How Slow Queries Affect Your Site (and How Redis Can Help)
Introduction
A slow website isn’t just annoying, it’s costly. When your database queries take too long to execute, every extra second adds up, frustrating visitors and reducing conversions. Slow queries delay page loading, overload server resources, and even increase your infrastructure costs.
Fortunately, there’s a solution: Redis, an in-memory database that acts as a lightning-fast cache layer. By combining Redis with query optimization best practices, you can dramatically improve response times, reduce server strain, and create a smoother browsing experience.
In this guide, we’ll break down:
- The common causes of slow queries
- The real impact of slow queries on your site and business
- How Redis helps eliminate query bottlenecks
1) What Constitutes a Slow Query?
A slow query refers to a database query that exceeds the expected duration for execution. This delay in execution time can be attributed to various factors, including complex SQL statements, lack of appropriate indexing, inefficient database schema design, hardware limitations, or network latency.
From a technical standpoint, slow queries result in long response times for retrieving data from the database, leading to decreased performance and responsiveness of the application or website. This delay query affects user experience, system efficiency, and overall application performance. Identifying and optimizing slow queries is essential for enhancing database performance and ensuring a seamless user experience.
2) Identifying the Causes of Slow Queries
Slow queries can be negatively impact the overall performance of your application or website. Understanding the root causess of slow queries is essential for optimizing database performance and improving user experience. Here are some common factors that contribute to slow queries –
Database Indexing
Indexes are essential for efficient query execution as they facilitate quick data retrieval by organizing and structuring the data. However, improperly configured indexes can down query performance. Ensuring that relevant columns are properly indexed and periodically optimizing index structures can improve query response times.
Complex SQL Statements
SQL queries are the primary means of interacting with databases. However, poorly optimized or overly complex SQL statements can significantly impact query performance. For example, queries that involve multiple joins, subqueries, or less effective use of keywords like “DISTINCT” can lead to slower execution times.
Locking and Blocking
Concurrent access to database resources by multiple users or transactions can result in locking and blocking issues, where one transaction prevents others from accessing or modifying data. Long held locks can cause delays in query execution and lead to performance bottlenecks. Implementing appropriate isolation levels, optimizing transaction management, and minimizing lock contention can mitigate these issues.
Server Configuration Issues
The configuration settings of your database server play a crucial role in determining its performance. Misconfigurations or failure to optimize settings based on factors like server hardware, user load, and database size can result in slow queries. Common configuration issues include inadequate memory allocation, sub-optimal indexing strategies, and inefficient query caching mechanisms.
Hardware Limitations
The underlying hardware infrastructure on which your database server runs can also contribute to slow query performance. Insufficient CPU, memory, or disk I/O resources can bottleneck database operations, leading to longer query execution times. Upgrading hardware or optimizing resource allocation can help alleviate these limitations.
Suboptimal Query Execution Plans
The database query optimizer generates execution plans to determine the most efficient way to retrieve data based on the query. However, factors such as outdated statistics, parameter sniffing, or cardinality estimation errors can lead to sub-optimal query plans, resulting in slower execution times. Regularly updating statistics, optimizing query parameters, and monitoring query performance can help identify and address these issues.
Network Latency
In distributed database environments or cloud based architectures, network latency can impact query performance. Slow network connections or high latency between application servers and database servers can introduce delays in data retrieval and query processing. Optimizing network configurations and utilizing content delivery networks (CDNs), or deploying database caching solutions can help reduce network related performance issues.
By identifying and addressing these underlying factors contributing to slow queries, you can optimize your database performance and enhance the overall responsiveness of your application or website. Regular monitoring performance tuning, and proactive maintenance are essential for mitigating slow query issues.
3) Developing Strategies to Address Slow Queries
Dealing with sluggish database queries is a common challenge, but there are ways to address them effectively. Addressing database slow queries requires a strategic approach aimed at optimizing query performance and enhancing overall system responsiveness. Here are some effective strategies to tackle slow queries –
Understanding the Requirements
Before diving into optimization techniques, it is crucial to understand the specific requirements of your application. This includes understanding the expected workload, data volume, and access patterns. Tailoring your optimization efforts to meet these requirements will yield more effective results.
Choosing the Right Database Management System (DBMS)
Not all database management systems are created equal. Depending on your application’s requirements and choosing the appropriate DBMS can have a significant impact on performance. Consider factors such as scalability, data integrity, and support for advanced features when selecting a DBMS.
Optimizing SQL Statements
SQL statements are the backbone of database interactions, and optimizing them is essential for improving performance.This includes –
- Using appropriate data types to minimize storage requirements and improve query execution speed.
- Avoiding subqueries whenever possible and as they can significantly impact performance.
- Refraining from using SELECT * to fetch all columns, an instead explicitly specifying the required columns to reduce unnecessary data retrieval.
Reviewing Configuration Files
The configuration of your database server plays a crucial role in its performance. Regularly review configuration files to ensure that settings such as memory allocation, cache size, and thread concurrency are optimized for your workload. Adjusting these parameters based on changing requirements can help alleviate performance problems.
Optimizing the Database Design
A well designed database schema can greatly improve performance – consider normalization techniques to minimize data redundancy and optimize storage efficiency. Additionally, using appropriate indexing strategies can speed up query execution by facilitating faster data retrieval.
Performing Log Analysis of Slow Queries
Monitoring and analyzing slow query logs can provide valuable insights into performance issues. By identifying and analyzing queries that take longer to execute, you can pinpoint areas for optimization. Look for common patterns or recurring queries that may indicate underlying issues in your database design.
Exploring Alternative Database Systems
In some cases, switching to a different database system may offer performance benefits. Evaluate alternative database systems based on factors such as performance, scalability, and compatibility with your existing infrastructure.
By implementing these strategies, you can proactively address slow queries and optimize the performance of your database system to meet the needs of your application effectively. Remember to regularly monitor performance metrics and adjust your optimization efforts as needed to maintain peak performance over time.
4) Monitoring Tools to Setect Slow Queries
Identifying slow queries requires robust monitoring tools. Tools like MySQL Slow Query Log, Workbench, Percona Toolkit, SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS), and Apache Cassandra are instrumental in detecting and diagnosing slow queries.
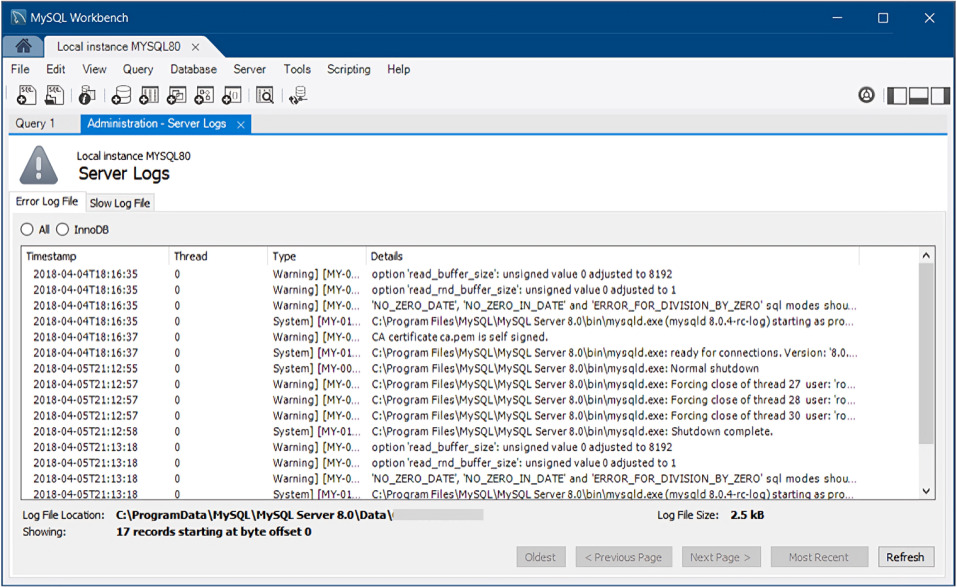
MySQL Slow Query Log
The MySQL Slow Query Log is a built-in feature of MySQL that logs slow queries based on a user defined threshold. When a query exceeds the specified execution time, it is logged in the slow query log file; this log file can then be analyzed to identify the slow queries.
The benefits of using the MySQL Slow Query Log are numerous. It allows database administrators to identify the queries that are causing performance issues and provides valuable information for query optimization. By analyzing the slow query log, administrators can identify patterns and trends in slow queries and take necessary actions to improve performance.
Workbench
MySQL Workbench is a powerful graphical tool that provides a comprehensive set of features for database administration. One of its key features is its ability to monitor and optimize slow queries. Workbench allows administrators to view the execution plan of queries, analyze query performance, and identify potential bottlenecks.
By using Workbench, administrators can gain valuable insights into query performance and make informed decisions for optimizing slow queries. This tool provides a user-friendly interface for query analysis and making it easier to identify and resolve performance issues.
Percona Toolkit –
Percona Toolkit is a collection of command line tools that are specifically designed for MySQL and MongoDB database systems. It includes a tool called “pt query” digest which is particularly useful for identifying slow queries.
pt query digest analyzes the slow query log file and provides a detailed report on query performance. It highlights the queries that are taking the most time to execute and provides recommendations for optimization. By using the Percona Toolkit, administrators can efficiently identify and address slow queries, leading to improved database performance.
SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS)
For SQL Server database systems, SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS) is a popular choice for monitoring and optimizing slow queries. SSMS provides a rich set of features for query analysis and performance tuning. With SSMS and administrators can capture and analyze query execution plans, monitor query performance in real time, and identify slow queries.
You can monitor your SQL Server instance’s activity using the activity monitor.

Apache Cassandra
Apache Cassandra is a highly scalable and distributed NoSQL database system. To detect and diagnose slow queries in Cassandra, there are several monitoring tools available, such as DataStax OpsCenter and Cassandra Reaper.
DataStax OpsCenter
provides a visual interface for monitoring query performance, analyzing query metrics, and identifying slow queries. It also offers features for capacity planning and workload management, helping administrators optimize query performance.
Cassandra Reaper
a tool specifically designed for identifying and repairing slow queries in Cassandra. It analyzes the query metrics and provides recommendations for query optimization. Administrators can efficiently diagnose and resolve slow queries, and ensuring optimal database performance by using Cassandra Reaper.
By effectively utilizing these tools, administrators can gain valuable insights into query performance and take necessary actions for query optimization.
5) Why is Redis Faster than MySQL?
Redis is an open source and in-memory data structure store, can be the solution to your slow query problems. Redis excels in speed due to its ability to hold the dataset in memory and reducing the time needed to access data. Compared to MySQL, Redis operations are atomic, which ensures data consistency even in cases of multiple concurrent operations.
In contrast to Redis, MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) that stores data in tables with pre-defined schemas. It is widely used in applications that require structured data storage and complex querying capabilities.
Factors Contributing to Redis Superior Speed
Now that we have a basic understanding of Redis and MySQL, let’s see the secret behind Redis’ superior speed and the factors that contribute to its exceptional performance –
In Memory Data Storage
Redis stores data in memory and eliminating the latency associated with disk I/O operations. By keeping the data repadily accessible in RAM, Redis ensures lightning fast read and write operations, making it an ideal choice for applications that require real time data processing.
Efficient Data Structures
Redis provides a wide range of data structures and optimized for different use cases. Whether it is strings, lists, sets, or hashes and Redis offers efficient data structures that allow for quick and seamless data manipulation. These data structures are designed to minimize memory usage, maximize performance, and enabling Redis to process data at incredible speeds.
Caching Mechanisms
Redis employs a sophisticated caching mechanism that significantly improves performance by storing frequently accessed data in memory; this reduces the need for repeated disk I/O operations and enhancing the overall speed of data retrieval. Redis caching capabilities make it an excellent choice for applications that heavily rely on fast access to frequently accessed data.
Difference Between Redis and MySQL
While both Redis and MySQL are powerful database systems, they serve different purposes and have different strengths. MySQL is a relational database management system (RDBMS) and perfect for storing structured data and executing complex queries.
On the other hand, Redis is a memory data structure store that excels in caching and session management, ensuring high performance and fast data processing.
1. Data Storage
Redis stores data in memory, while MySQL stores data on disk. This fundamental difference gives Redis a significant advantage in terms of speed, as accessing data from memory is much faster compared to disk based operations.
2. Read and Write Operations
Redis excels in read heavy workloads, where data needs to be retrieved quickly. It can handle thousands of reads per second with sub-millisecond latency. On the other hand, MySQL performs well in write-heavy workloads, where data needs to be written or updated frequently. It can efficiently handle concurrent write operations and maintain data consistency.
3. Caching
Redis is often used as a caching layer to improve performance in applications. It can store frequently accessed data in memory and reducing the need to query the underlying database repeatedly. This caching mechanism significantly speeds up data retrieval and reduces the load on the database server. MySQL also supports caching, but it is not as efficient as Redis due to its disk based architecture.
4. Latency and Response Time
In this aspect, Redis outshines MySQL due to its in-memory nature. Since Redis keeps the data in memory, it can deliver extremely low latency and near instantaneous response times, making it an excellent choice for applications that require real time data processing.
On the other hand, MySQL, being a disk-based database, typically exhibits higher latency due to the disk I/O operations involved. Although MySQL has mechanisms like query caching to reduce latency it may not match the lightning fast response times of Redis.
5. Throughput and Scalability
Another crucial aspect of database performance is throughput, which refers to the number of requests a database can handle per unit of time. Redis demonstrates exceptional throughput capabilities. It can handle a massive number of concurrent connections. It can process thousands of operations per second making it suitable for high-traffic applications that demand rapid data processing.
MySQL, while not as performant as Redis in terms of throughput and offers impressive scalability options. It can handle large datasets and concurrent connections by leveraging techniques such as sharding and replication. With proper configuration and optimization, MySQL can deliver solid performance even under heavy loads.
Redis Key Concepts
It operates based on several key concepts including –
- Keys – In Redis, data is stored as a key value pair. The key serves as the unique identifier for the data.
- Data Types – Redis supports several data types like strings, lists, sets, sorted sets, hashes, bitmaps, hyperlogs, and geospatial indexes.
- Persistence – Redis provides two methods for data persistence – snapshotting and append only file (AOF).
- Replication – Redis supports master slave replication, allowing slaves to have other slaves and providing automatic failover.
- Commands – Redis provides a rich set of commands that can be used to interact with the server and manipulate data. Each command is associated with a specific operation, such as setting a value, retrieving a value, or performing an operation on a data structure.
Redis Architecture
Redis follows a single threaded architecture, which means it processes one command at a time. By storing data in memory and avoiding the need for context switches, Redis can execute commands at lightning speed.
Redis architecture comprises two main components: the Redis client and the Redis server. The server is responsible for housing data within memory and controlling all aspects crucial to the architecture. On the other hand, a Redis client is essentially a Redis console integrated with a programming language tailored for the Redis API.

The Redis architecture has several deployment options –
- Single Redis Instance
- Redis High Availability (HA)
- Redis Clustered Database
- Redis HA Clustered Database
Redis Features
It comes with a host of features that make it an attractive choice for high performance applications –
- In-Memory Storage – Redis stores data in-memory, resulting in significantly faster access times compared to disk-based storage.
- Data Structures – Redis supports a variety of data structures and allows developers to use the right tool for the job.
- Pub/Sub Capabilities – Redis supports pub/sub messaging paradigms, making it a great choice for real-time messaging applications.
- Memory Management – Redis employs diverse memory optimization techniques to manage memory effectively.
- Data Replication – Redis supports master-slave replication, ensuring fault tolerance and read scalability.
- Lua Scripting – Redis allows for server side scripting using Lua and enabling complex operations to be executed atomically in the server.
- Cluster Management – Redis incorporates built tools for managing Redis Cluster instances, simplifying deployment, scalability, and monitoring tasks.
- Transactions – Redis supports transactions, ensuring that a group of commands is executed as a single and isolated operation.
- Persistence Choices – Redis offers options for both snapshot-based persistence and append-only files, enhancing data durability.
In conclusion, Redis is a powerful and versatile data store that offers high performance, scalability, and a wide range of features.
Redis Use Cases
It can be used for a variety of use cases, including caching, session management, real time analytics, pub/sub messaging, rate limiting, distributed locking, content and object caching, and e-commerce.
Here are some common use cases where Redis can be useful –
Caching
One of the most popular use cases for Redis is caching. By storing frequently accessed data in Redis, you can significantly reduce the load on your primary database and improve the performance of your application.
Real-Time Analytics
Redis ability to process large volumes of data in real-time makes it well-suited for real time analytics. By storing and processing data in Redis, you can generate real time insights and make data-driven decisions.
Pub/Sub Messaging
Redis pub/sub messaging feature allows for real-time communication between clients. Publishers can send messages to specific channels, and subscribers can receive those messages in real-time. This makes Redis a great choice for building real time chat applications, notifications systems, and event driven architectures.
Conclusion
Redis is a powerful and versatile data storage that offers high performance, scalability, and a wide range of features. Whether you need to cache data, perform real-time analytics, or build a pub/sub messaging system, Redis has got you covered. Its simple and intuitive architecture, coupled with its rich set of commands and data structures, make it a popular choice among developers. On the other hand, MySQL provides a reliable and scalable solution for managing structured data and complex queries.
People Also Ask(And You Should Too!)
1. What are slow queries in databases?
Slow queries are database requests that take longer than expected to execute, often due to poor indexing, inefficient SQL statements, or large data volumes. They delay page rendering and increase server load.
2. How do slow queries affect website performance?
Slow queries increase page load time, cause timeouts, reduce responsiveness, and negatively impact SEO rankings. They also strain server resources, leading to higher hosting costs.
3. Why does Redis help with slow queries?
Redis is an in-memory data store that caches frequently accessed data. Instead of repeatedly running complex queries on the database, Redis serves results instantly from memory, reducing query execution time.
4. Can Redis completely eliminate slow queries?
Redis won’t eliminate poorly written or unoptimized queries, but it drastically reduces their frequency and impact by caching results. Pairing Redis with query optimization offers the best performance.
5. Is Redis only useful for large websites?
No. Redis benefits small, medium, and large websites. Even moderate traffic sites can see faster response times, better scalability, and reduced database strain with Redis caching.
6. How does Redis caching improve SEO?
Faster websites rank higher on Google. By reducing slow query delays, Redis speeds up page loads, lowers bounce rates, and improves overall user experience all of which are SEO ranking factors.
7. Can Redis be used with MySQL, PostgreSQL, or MongoDB?
Yes. Redis works as a caching layer alongside most databases, including MySQL, PostgreSQL, and MongoDB. It stores frequently used query results in memory, speeding up response times regardless of the backend database.
8. How does AccuWeb.Cloud support Redis for query optimization?
AccuWeb.Cloud offers fully managed Redis hosting integrated with databases and applications. You can easily deploy Redis clusters, configure caching, and scale resources to handle slow queries more effectively.

Jilesh Patadiya, the visionary Founder and Chief Technology Officer (CTO) behind AccuWeb.Cloud. Founder & CTO at AccuWebHosting.com. He shares his web hosting insights on the AccuWeb.Cloud blog. He mostly writes on the latest web hosting trends, WordPress, storage technologies, and Windows and Linux hosting platforms.