. Prepare the Configuration
Each node in the replica set requires a properly defined configuration file or equivalent command-line options. Below is an example configuration for the mongod.conf file:
# mongod.conf
replication:
replSetName: rs0 # Name of the replica set (must match on all nodes)
net:
port: 27017 # Port for the MongoDB instance
bindIp: 0.0.0.0 # Allows connections from any network interfaceTo start MongoDB with the above configuration, run the following command on each node:
mongod --config /path/to/mongod.confAlternatively, use command-line options directly without a configuration file:
mongod --replSet rs0 --port 27017 --dbpath /data/db1 --bind_ip 0.0.0.0Parameter Explanations:
- –replSet rs0:
Specifies the replica set’s name. This must be consistent across all nodes in the replica set. - –port 27017:
Defines the port the MongoDB instance listens on. The default is 27017. - –dbpath /data/db1:
Points to the directory where MongoDB stores its data. Verify that the directory exists and has the correct permissions set. - –bind_ip 0.0.0.0:
Configures the server to listen on all available network interfaces, allowing connections from other machines.
2. Initiate the Replica Set
Log into the primary node using the MongoDB shell (with authentication enabled):
Replace <username> and <password> with appropriate credentials.
mongo --port 27017 -u <username> -p <password> --authenticationDatabase adminOR
mongo --host <IP_ADDRESS> --port 27017 -u <username> -p <password> --authenticationDatabase adminInitiate the replica set:
rs.initiate({
_id: "rs0", // Define the name of the replica set
members: [
{ _id: 0, host: "node1.example.com:27017" }, // Primary node
{ _id: 1, host: "node2.example.com:27017" }, // Secondary node
{ _id: 2, host: "node3.example.com:27017" } // Secondary node
]
});OR [You can also use IP addresses instead of hostnames while defining the replica set members.]
rs.initiate({
_id: "rs0", // Name of the replica set
members: [
{ _id: 0, host: "12.xx.x.1:27017" }, // Primary node (use IP instead of hostname)
{ _id: 1, host: "12.xx.x.2:27017" }, // Secondary node (use IP instead of hostname)
{ _id: 2, host: "12.xx.x.3:27017" } // Secondary node (use IP instead of hostname)
]
});- _id: The unique identifier for each member.
- host: The IP address (public or private) or hostname along with the port of the replica set member.
To check the status of the replica set:
rs.status();3. Add Members (Optional)
Additional nodes can be added using:
rs.add("node4.example.com:27017");- rs.add(): Adds a new secondary member to the replica set.
4. Configure Priority and Voting
Control which nodes are eligible to become primary by configuring their priority:
cfg = rs.conf();
cfg.members[1].priority = 2;
cfg.members[2].priority = 0; // Prevent from becoming primary
rs.reconfig(cfg);- priority: A higher value increases the chance of a node becoming primary.
- rs.reconfig(): Applies the updated configuration.
5. Arbiters (Optional)
An arbiter votes in elections but does not store data. Useful to break ties:
rs.addArb("arbiter1.example.com:27017");- rs.addArb(): Adds an arbiter node.
6. Test Failover
Simulate failover by shutting down the primary:
mongo --host node1.example.com --port 27017
db.adminCommand({ shutdown: 1 });Verify the new primary:
rs.status();7. Important Commands
| Command | Use Case |
| rs.initiate() | Starts a new replica set. |
| rs.add(host) | Adds a new secondary member. |
| rs.addArb(host) | Adds an arbiter. |
| rs.remove(host) | Removes a member. |
| rs.conf() | Fetches the current configuration. |
| rs.reconfig(cfg) | Applies a new configuration. |
| rs.status() | Provides the status of the replica set. |
| db.adminCommand({ shutdown: 1 }) | Shuts down the current node. |
Tips
- Backups: Take regular backups of the primary to prevent data loss.
- Monitoring: Use rs.status() frequently to ensure all nodes are operational.
- Network: Ensure proper firewall rules are in place to allow communication between nodes.
Setting Up a Hidden Node in MongoDB Replica Set
This guide explains multi-region MongoDB replication hosting and why AccuWeb.Cloud is the ideal choice for setting up a reliable system to ensure your data is always available for your business.
Retrieve and Update Replica Set Configuration:
let cfg = rs.conf();
cfg.members.push({
_id: 4, // Unique ID for the hidden node
host: "10.xxx.x.xx0:27017", // Hidden node's private IP and port
priority: 0, // Prevent election as primary
hidden: true // Mark this node as hidden
});
rs.reconfig(cfg);Optional: Add Delayed Replication
To delay replication on the hidden node:
cfg.members[4].secondaryDelaySecs = 3600; // 1-hour delay
rs.reconfig(cfg);Monitoring Secondary Node Synchronization with rs.printSecondaryReplicationInfo()
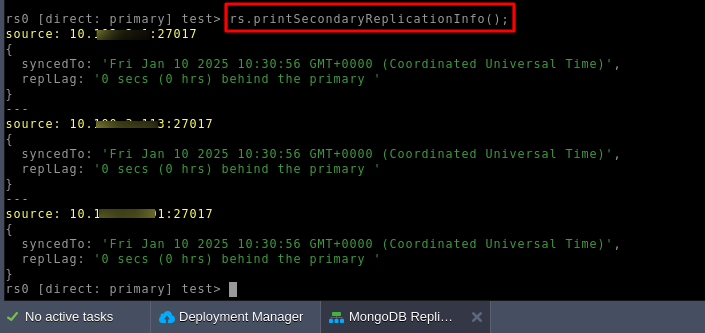
The rs.printSecondaryReplicationInfo() command in MongoDB offers a comprehensive view of the replication status across all secondary nodes in a replica set. It is an indispensable tool for database administrators to verify synchronization with the primary node and monitor replication lag.
Output Breakdown:
- source: Displays the hostname or IP address and port of the secondary node.
- syncedTo: Indicates the latest timestamp to which the secondary node has synchronized with the primary.
- replLag: Shows the time delay (replication lag) between the primary and secondary node in seconds or hours.
Example Output:
source: 10.xx.x.1:27017
{
syncedTo: 'Fri Jan 10 2025 13:29:26 GMT+0000 (Coordinated Universal Time)',
replLag: '0 secs (0 hrs) behind the primary '
}- Node IP (10.xx.x.1:27017): This node is fully synchronized with the primary as of the timestamp shown.
- Replication Lag: The lag is 0 seconds, confirming real-time synchronization with no delay.
Use Case:
- Routine Monitoring: Run rs.printSecondaryReplicationInfo() as part of regular database health checks to ensure all secondary nodes are synchronized.
- Troubleshooting Replication Lag: Identify and address potential bottlenecks like network latency, disk I/O issues, or resource contention when lag increases.
- Failover Preparation: Verify that secondary nodes are up-to-date to ensure a seamless failover in case the primary node becomes unavailable.
Important Considerations for MongoDB Replica Set Hosting Setup
When configuring and maintaining a MongoDB Replica Set Hosting, it’s crucial to follow best practices and be aware of potential pitfalls. Below are key points to consider:
1. Naming and Configuration
- Replica Set Name: The name of the replica set (rs0, etc.) must be consistent across all nodes.
- Unique Hostnames: Ensure all nodes have unique and resolvable hostnames or IPs.
- Port Numbers: Avoid port conflicts; ensure all nodes have the same port.
2. Deployment and Architecture
- Odd Number of Nodes: Aim for an odd number of voting members (primary, secondaries, and arbiters) to avoid election ties.
- Arbiters: Use arbiters to save resources but avoid using them in critical production setups due to their inability to store data.
- Priority Configuration: Set priority carefully to control which node becomes the primary.
- Data Centers: Distribute nodes across data centers for high availability, but ensure low latency between them.
3. Security
- Authentication: Enable authentication (–auth) to prevent unauthorized access.
- TLS/SSL: Use TLS/SSL encryption for secure communication between nodes.
- Firewall Rules: Configure firewalls to allow communication only between replica set members and trusted clients.
4. Backup and Data Integrity
- Backups: Regularly backup your data, even with a replica set in place, to protect against accidental data loss or corruption.
- Journaling: Enable journaling (–journal) for data durability in case of unexpected shutdowns.
5. Network and Performance
- Latency: Ensure minimal network latency between nodes to prevent replication lag.
- Bandwidth: Monitor bandwidth usage; replication can consume significant resources.
- Heartbeat Frequency: Keep the default heartbeat settings unless specific conditions require tuning.
6. Election and Failover
- Primary Election: Understand the election process to predict how the system will behave during node failures.
- Secondary Lag: Avoid significant replication lag by monitoring and tuning write operations.
7. Node Configuration
- Hidden Members: Use hidden nodes for analytics workloads to prevent impact on production.
- Delayed Nodes: Set up delayed secondaries as a fallback in case of accidental deletions or updates.
- Secondary Reads: If secondary reads are enabled, ensure that your application can handle eventual consistency.
8. Monitoring and Maintenance
- Replica Set Status: Regularly check the status using rs.status().
- Logs: Monitor MongoDB logs for issues such as replication failures or election problems.
- Reconfigurations: Make configuration changes during low-traffic periods to minimize disruptions.
9. Upgrades and Compatibility
- Version Matching: All nodes should run the same version of MongoDB to avoid compatibility issues.
- Rolling Upgrades: Upgrade one node at a time, starting with secondaries, then the primary.
10. Additional Best Practices
- Clock Synchronization: Ensure system clocks are synchronized across all nodes using NTP (Network Time Protocol).
- Disk Space: Monitor disk space usage to prevent issues due to full storage.
- Hidden Replica Set Members: Use hidden members for backups or analytics to avoid affecting primary/secondary performance.
- Replica Set Reconfiguration: Be cautious with rs.reconfig() as it can temporarily make the set unavailable.
Conclusion
Setting up multi-region MongoDB replication hosting on AccuWeb.Cloud transforms your database operations, delivering unmatched high availability, ultra-low latency, and resilient disaster recovery. With advanced private IP configurations and intuitive management tools, AccuWeb.Cloud enables you to build a secure, efficient, and scalable database infrastructure tailored for global applications.
Elevate your MongoDB replication Hosting capabilities with AccuWeb.Cloud. Start today to experience cutting-edge performance, ironclad security, and unmatched reliability for your business.