CDN vs Caching: A Comparative Analysis
CDN stands for the Content Delivery Network.
It is a geographically distributed group of servers that deliver content to users and accelerate the delivery of website content by bringing it closer to the users.
CDN stores copies of files (such as images, CSS, JS, and videos) on servers worldwide, enabling users to access content from the nearest server to them. By caching content, images, and video in the nearest servers to the user’s physical location, CDNs reduce page load time and improve performance.
CDN offloads some or all of the (mainly static content) content delivery burden from the origin server. A replica server called an edge/CDN server will deliver content on behalf of the origin servers.
Why is CDN essential?
When a user visits a website, the content from the web server has to travel across the internet to reach their computer. If the user’s location is far from the origin server, loading large files such as videos or website images will take considerable time.
However, if the website owner has implemented CDN, the requested content will be delivered from the closest edge server to the user location.
For example, when someone in Denver visits your website hosted in Singapore, the user’s request would have to travel the entire distance from Denver to Singapore to reach the origin server if you are not using CDN.
If the requested content is not in the edge server cache, the edge server retrieves the content from the origin server.
How Does a CDN Work?
The Content Delivery Network component consists of the origin server and a set of Edge servers that deliver copies of content to the end-users;
Origin Server: The origin server contains/hosts the original version of your web content.
Edge Servers: It is a geographically distributed group of servers called points of presence(PoPs). It stores the copy of the content as a cache from the origin server, and they are responsible for delivering that content to nearby users.
CDN Workflow:
- A user makes the first request for the content, such as a web page, image, or video, from a website.
- The request reaches the origin server. The origin server delivers content to the user. At the same time, it also sends a copy of the response to the edge server geographically nearest to that user.
- The edge server stores a cached version of the content to reduce the distance between the user and the origin server.
- Next time, if any other visitor from that location makes the same request for the content, then the edge server delivers it instead of the origin server.
What is Caching?
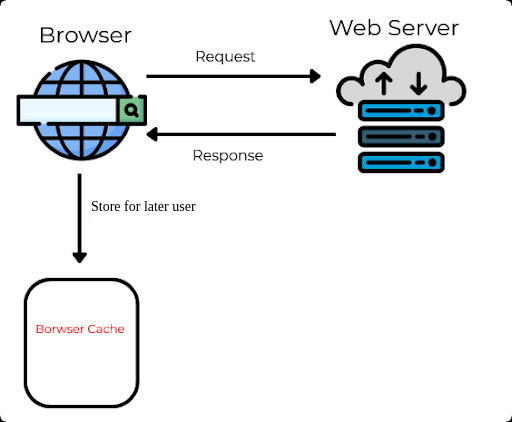
Caching stores frequently accessed data or web content such as images, videos, HTML pages, and other resources in a cache. Caching reduces the time it takes to retrieve content when it is requested again.
Implementing caching makes web browsing faster and more efficient since it eliminates the need to retrieve data from the origin server repeatedly.
The browser/server caches a copy of the requested content. Whenever a user requests that content again, the cache will deliver it without requiring retrieval from the original server. Consequently, less data must be transferred, and web pages load faster.
Server-side and client-side caching are two approaches used to cache data in the context of web applications.
Client Side Caching:
Client Side Caching is often called Browser Caching.
Once the browser has requested the data from the server, it stores it locally in the browser. The next time you request the same data, it won’t go to the server for the data; it will load it from the Browser Cache.
Server Side Caching:
In server-side caching, the data/response is stored on the web server or in a proxy server, such as a reverse proxy or a content delivery network (CDN).
Consequently, the load on the web server and the bandwidth usage are reduced, as well as the latency for users.
A Comparative Analysis CDN vs Caching:
Content Scope:
CDN: The primary goal of a CDN is to enhance the speed and performance of web content. CDN provides high content availability by distributing it to geographically distributed groups of servers
CDNs store copies of files (such as images, CSS, JS, and videos) to reduce latency and improve the user experience.
Caching: Caching involves storing frequently accessed data or web content in a browser/server cache. The purpose of caching is to minimize the need to fetch accessed data from its source.
Geographic Coverage:
CDN uses a network of a geographically distributed group of servers to deliver content to users. In contrast, caching enhances performance for individual users or within a user’s local network.
In a CDN, data is stored and delivered from edge servers, while in caching, data is stored and delivered from the browser cache/proxy server.
Content Handling:
Traditionally, CDN is commonly used for caching static content. However, they may have limited support for dynamic content caching. On the other hand, caching at the server or application level can be configured to handle content effectively.
Network Architecture:
Content Delivery Network (CDN) uses distributed servers across regions to store and distribute content. Meanwhile, cache involves storing data in a cache through client-side or server-side caching.
Implementation:
CDN requires setting up infrastructure and configurations, whereas caching can be implemented within a web a class=”ac-link-text” href=”https://accuweb.cloud/applications” target=”_blank” rel=”noopener”>application or server using caching rules & directives.
Configuration and Control:
CDN is usually managed through a control panel provided by the CDN provider. Users may have limited control over caching settings and rely on default configurations.
On the other hand, caching offers fine-grained control and is directly managed by website administrators. Caching has the flexibility to define caching rules and expiration times per website requirements.
Cost:
Implementing CDN can be more expensive due to the need for infrastructure setup and network maintenance costs. On the contrary, caching can be implemented using existing infrastructure and server resources.
Conclusion
In summary, CDNs and caching improve website performance, reduce latency, and optimize user experience. CDNs are highly effective in distributing content globally using geographically distributed groups of servers to deliver content closer to end users. Meanwhile, caching involves storing and retrieving frequently accessed data on the server or client side, reducing redundant requests.
The choice between CDNs and caching depends on specific use, organizational needs & the geographic distribution of the target audience.

Jilesh Patadiya, the visionary Founder and Chief Technology Officer (CTO) behind AccuWeb.Cloud. Founder & CTO at AccuWebHosting.com. He shares his web hosting insights on the AccuWeb.Cloud blog. He mostly writes on the latest web hosting trends, WordPress, storage technologies, and Windows and Linux hosting platforms.