Common Issues Faced by Developers When Using MongoDB with PHP
MongoDB is an open-source, NoSQL database designed to handle modern application needs where flexibility and scalability are essential. Unlike traditional SQL databases, MongoDB stores data in JSON-like documents, making it a perfect choice for managing unstructured or semi-structured data. Developers often prefer it because it can efficiently handle large-scale applications, real-time analytics, and high-traffic workloads.
For teams working with PHP and MongoDB, this combination is popular for building dynamic websites, REST APIs, and cloud-native applications. However, developers may encounter challenges such as connection errors, query optimizations, or integration issues. This guide explores common MongoDB with PHP issues and their solutions, helping you save time and improve performance.
Why Use MongoDB?
MongoDB is more than just a database; it’s a developer-friendly data platform built for scalability, speed, and flexibility. Whether you are building a startup project or managing enterprise-scale applications, MongoDB provides a foundation for growth. Here’s why developers choose MongoDB:
- Flexible Document Model
MongoDB stores data in BSON (binary JSON) documents, which naturally map to objects in PHP and other programming languages. This makes development faster and reduces the gap between your data and code. - Ease of Use for Beginners
With a simple installation process and extensive documentation, MongoDB lets developers start coding quickly without worrying about complex database configurations. - Scalability for High-Traffic Apps
Thanks to its horizontal scaling (sharding), MongoDB can handle massive amounts of data and high user loads, making it ideal for e-commerce, social media, and SaaS platforms. - Robust Querying & Indexing
MongoDB supports rich queries, secondary indexes, text search, and aggregation pipelines, enabling developers to perform advanced data analysis without additional tools. - Thriving Global Community
With a large ecosystem of developers, tutorials, and enterprise support, MongoDB ensures that help is always available, whether you’re troubleshooting or optimizing performance.
Common MongoDB Issues and Their Solutions
When developers integrate a MongoDB database with a PHP application, they often face a few common problems. In this blog, we have a simple breakdown of each problem and what might cause it:
Case 1. MongoDB Extension Not Installed or Enabled
PHP applications need the MongoDB extension to connect with MongoDB. If this extension isn’t installed or turned on in the new environment, the application won’t be able to talk to the database.
Example Error:
Fatal error: Class ‘MongoDB\Driver\Manager’ not found.
This error occurs when you move your application to a new server and set up the MongoDB database but forget to install or enable the MongoDB extension in the php.ini file.
You must run the following command in the terminal to install the MongoDB extension on the new server.
# pecl install MongoDBIf you get an error message “Command ‘pecl’ not found” after running the above command, it means that the pear application is not installed on your server. To install it, you need to run apt install php-pear in the terminal.
# apt install PHP-pearOnce you install the Pear application, you need to run the pecl install MongoDB command again.
# pecl install MongoDBIf you are getting a warning message mentioned below. It means that the PECL channel for PHP extensions has updated its protocols, and you should update your local PECL channel. Here’s how to handle this warning and complete the installation of the MongoDB extension:
Run the following command to update the PECL channel:
# pecl channel-update pecl.php.netNow, you need to install the PHP development package, which includes phpize. The package name may vary depending on your Linux distribution and the version of PHP you are using.
If you’re using Ubuntu or a Debian-based system, you can install the required packages with the following command:
# apt-get install php-devIf you are using a specific PHP version (e.g., PHP 8.1), you can install it like this:
# apt-get install php8.2-devAfter updating the PECL channel, proceed to install the MongoDB extension again using the following command.
# pecl install MongoDBThe system will ask for your preference to enable certain extensions. You need to type yes to enable it or no to disable it. If you need the default one, then just press enter, and the system will install the MongoDB extension on your system.
After that, you need to enable it from the php.ini file. Go to the PHP Configuration File Path and open the php.ini with a text editor like Nano or Vim.
Add the following line to the php.ini file and save it.
extension=mongodb.soAfter that, restart the Apache service. To restart the Apache service, run the following command in the terminal.
# systemctl restart apache2Then restart the PHP-FPM
# systemctl restart php-fpmOnce you enable it, you can verify it by running the PHP info page in the browser.
http://yourdomainname/phpinfor.php
Case 2. Incorrect MongoDB PHP Library Version
The MongoDB PHP driver (or library) is an essential component for enabling communication between a PHP application and a MongoDB database server. It allows PHP to:
-> Perform CRUD operations, and queries, and manage databases/collections.
-> Execute complex MongoDB operations like aggregation and indexing.
-> Manage connections efficiently with connection pooling for performance.
-> Handle errors with proper exception handling.
-> Ensure compatibility between PHP applications and MongoDB server versions.
In short, it’s essential to use MongoDB in PHP applications by offering a simple API to interact with the database.
PHP Fatal error: Uncaught MongoDB\Driver\Exception\ConnectionException: Unsupported wire version: (X), please upgrade your MongoDB library or server.
The above error indicates that there is a version mismatch between the MongoDB PHP driver (library) and the MongoDB server. The wire protocol used by MongoDB changes between versions, and this error happens when the driver and server versions are incompatible.
Here are the steps to fix it.
Step 1. Check the Current Versions
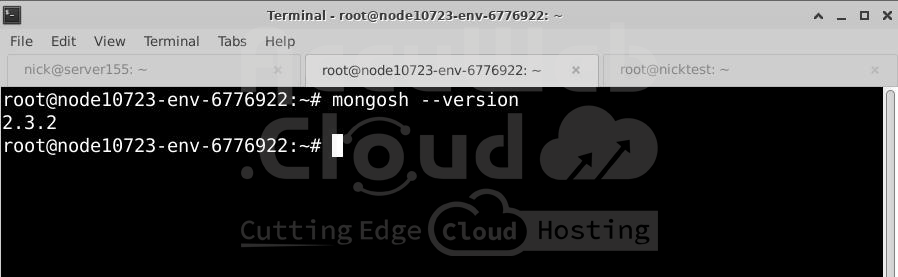
Run the following command to check which version of MongoDB is running on your server:
# mongosh --versionStep 2. Check the PHP MongoDB Driver Version
You can check the installed version of the MongoDB PHP driver with the following command:
php -r 'echo phpversion("mongodb") . "\n";'You can refer to the MongoDB PHP Driver documentation to determine compatibility between the MongoDB server version and the PHP driver version. Below are details of the few MongoDB versions that require PHP drivers.
MongoDB 5.x: Requires MongoDB PHP Driver 1.10 or higher.
MongoDB 6.x: Requires MongoDB PHP Driver 1.14 or higher.
MongoDB 7.x: Requires MongoDB PHP Driver 1.16 or higher
MongoDB 8.x: Requires MongoDB PHP Driver 1.20 or higher
Step 3. Upgrade the MongoDB Server You can verify this by checking th
If your MongoDB server version is too old and incompatible with your PHP driver, you need to upgrade it to a compatible version. To do so, use the following command to upgrade the MongoDB Server.
# apt update# apt upgrade MongoDB-orgIf you want to upgrade the MongoDB server to a specific version, then replace Mongodb-org with your specific MongoDB version.
Step 4. Upgrade the MongoDB PHP Driver
If your MongoDB server is already on a supported version, make sure your PHP driver is also up to date. You can upgrade the driver using PECL:
# pecl upgrade MongoDBAfter upgrading, ensure the driver is enabled in your php.ini file.
Step 5. Restart Services the Apache service
After making any changes, restart your web server or PHP service to apply the new configurations.
For Apache:
# systemctl restart apache2For PHP-FPM:
# systemctl restart php8.1-fpmReplace the PHP version as necessary
Step 6. Test the Connection
After upgrading either the MongoDB server or the PHP driver, test the connection again in your PHP application.
Case 3: MongoDB Library is missing:
If you do not install the MongoDB library on the server where your application is loaded, you will receive the following error.
The error you encountered indicates that the Composer autoloader file (vendor/autoload.php) is not found. This usually happens if:
The composer has not been installed or hasn’t been used to install the required MongoDB library.
The vendor directory is missing, or the path to the autoload.php file is incorrect.
To fix the above error, you can follow the following steps.
Step 1. Ensure Composer is Installed
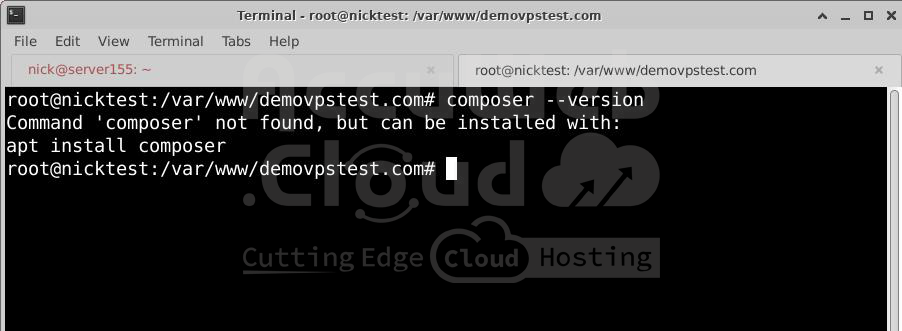
You need to check if Composer is installed on your server. For that, you need to run the following command in the terminal.
composer --versionIf Composer is not installed, you will receive an error message Command “composer” not found, but can be installed with:
To install the composer, you must run the following command in the terminal.
# apt update# apt install composerStep 2. Install the MongoDB PHP Library
Go to the project directory from where your project or application is loaded.
For example:
# cd /var/www/demovpstest.com/Use the below command to install the MongoDB library:
# composer requires MongoDB/MongoDBThis command will create a vendor/ directory with the necessary libraries, including the autoload.php file.
Step 3. Verify the vendor/autoload.php Path
You need to ensure that the vendor folder is in the application folder from where your application is loaded. For example, if your application is loaded from the path /var/www/demovpstest.com/, then ensure that the vendor folder is presented under it. Then, open the vendor folder and ensure that autoload.php is there.
Step 4: Restart Apache service
After making the above changes, you need to restart the Apache service to apply them and ensure that everything loads properly.
# systemctl restart apache2Case 4: MongoDB PHP Extension is missing
If you have not installed MongoDB PHP Extension on the server, you will receive the following error.
The “Class MongoDB\Driver\Manager not found” error occurs when the MongoDB PHP extension is missing or not properly installed. The MongoDB PHP library (MongoDB/MongoDB) depends on this extension, which provides the core functionality to connect to MongoDB.
To fix the above error, you need to follow the following steps.
Step 1. Install the MongoDB PHP Extension
To install the MongoDB PHP extension on your server run the following command.
# apt update# apt install php-mongodbStep 2: Enable the extension
Then, you need to enable the extension on the server. Run the following command for it.
# phpenmod MongoDBStep 3: Restart Apache service
After making the above changes, you need to restart the Apache service to apply them and ensure that everything loads properly.
# systemctl restart apache2Once you install the missing MongoDB PHP Extension on the server and restart the Apache service, you will be able to connect to the MongoDB server successfully. You can see that we are successfully able to connect to the MongoDB server through PHP.
Case 5: Connection error
If you have entered incorrect details, such as the server IP address where the MongoDB server is installed and the port number on which the MongoDB is listening for the connection, you will receive the following error. Also, if the MongoDB server is in the stop status and you have entered incorrect database login details, you will receive the same error.
The error message you’re seeing indicates that your PHP script cannot connect to the MongoDB server running on localhost:27017. This could be due to several reasons. Here’s how to fix this issue:
Step to fix the connection error
Step 1: Check MongoDB Service Status:
You need to make sure that the MongoDB service is running on your server. Run the following command to check if the MongoDB service is running.
# systemctl status mongodIf the service is not active (running), you can start it by running the below-mentioned command:
# systemctl start mongodStep 2: Verify MongoDB Listening Port:
By default, MongoDB listens on port 27017. You can verify this by checking the MongoDB configuration file, usually located at /etc/mongod.conf.
Look for the net section:
net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 127.0.0.1 # This line allows connections only from localhost
If you installed and configured a firewall on your server, you need to ensure that port number 27017 is allowed in the firewall.
If bindIp is set to 127.0.0.1, the server will only accept connections from the local machine.
If you want to access the MongoDB server remotely, then you need to mention the server’s public IP address where the MongoDB is installed.
For example:
Net:
port: 27017
bindIp: 127.0.01,192.168.2.155
Done!
If you add 0.0.0.0 in the bindIP field, it allows connections from all other systems. However, we highly recommend against this, as it can have security implications, so use it cautiously.
Step 3: Firewall Settings:
If MongoDB is running on a remote server, ensure that your firewall is allowing traffic on port 27017. You can check and adjust your firewall settings using ufw (if installed):
# ufw allow 27017Step 4: Check MongoDB Logs:
If you are still receiving the error, then you need to check the MongoDB log file for any errors or warnings that might indicate why the connection is being refused. You can usually find the log file at /var/log/mongodb/mongod.log.
# cat /var/log/mongodb/mongod.logStep 5: Try Connecting with MongoDB Shell:
You can also use the MongoDB shell to attempt a connection directly and see if it works:
You can also use the MongoDB shell to check whether you can connect directly to the MongoDB server. Below is the command to check and verify this.
mongo --host localhost --port 27017If you can connect using the shell but not via PHP, there might be an issue with the PHP setup.
Step 6: Test with Different Connection String:
If you are trying to connect from a remote server, change the connection URI in your PHP script to:
$uri = "mongodb://<username>:<password>@<host>:<port>";Need to replace <username>, <password>, <host>, and <port> with the appropriate values. If you’re using authentication, ensure that the user has access to the database.
Conclusion:
A common issue faced by developers using MongoDB with PHP is managing connection stability and performance. Challenges include handling connection timeouts, properly configuring connection pools, and dealing with driver compatibility between PHP versions and MongoDB.
This blog explains all the possible causes and fixes. By addressing these challenges, developers can improve their experience with MongoDB in PHP, leading to more robust applications and efficient data handling. Continuous learning and loyalty to best practices are important for successfully leveraging MongoDB’s capabilities.
People Also Ask(And You Should Too!)
1. Why do developers face issues when connecting PHP with MongoDB?
Most connection issues occur due to missing PHP MongoDB drivers, incorrect connection strings, or firewall restrictions on database ports. Always install the official PHP MongoDB extension, use the correct mongodb:// URI format, and check that port 27017 is open on your server.
2. What is the correct way to install MongoDB PHP driver on Ubuntu 22.04?
You can install it with:
sudo apt-get install php-mongodbThen enable it in php.ini or using:
sudo phpenmod mongodbsudo systemctl restart apache2This ensures PHP can communicate with MongoDB seamlessly.
3. How can I fix “MongoDB\Driver\Exception\ConnectionTimeoutException” in PHP?
This error usually means PHP cannot reach MongoDB. Check:
- If MongoDB service is running: sudo systemctl status mongod
- Correct host/IP in your PHP code (use 127.0.0.1 or server IP).
- Open firewall/Atlas network access if remote.
4. Is MongoDB better than MySQL for PHP projects?
MongoDB is better suited for applications that require scalability, flexible schemas, and handling unstructured or semi-structured data. MySQL is better for projects needing structured relational data with strict schemas. Many PHP developers choose MongoDB for modern apps like CMS, e-commerce, and analytics dashboards.
5. Can I use MongoDB with Laravel or Symfony PHP frameworks?
Yes. Popular PHP frameworks like Laravel, Symfony, and CodeIgniter support MongoDB with the help of extensions or ODM libraries like Laravel MongoDB (jenssegers/laravel-mongodb). This allows you to integrate MongoDB models directly into your PHP project.
6. Why is my MongoDB query slow in PHP?
Slow queries often happen due to missing indexes, large datasets, or inefficient queries. Use:
db.collection.createIndex({ fieldname: 1 })to improve query performance. Also, avoid fetching unnecessary fields by projecting only what you need.

Jilesh Patadiya, the visionary Founder and Chief Technology Officer (CTO) behind AccuWeb.Cloud. Founder & CTO at AccuWebHosting.com. He shares his web hosting insights on the AccuWeb.Cloud blog. He mostly writes on the latest web hosting trends, WordPress, storage technologies, and Windows and Linux hosting platforms.