Secure SSH Access to Private GIT Repositories
With the AccuWeb.Cloud platform, you can effortlessly deploy your application from any remote public or private GIT/SVN repository, supporting various programming languages such as Java, PHP, Ruby, Python, and Node.js.
To increase security, you can access your private GIT repositories via SSH, allowing for easy cloning and updating of your applications. This capability also enables you to work with repositories hosted on private servers, as opposed to common web-based services like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
Accessing Your Private GIT Repository Using the Secured SSH Protocol
Follow these steps to access your private GIT repository securely via SSH:
- Generate SSH Keychain
- Add Private SSH Key to Platform Account
- Add Public SSH Key to Git Account
- Deploy Project via SSH
Generate SSH Keychain
To begin, create an SSH key pair (consisting of a private key and a public key) to bind your GIT repository to your AccuWeb.Cloud account. If you haven’t generated a keychain before, follow the Generate SSH Key instructions.
Add Private SSH Key to Platform Account
Once you have generated your SSH key pair, add your private key to your AccuWeb.Cloud account by following these steps:
Step 1. Log in to your AccuWeb.Cloud account and navigate to the settings by clicking the “Settings” button at the top-right section of the dashboard.
Step 2. In the opened User Settings tab, switch to the SSH Keys > Private Keys option and click on the Add Private Key button.
Step 3. Copy your private SSH key and insert it into the Key input field. Provide a Name for this key (e.g., git-key) and finalize the addition by clicking the Add button.
Step 4. Your new private key will appear in the corresponding tab shortly.
You can delete keys that are no longer needed by clicking the appropriate red cross button. Deleting the key from the manager won’t remove it from existing GIT projects on the platform, allowing you to continue working with them as before.
Add Public SSH Key to Git Account
After uploading your private key to your AccuWeb.Cloud account, you need to configure your GIT repository account.
For repositories on a remote private server, upload the corresponding SSH public key and add it to the list of authorized keys.
For web-based project hosting services, follow the detailed steps for each service below. We will cover the setup for three popular platforms:
- GitHub
- GitLab
- Bitbucket
GitHub
Step 1. Log in to your GitHub account and go to Settings (top-right corner). Select the SSH and GPG keys tab from the left panel and click the New SSH key button.
Step 2. Paste your public SSH key into the Key field, assign a Title, and click Add SSH key.
Step 3. Verify that your newly added key appears in the SSH keys tab.
Step 4. To obtain the SSH link for your project, navigate to the desired repository (ensure you are logged in), and switch the link type to SSH in the Clone URL section on the right-hand pane. Click the Copy to Clipboard button or copy the link manually.
GitLab
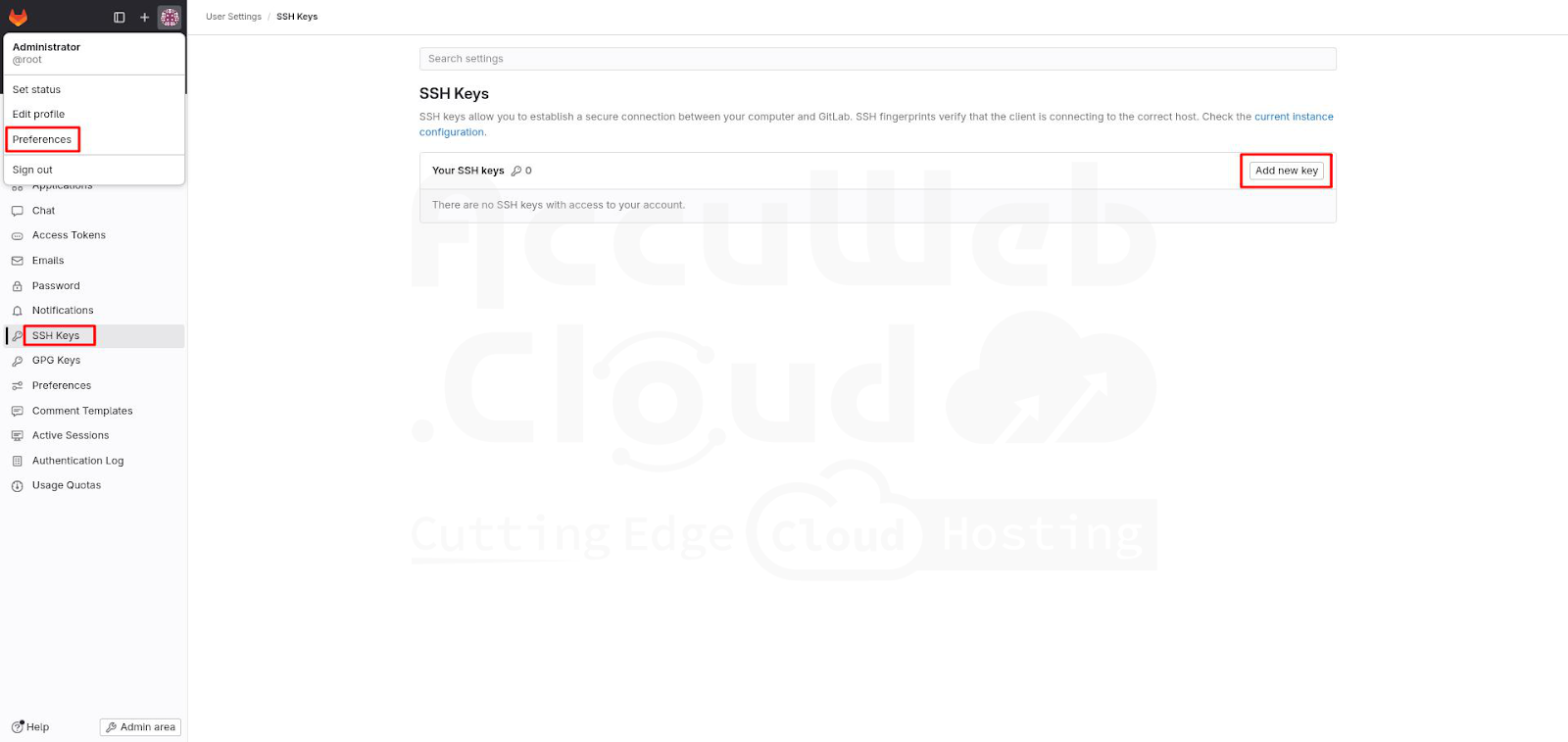
Step 1. Log in to your GitLab account. Go to Preferences and select the SSH Keys tab from the left menu.
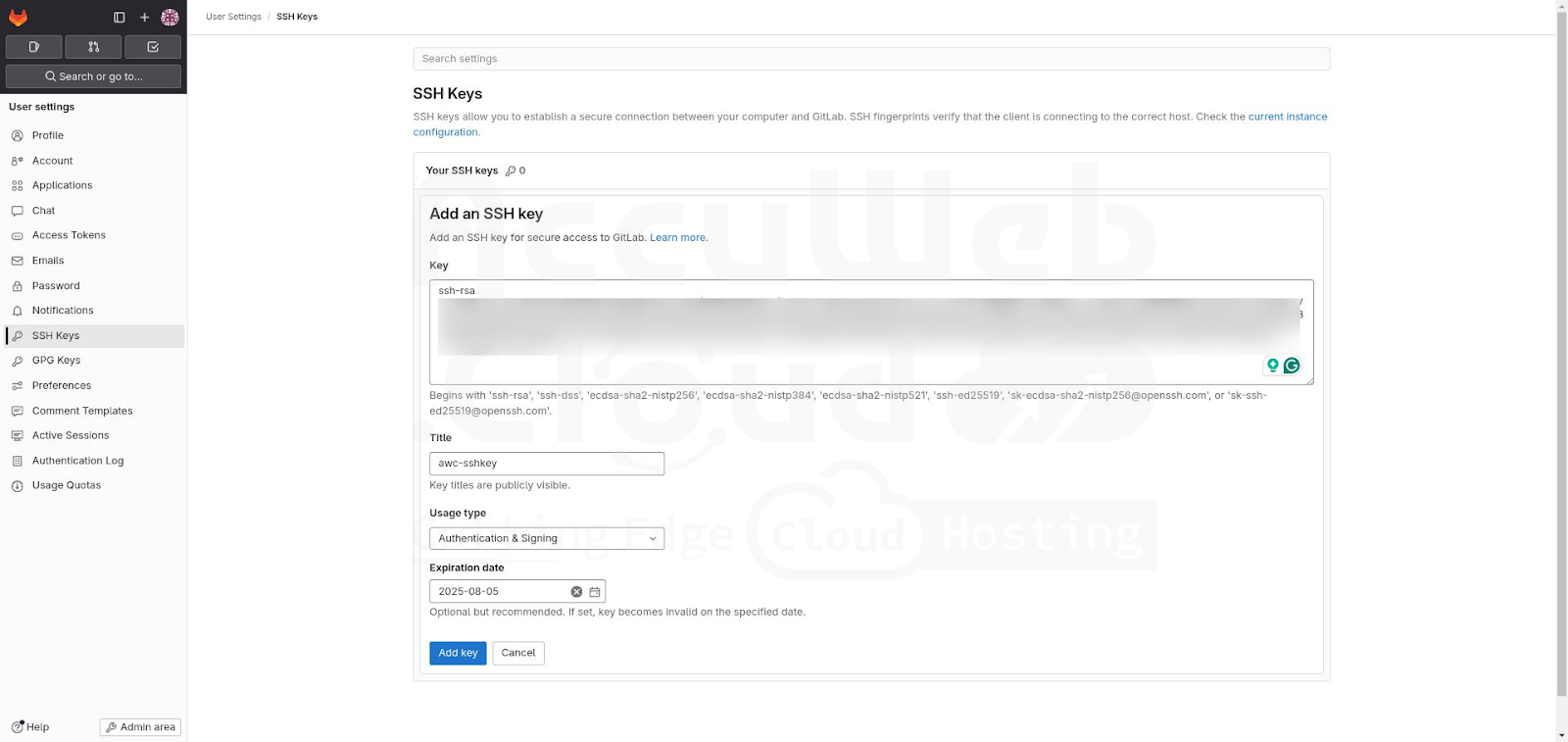
Step 2. Paste your public SSH key into the Key field, provide a Title, and optionally set an Expires at a date for the key.
Step 3. Click the Add key button.
Step 4. Verify that your key appears in the Your SSH keys list below.
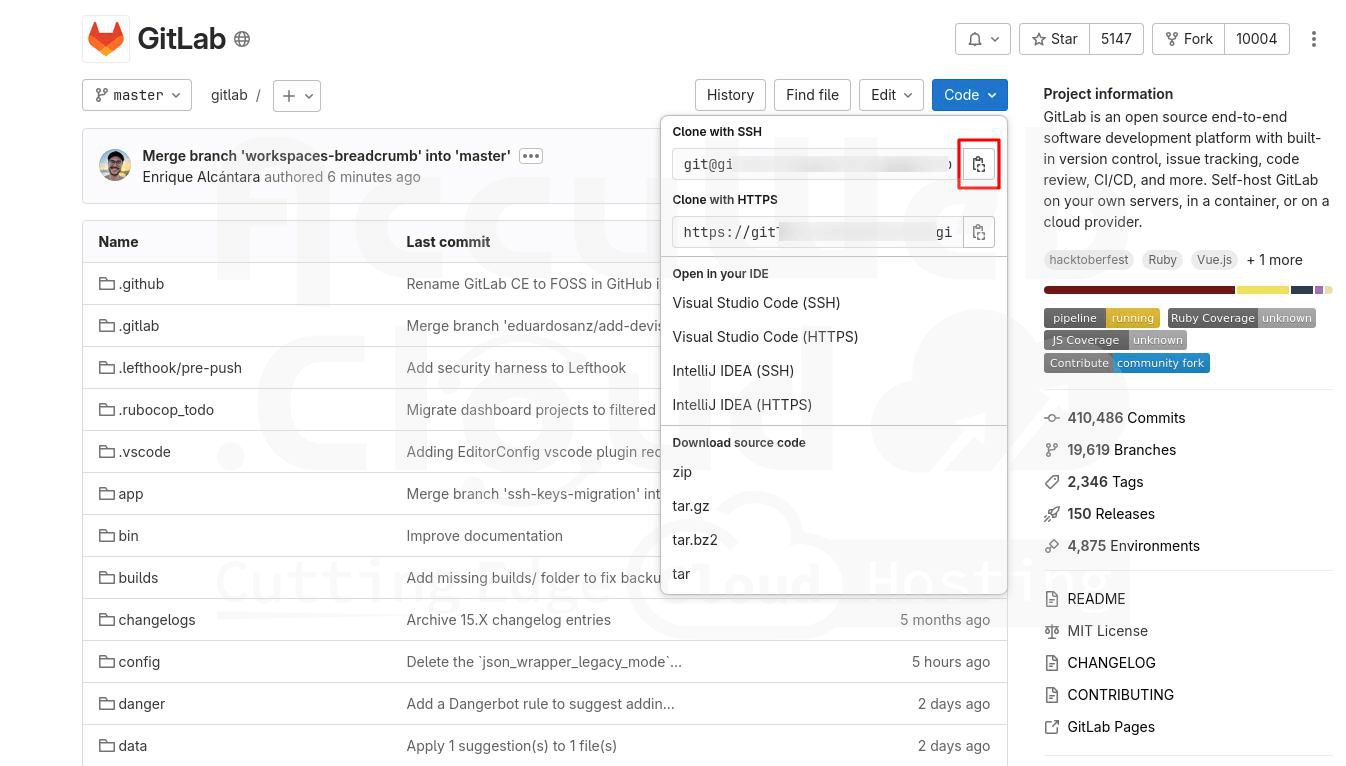
Step 5. To obtain the SSH link for your project, navigate to the desired repository (ensure you are logged in), expand the Clone menu, and copy the Clone with SSH link.
Bitbucket
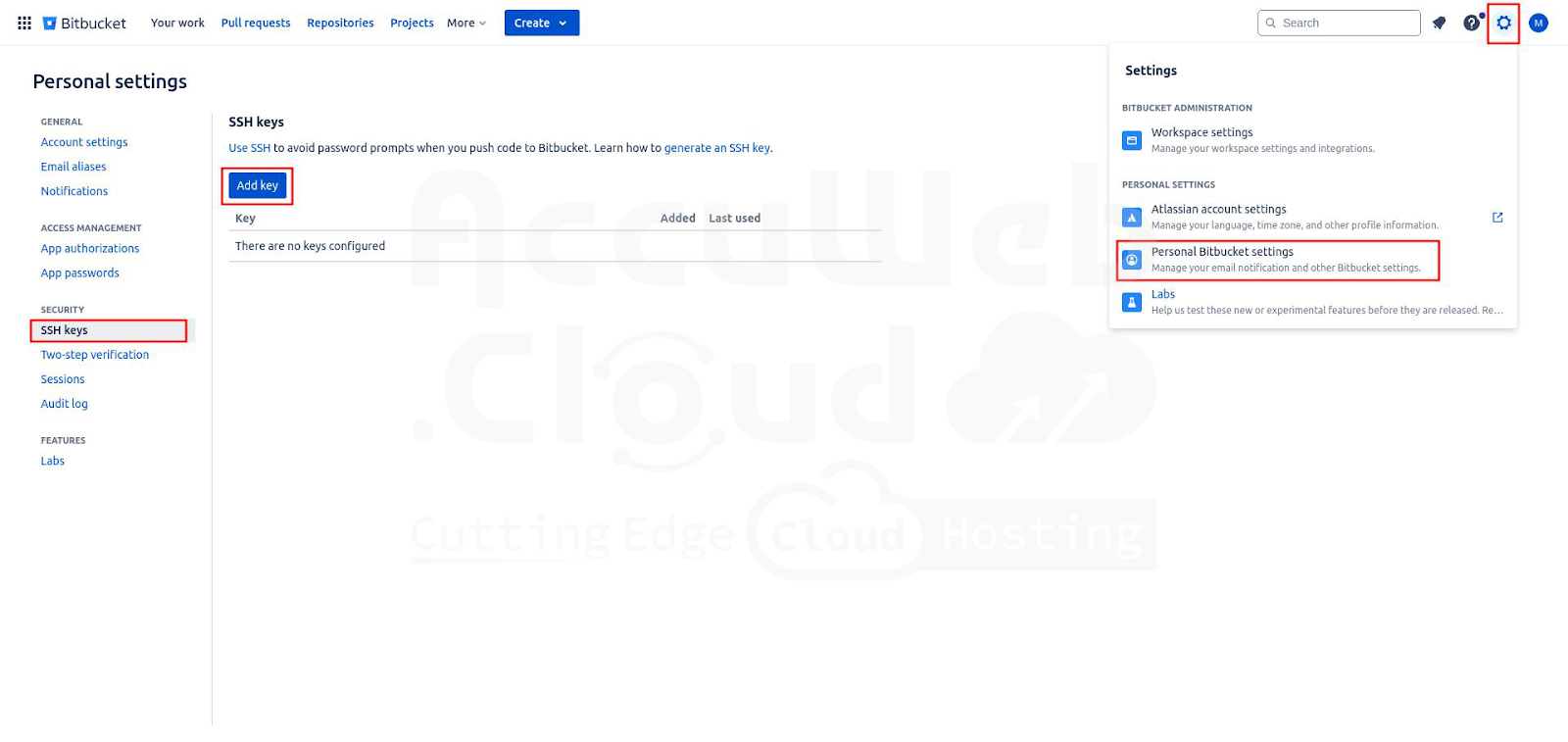
Step 1. Log in to your Bitbucket account and select the Settings icon from the top-right corner and click Personal Bitbucket settings.
Step 2. In the account settings page, go to the SSH keys tab found under the Security section using the left-hand menu. Click the Add key in the central area of the page.
Step 3. In the prompt that appears, paste your public SSH key into the Key field, provide a Label, and click Add key.
Step 4. Confirm that your new key appears in the SSH keys tab.
Step 5. To get the SSH link for your project, go to the desired repository (ensure you are logged in). Click the Clone and copy the displayed string.
Deploy Project via SSH
Finally, you can proceed with deploying your project via the secured connection.
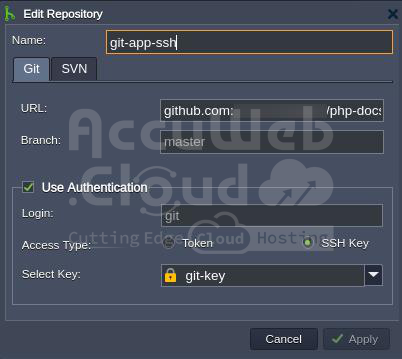
Step 1. Navigate to the Deployment Manager at the bottom of the dashboard and click on Add repo. Provide the following information in the form:
- Name: The name of your application (no spaces or special symbols allowed).
- URL: The appropriate git URL for the repository.
- Branch: The required branch of the project (default is master).
- Tick the Use Authentication checkbox, choose SSH Key as your Access Type, and select the key from the list.
Step 2. Click Apply to save your project information.
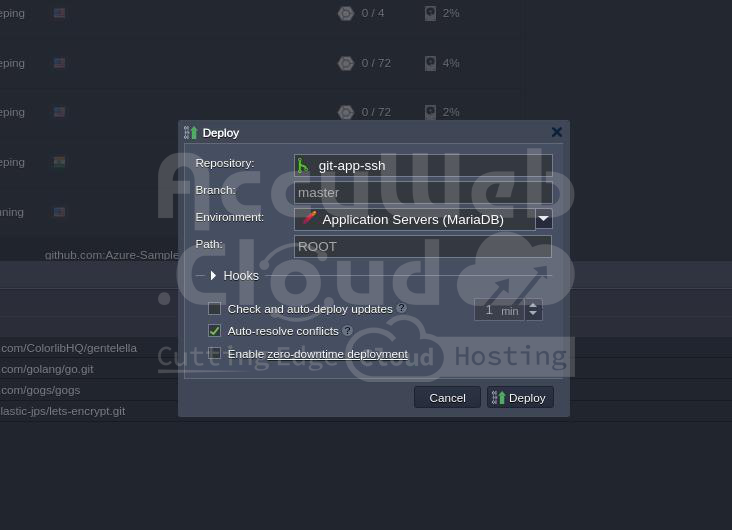
Step 3. Once the project is added to the Deployment Manager, hover over it and click the Deploy button to deploy your application.
In the opened window, specify the deployment target and additional configurations:
- Environment: Choose a target environment from the list.
- Path: Enter the context where you want your application to be deployed (or leave the default).
- Hooks: Include pre- and post-deployment operations as necessary.
- Check and auto-deploy updates: Enable automatic periodic updates of your project from the repository (performed only if there are code changes) with a set interval.
- Auto-resolve conflicts: Prevent merge conflicts by using the “git reset –hard” command during each subsequent project update (contradictory files will be updated according to the repository version, discarding locally made changes).
- Enable zero-downtime deployment: Adjust the deployment flow to avoid application downtime (for PHP servers only).
Step 4. After entering all the required data, click Deploy to start the process and wait until your project is successfully deployed.
Step 5. Verify that your project files are available. Open the Configuration File Manager for your environment, navigate to the webroot directory, and check for a folder named after the specified context (ROOT by default) inside.
Step 6. Finally, click Open in Browser for your environment to ensure your application is running.
That’s it! Enjoy secure interaction with your version control system – clone and update your projects hosted on the platform directly from your private GIT repositories via SSH.